AWS New York City Meetup AWS IoT & GreenGrass Chris Munns – Senior Developer Advocate - munns@amazon.com + Andy, Pat, & Nate from Solstice
A presentation at AWS NYC Meetup - May 2017 - AWS IoT and Greengrass in May 2017 in New York, NY, USA by Chris Munns

AWS New York City Meetup AWS IoT & GreenGrass Chris Munns – Senior Developer Advocate - munns@amazon.com + Andy, Pat, & Nate from Solstice

About me: Chris Munns - munns@amazon.com, @chrismunns – Senior Developer Advocate - Serverless – New Yorker – Previously: • • • • Business Development Manager – DevOps, July ’15 - Feb ‘17 AWS Solutions Architect Nov, 2011- Dec 2014 Formerly on operations teams @Etsy and @Meetup Little time at a hedge fund, Xerox and a few other startups – Rochester Institute of Technology: Applied Networking and Systems Administration ’05 – Internet infrastructure geek

Why are we here today? https://secure.flickr.com/photos/mgifford/4525333972

25 billion devices by 2020

Everyday things will be connected… http://www.washingtonpost.com/sf/brand-connect/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2015/05/cc_heroimage_v2.jpg




Mobile = IoT? No…and Yes. Wearables Home Automation Apps Industrial Control Equipment Companion Apps Connected Device & Mobile Apps ßà Industrial Devices & B2B channels
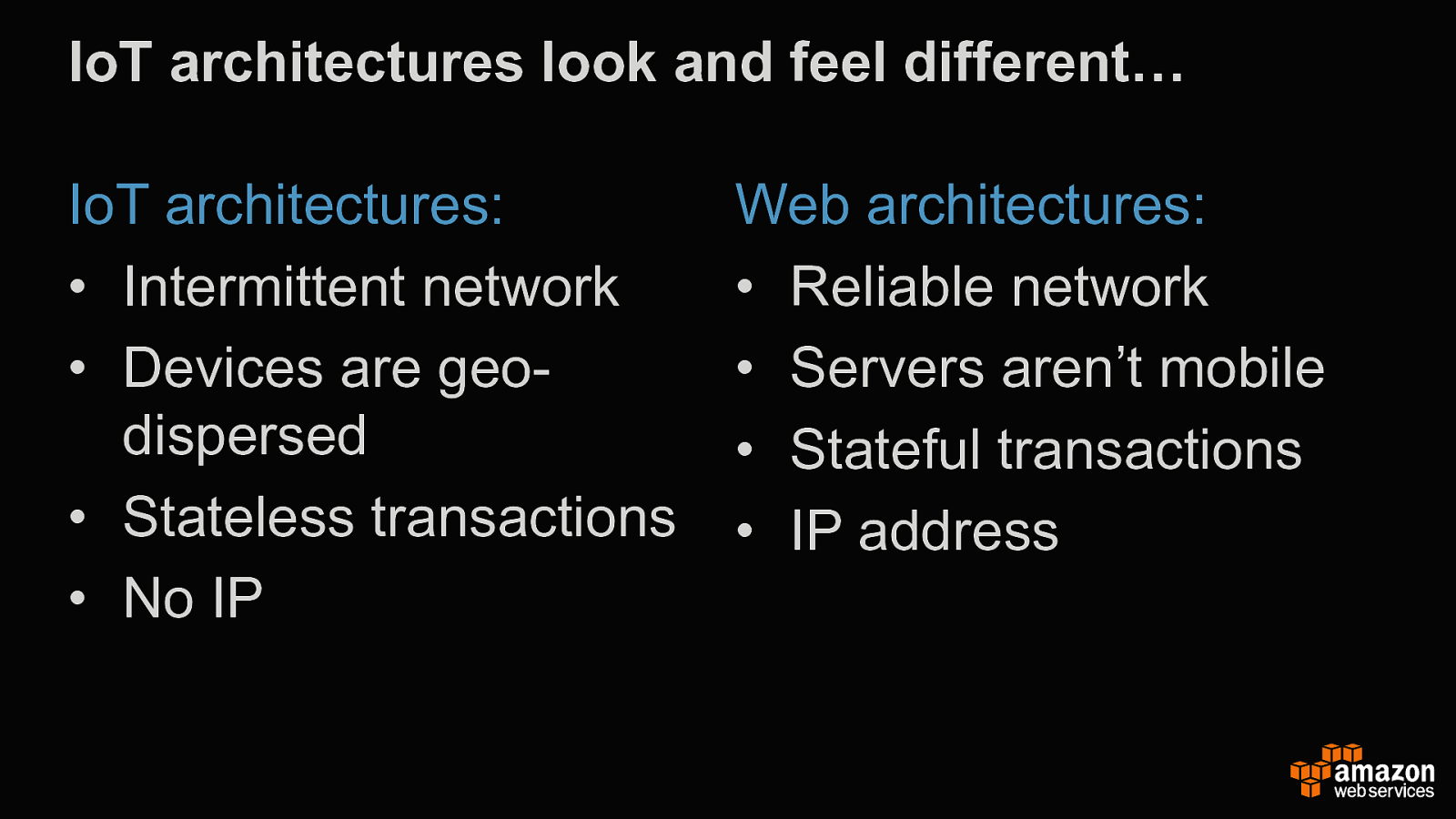
IoT architectures look and feel different… IoT architectures: • Intermittent network • Devices are geo- dispersed • Stateless transactions • No IP Web architectures: • Reliable network • Servers aren’t mobile • Stateful transactions • IP address
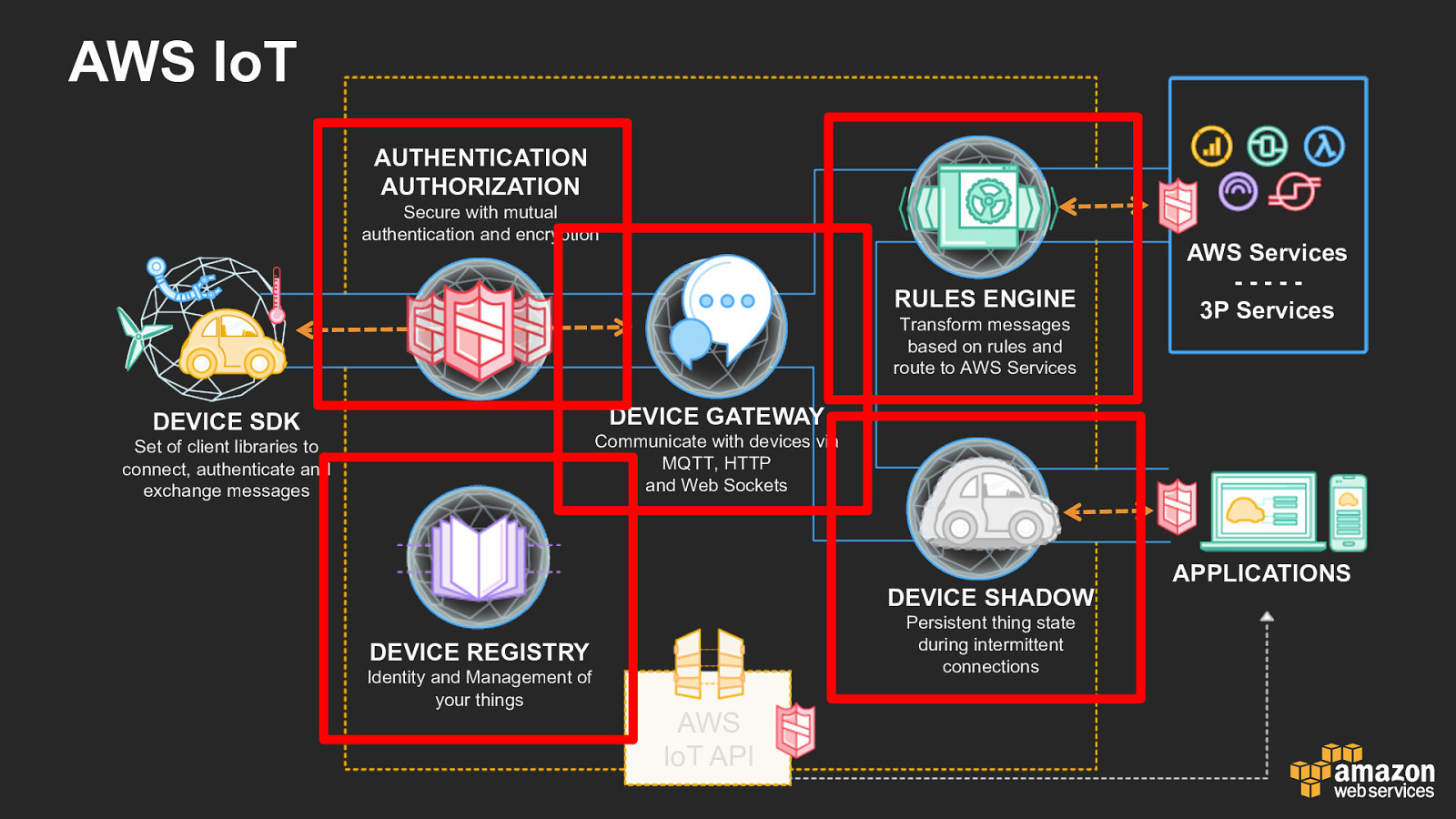
AWS IoT AUTHENTICATION AUTHORIZATION Secure with mutual authentication and encryption RULES ENGINE Transform messages based on rules and route to AWS Services AWS Services - - - - - 3P Services DEVICE GATEWAY DEVICE SDK Communicate with devices via MQTT, HTTP and Web Sockets Set of client libraries to connect, authenticate and exchange messages DEVICE SHADOW Persistent thing state during intermittent connections DEVICE REGISTRY Identity and Management of your things AWS IoT API APPLICATIONS

MQTT Primer MQ Telemetry Transport – the IoT protocol Ø Ø Ø Ø Senders ‘Publish’ to topics and send messages Receivers ‘Subscribe’ to topics and receive messages All subscribers receive all messages sent to a topic Topic names can be subscribed to using ‘wildcards’ topicname/path Use the path depth that makes sense for your application
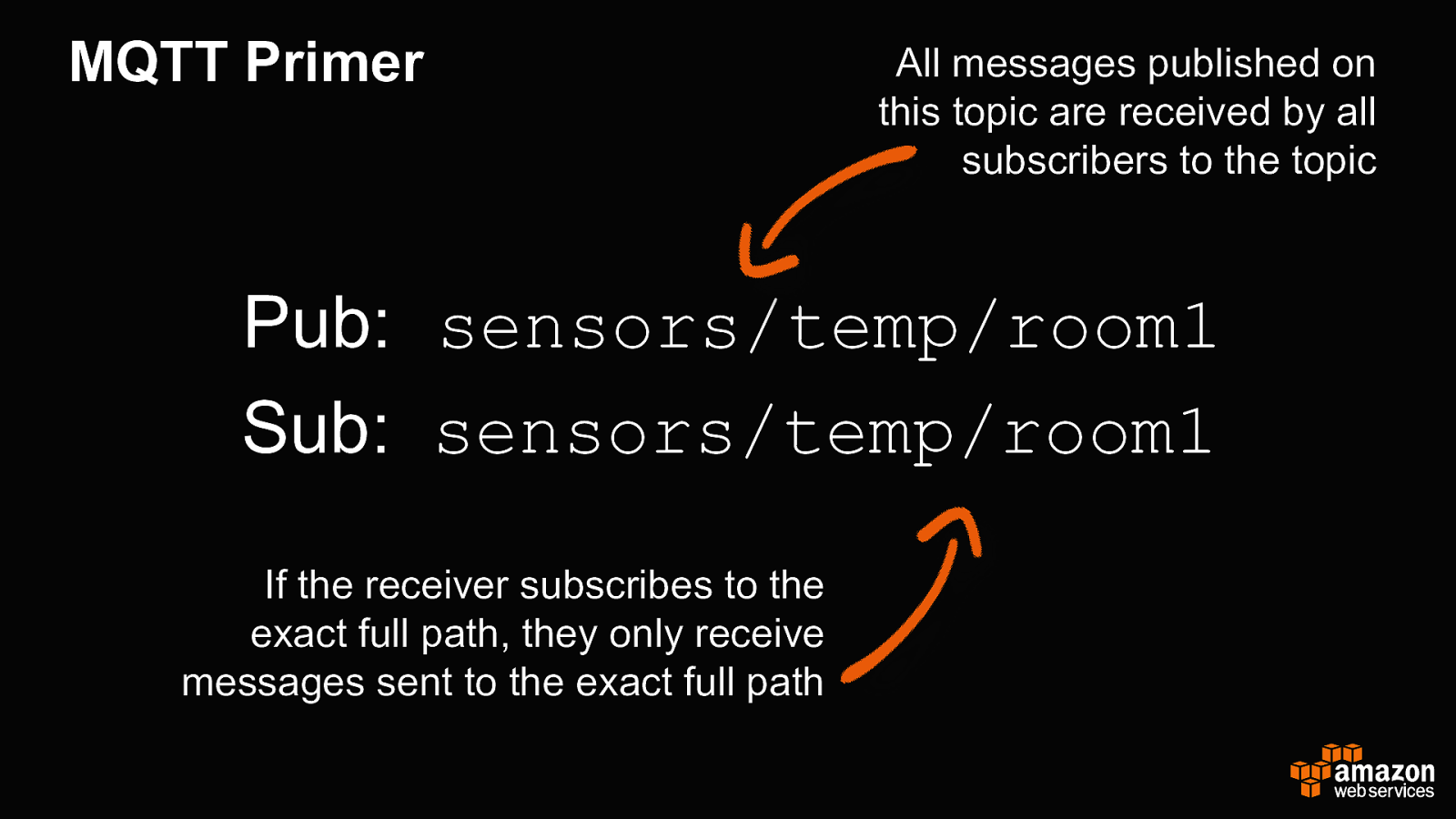
MQTT Primer All messages published on this topic are received by all subscribers to the topic Pub: sensors/temp/room1 Sub: sensors/temp/room1 If the receiver subscribes to the exact full path, they only receive messages sent to the exact full path

MQTT Primer All messages published on this topic are received by all subscribers to the topic Pub: sensors/temp/room1 Sub: sensors/+/room1 The plus (+) matches exactly one item in the topic hierarchy so here the subscriber will receive messages for all sensors in room 1
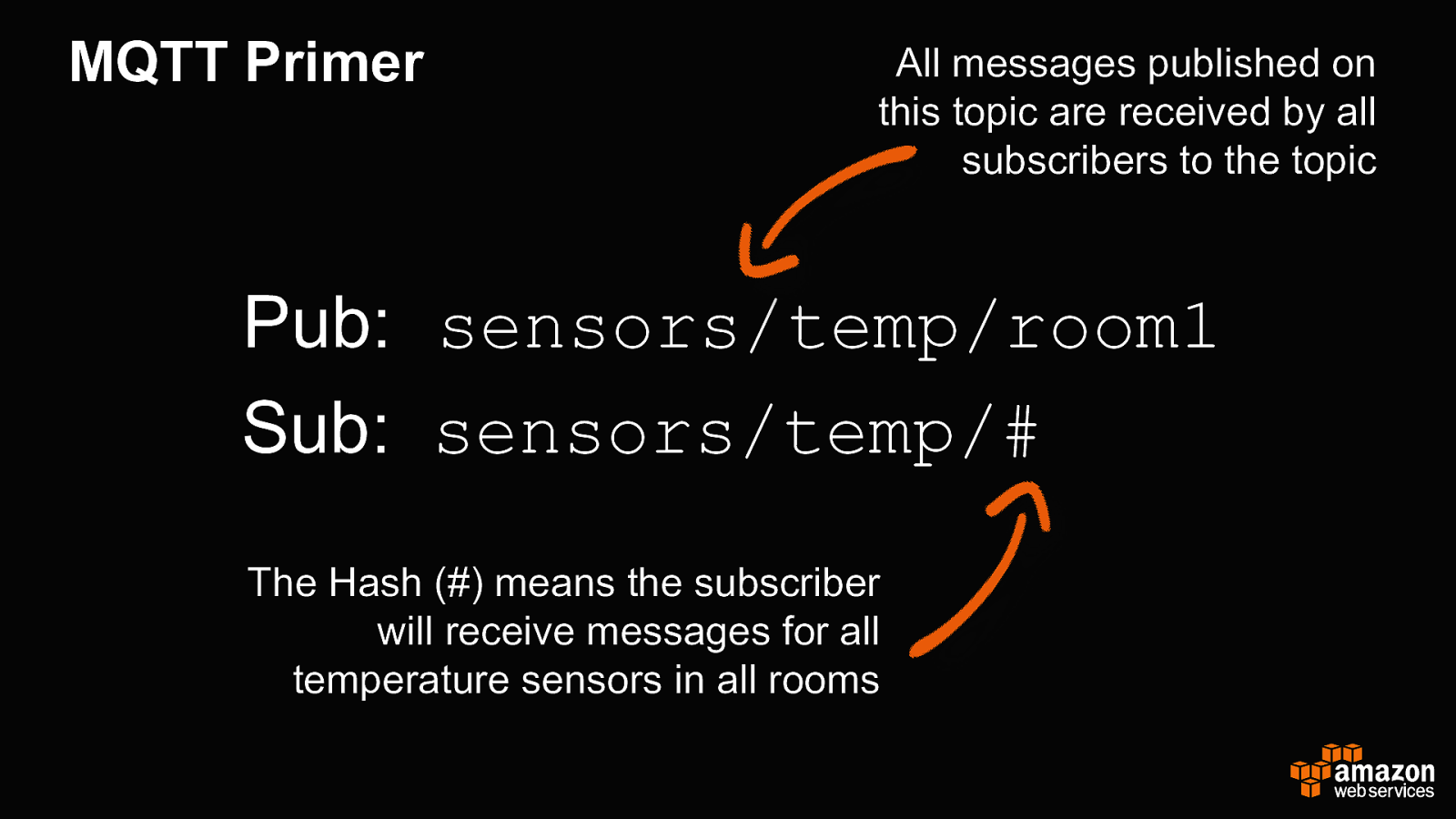
MQTT Primer All messages published on this topic are received by all subscribers to the topic Pub: sensors/temp/room1 Sub: sensors/temp/# The Hash (#) means the subscriber will receive messages for all temperature sensors in all rooms
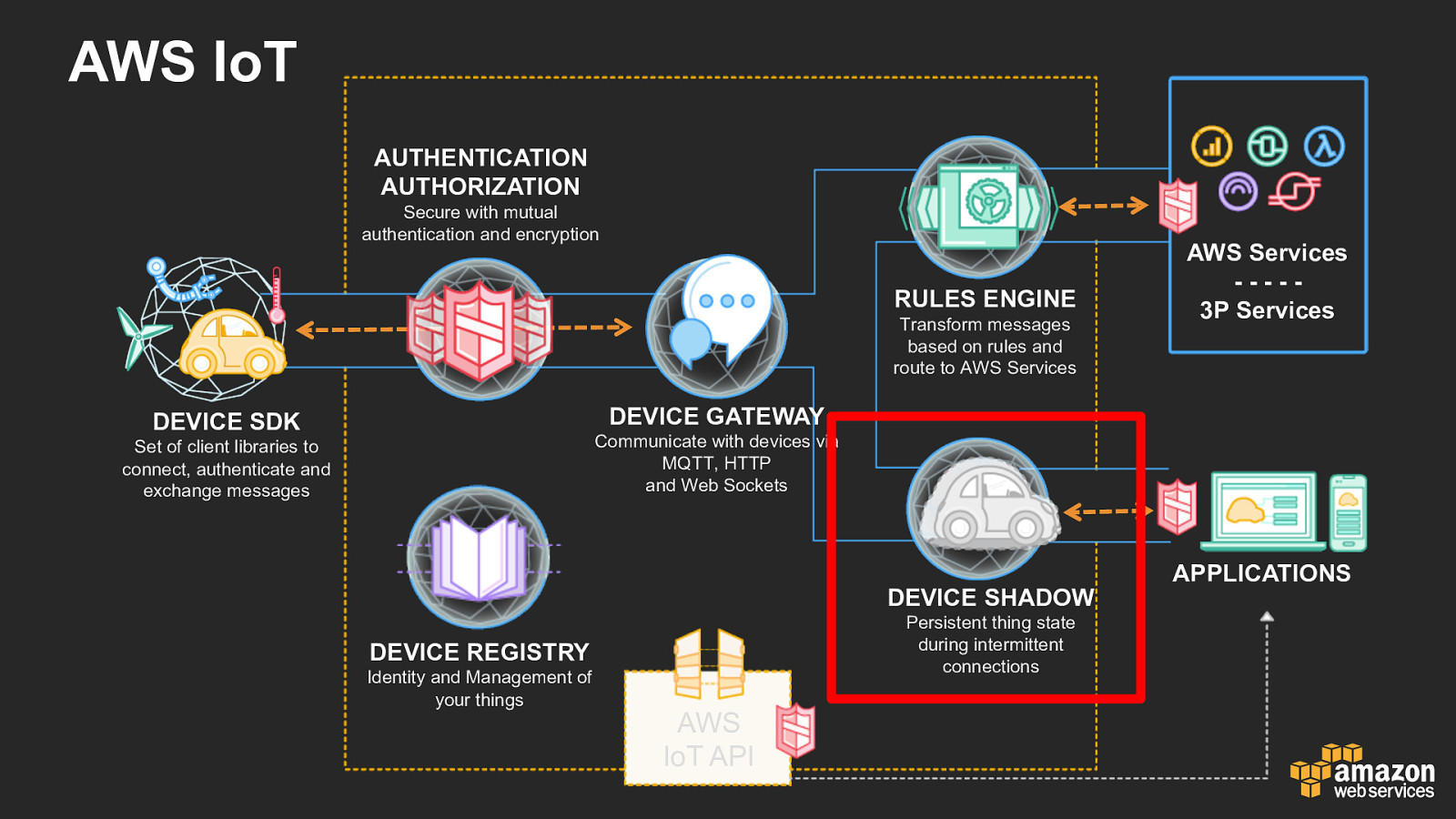
AWS IoT AUTHENTICATION AUTHORIZATION Secure with mutual authentication and encryption RULES ENGINE Transform messages based on rules and route to AWS Services AWS Services - - - - - 3P Services DEVICE GATEWAY DEVICE SDK Communicate with devices via MQTT, HTTP and Web Sockets Set of client libraries to connect, authenticate and exchange messages DEVICE SHADOW Persistent thing state during intermittent connections DEVICE REGISTRY Identity and Management of your things AWS IoT API APPLICATIONS
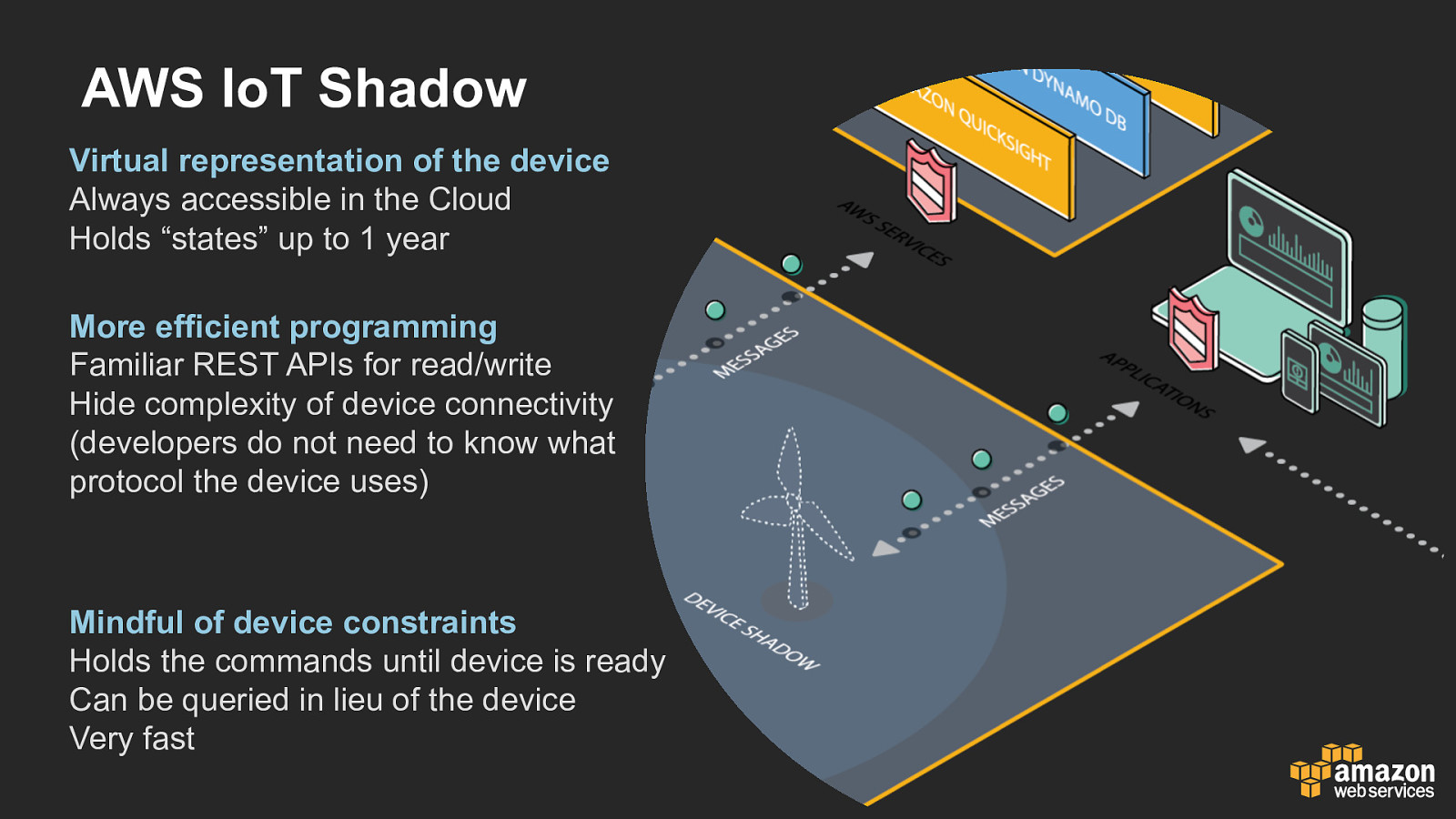
AWS IoT Shadow Virtual representation of the device Always accessible in the Cloud Holds “states” up to 1 year More efficient programming Familiar REST APIs for read/write Hide complexity of device connectivity (developers do not need to know what protocol the device uses) Mindful of device constraints Holds the commands until device is ready Can be queried in lieu of the device Very fast

Device Shadow • Plan for devices to lose connectivity – Device may need to shut down when idle to conserve battery. – Device may be stable, but the network could be unreliable. • Send devices commands through Shadows – Instead of wrangling custom topics and keeping state yourself, use the Device Shadow to abstract away the topics and connectivity issues. • Query device state through Shadows – The Device Shadow is always available, even if the device is not. • Addresses message ordering for command and control – Uses optimistic locking (version number)
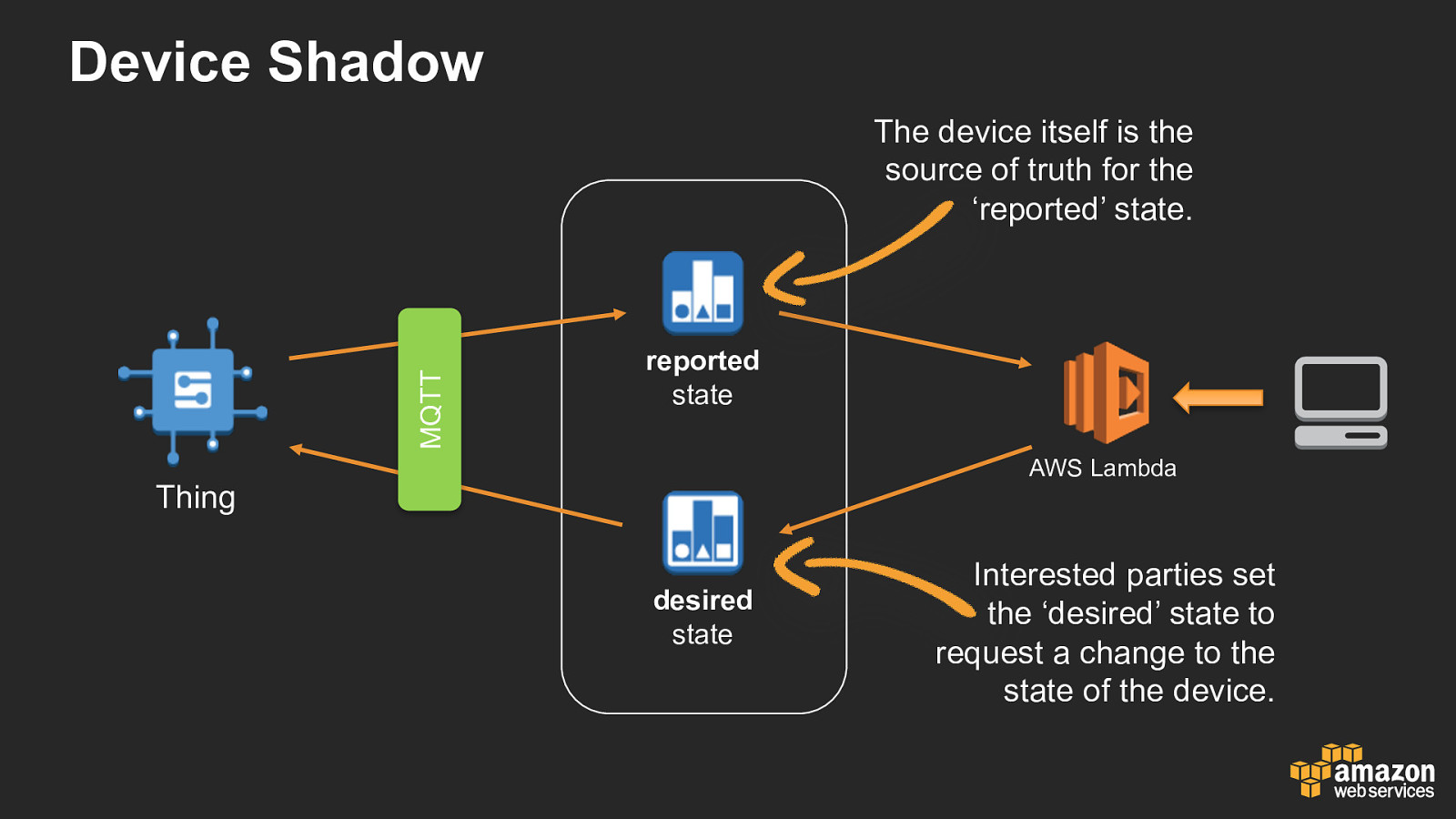
Device Shadow MQTT The device itself is the source of truth for the ‘reported’ state. reported state AWS Lambda Thing desired state Interested parties set the ‘desired’ state to request a change to the state of the device.

‘Desired’ state • Used to request a change to device state Interested parties request device state change through the JSON payload. • Difference between ‘reported’ and ‘desired’ triggers a ‘delta’ message to the device The AWS IoT device shadow compares the ‘reported’ state with the ‘desired’ state, and any properties of ‘desired’ not present or different in the ‘reported’ state are notified via a ‘delta’ message.
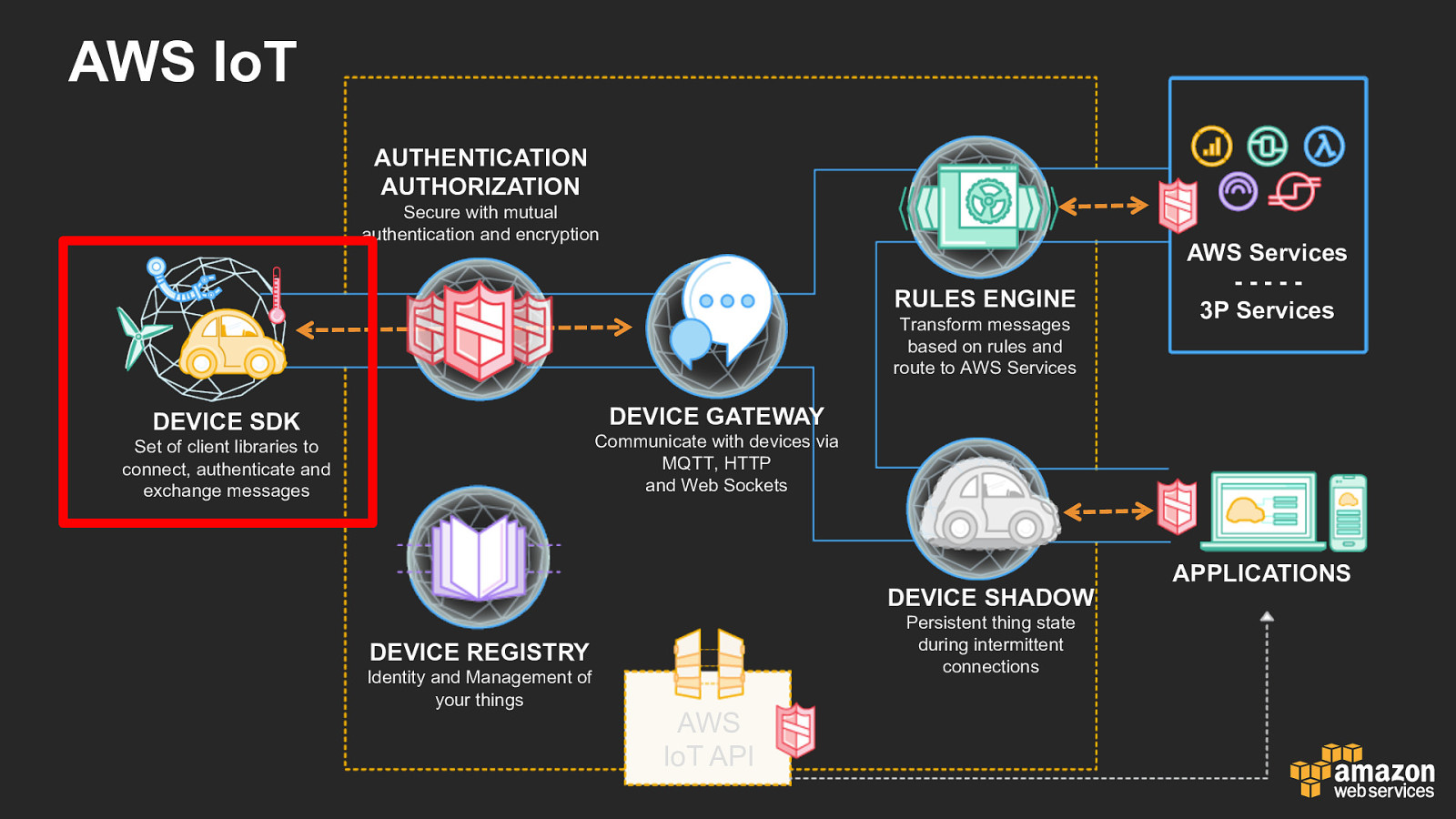
AWS IoT AUTHENTICATION AUTHORIZATION Secure with mutual authentication and encryption RULES ENGINE Transform messages based on rules and route to AWS Services AWS Services - - - - - 3P Services DEVICE GATEWAY DEVICE SDK Communicate with devices via MQTT, HTTP and Web Sockets Set of client libraries to connect, authenticate and exchange messages DEVICE SHADOW Persistent thing state during intermittent connections DEVICE REGISTRY Identity and Management of your things AWS IoT API APPLICATIONS
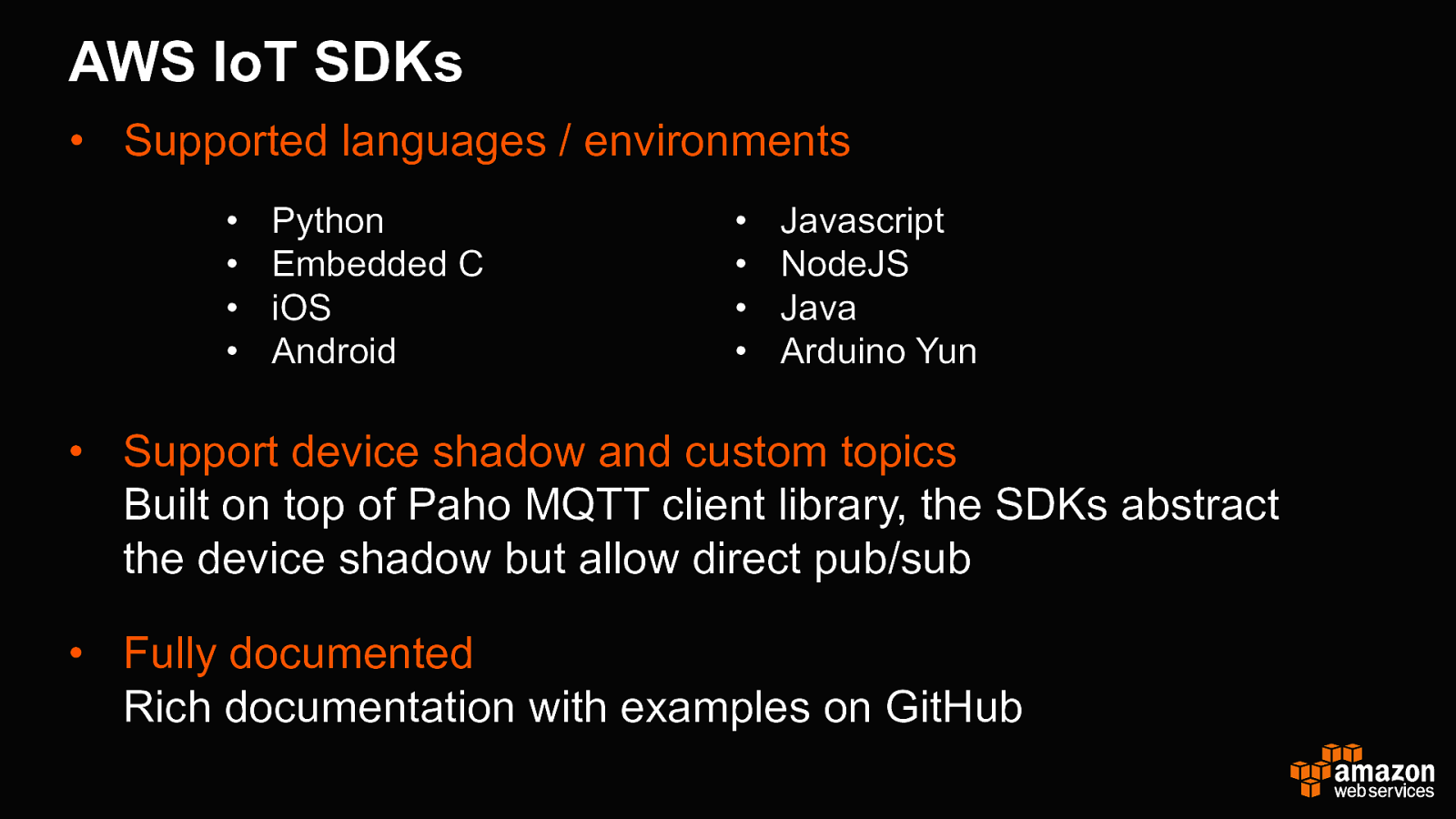
AWS IoT SDKs • Supported languages / environments • • • • Python Embedded C iOS Android • • • • Javascript NodeJS Java Arduino Yun • Support device shadow and custom topics Built on top of Paho MQTT client library, the SDKs abstract the device shadow but allow direct pub/sub • Fully documented Rich documentation with examples on GitHub
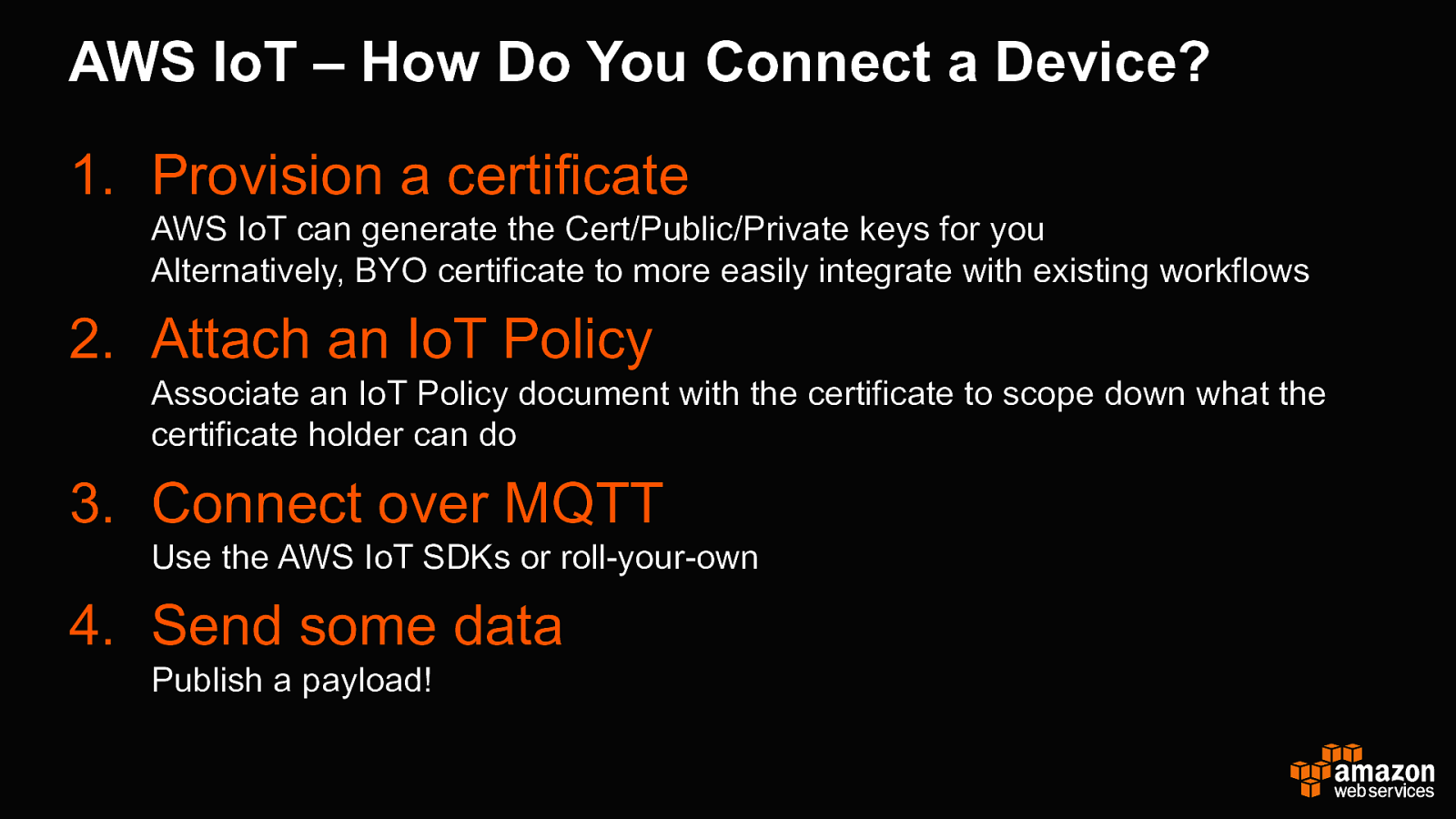
AWS IoT – How Do You Connect a Device? 1. Provision a certificate AWS IoT can generate the Cert/Public/Private keys for you Alternatively, BYO certificate to more easily integrate with existing workflows 2. Attach an IoT Policy Associate an IoT Policy document with the certificate to scope down what the certificate holder can do 3. Connect over MQTT Use the AWS IoT SDKs or roll-your-own 4. Send some data Publish a payload!
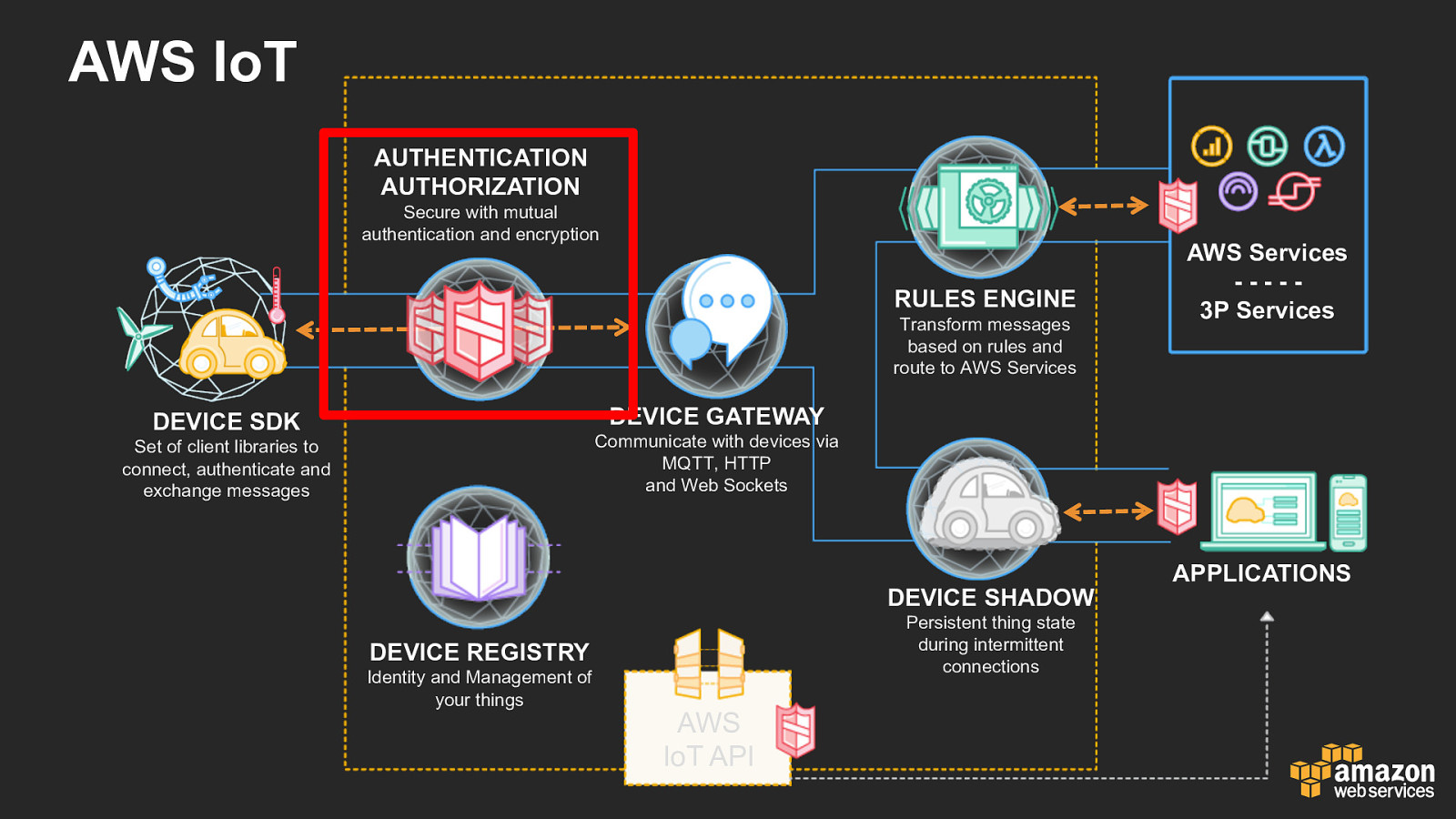
AWS IoT AUTHENTICATION AUTHORIZATION Secure with mutual authentication and encryption RULES ENGINE Transform messages based on rules and route to AWS Services AWS Services - - - - - 3P Services DEVICE GATEWAY DEVICE SDK Communicate with devices via MQTT, HTTP and Web Sockets Set of client libraries to connect, authenticate and exchange messages DEVICE SHADOW Persistent thing state during intermittent connections DEVICE REGISTRY Identity and Management of your things AWS IoT API APPLICATIONS

AWS IoT – How Do You Secure Communications? • Mutual authentication X.509 certificate-based auth – When devices connect to the AWS IoT broker, they use certificate-based authentication. You assign policies to certificates. • AWS SigV4 – When browsers use WebSockets, connections are signed using SigV4, which identifies the user principal that you can attach AWS IoT policies to. • Amazon Cognito simplifies signing SigV4 requests – Takes care of steps necessary to create a unique identifier for users and retrieve temporary, limited-privilege AWS credentials.
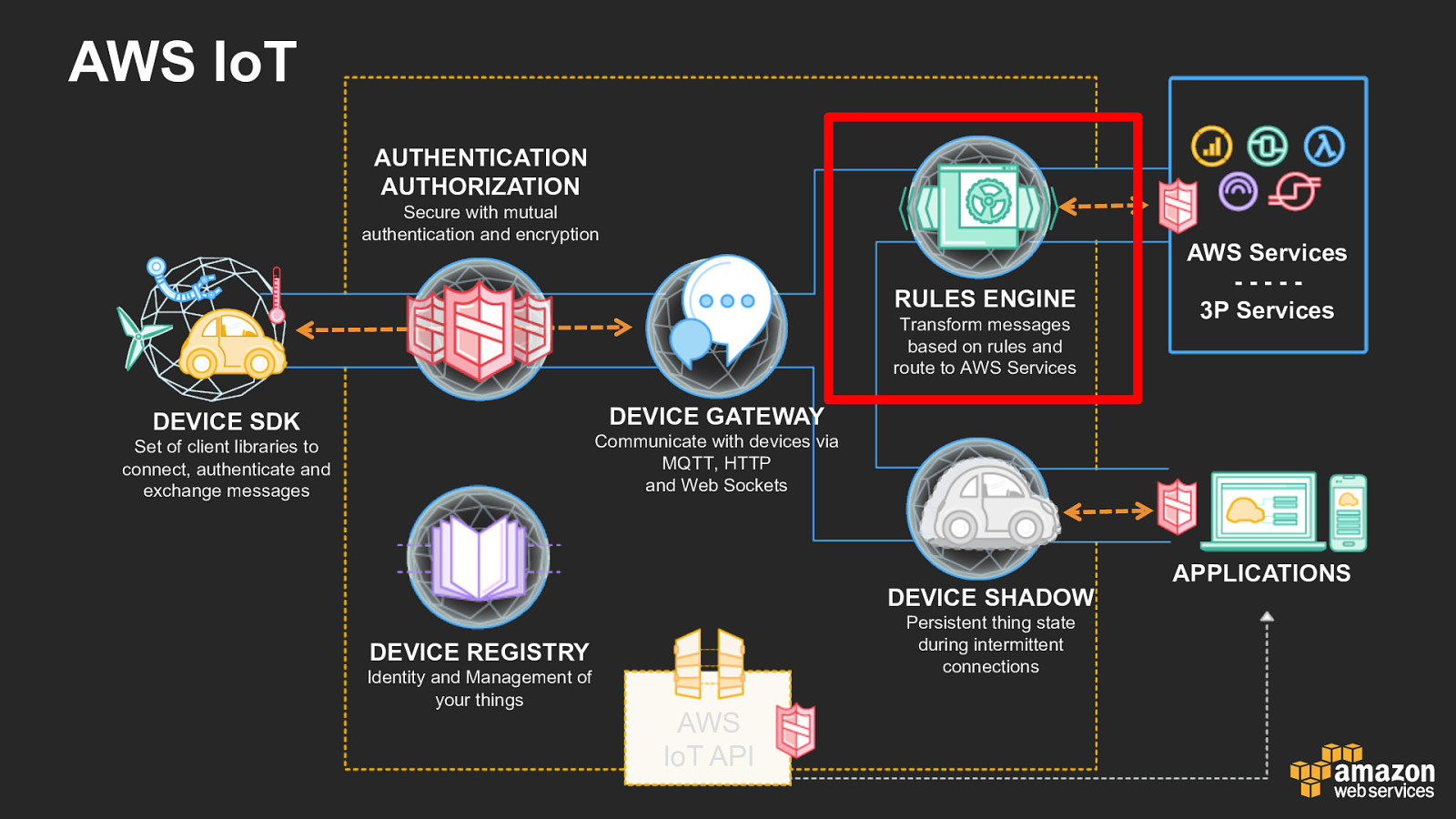
AWS IoT AUTHENTICATION AUTHORIZATION Secure with mutual authentication and encryption RULES ENGINE Transform messages based on rules and route to AWS Services AWS Services - - - - - 3P Services DEVICE GATEWAY DEVICE SDK Communicate with devices via MQTT, HTTP and Web Sockets Set of client libraries to connect, authenticate and exchange messages DEVICE SHADOW Persistent thing state during intermittent connections DEVICE REGISTRY Identity and Management of your things AWS IoT API APPLICATIONS
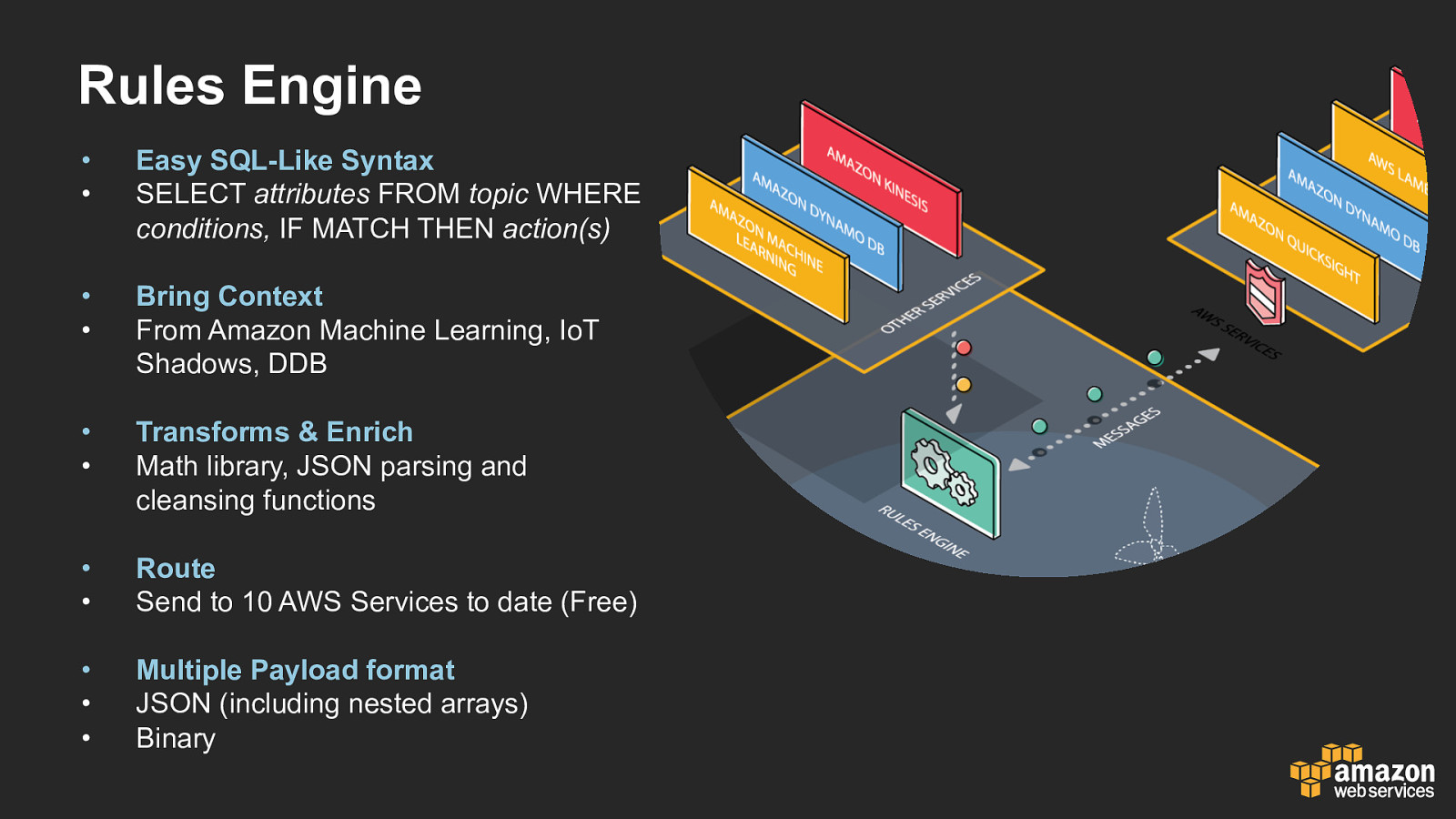
Rules Engine • • Easy SQL-Like Syntax SELECT attributes FROM topic WHERE conditions, IF MATCH THEN action(s) • • Bring Context From Amazon Machine Learning, IoT Shadows, DDB • • Transforms & Enrich Math library, JSON parsing and cleansing functions • • Route Send to 10 AWS Services to date (Free) • • • Multiple Payload format JSON (including nested arrays) Binary

Rules Engine • • • • • • • • • Augment or filter data received from a device. Write data received to an Amazon DynamoDB database. Save a file to Amazon S3. Send a push notification to all users of Amazon SNS. Publish data to an Amazon SQS queue. Invoke a Lambda function to extract data. Push data into Elastic Search. Process messages from a large number of devices using Amazon Kinesis. Republish the message to another MQTT topic.
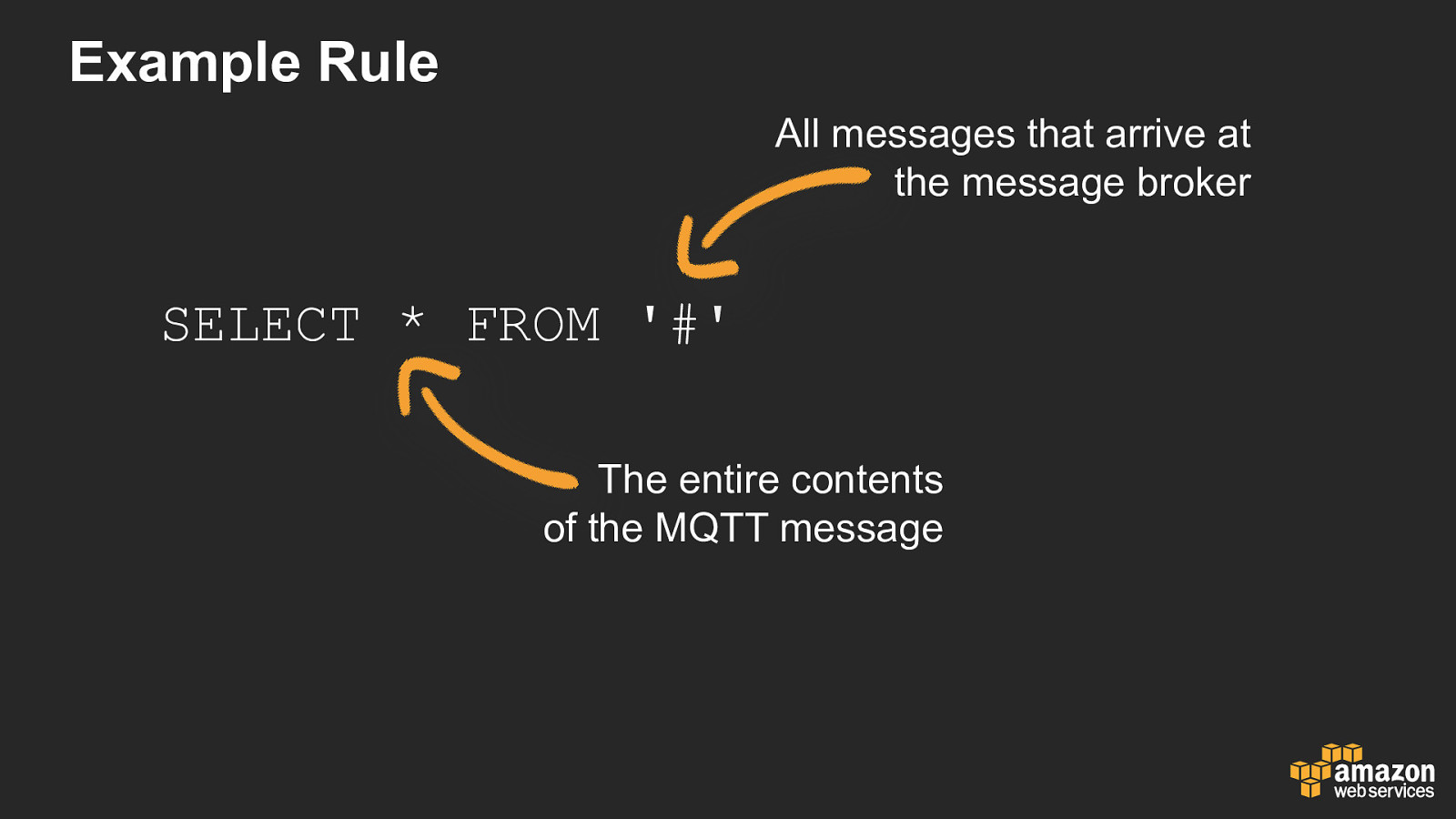
Example Rule All messages that arrive at the message broker SELECT * FROM ‘#’ The entire contents of the MQTT message
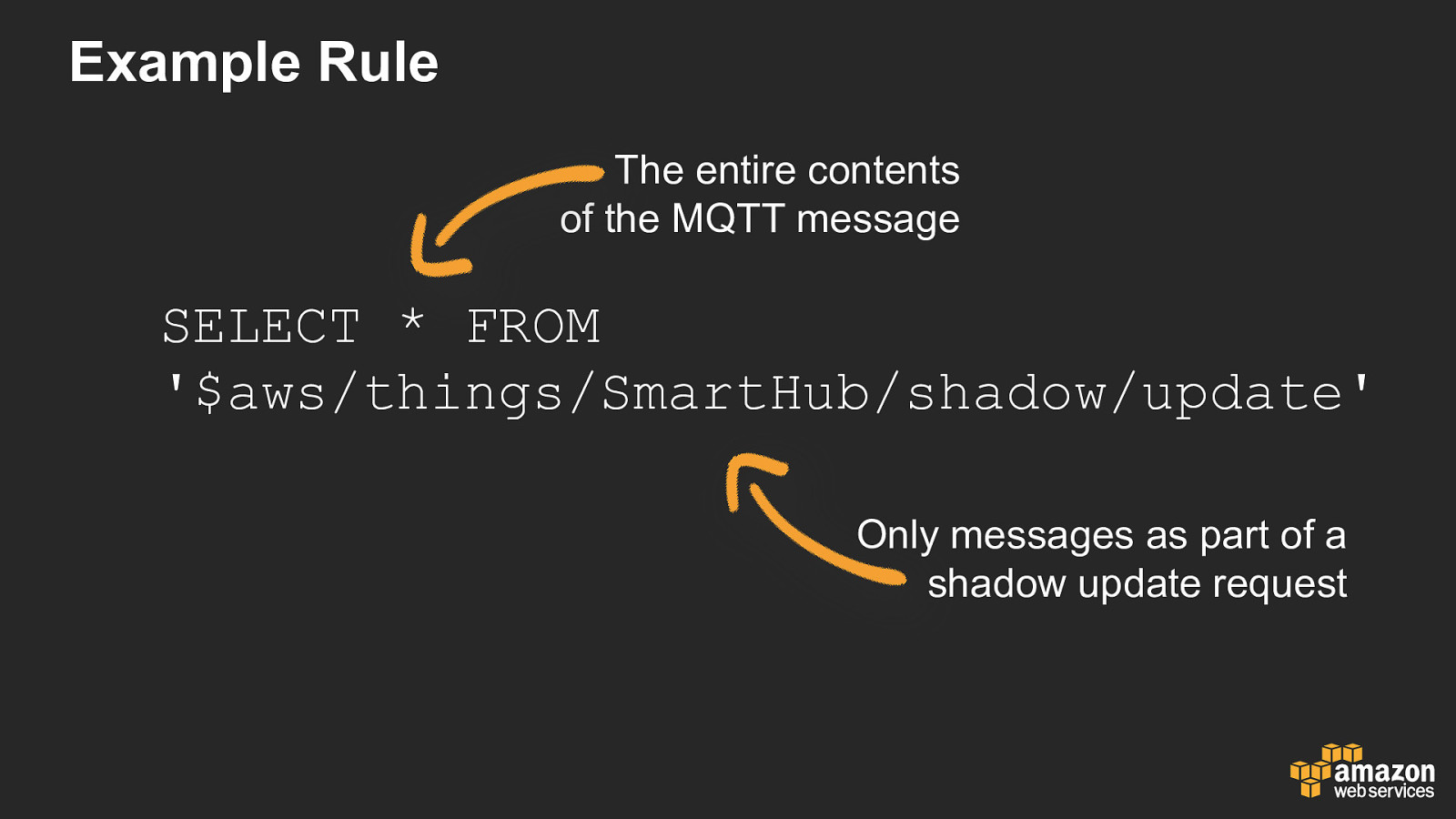
Example Rule The entire contents of the MQTT message SELECT * FROM ‘$aws/things/SmartHub/shadow/update’ Only messages as part of a shadow update request

Example Rule Just the ‘info’ property in the reported state message SELECT state.reported.info as info FROM ‘$aws/things/SmartHub/shadow/update’ WHERE state.reported.target=”LightBulb” Only messages that have a ‘target’ value set to ‘LightBulb’

Demo: Street lighting system

bit.ly/nycbulb01
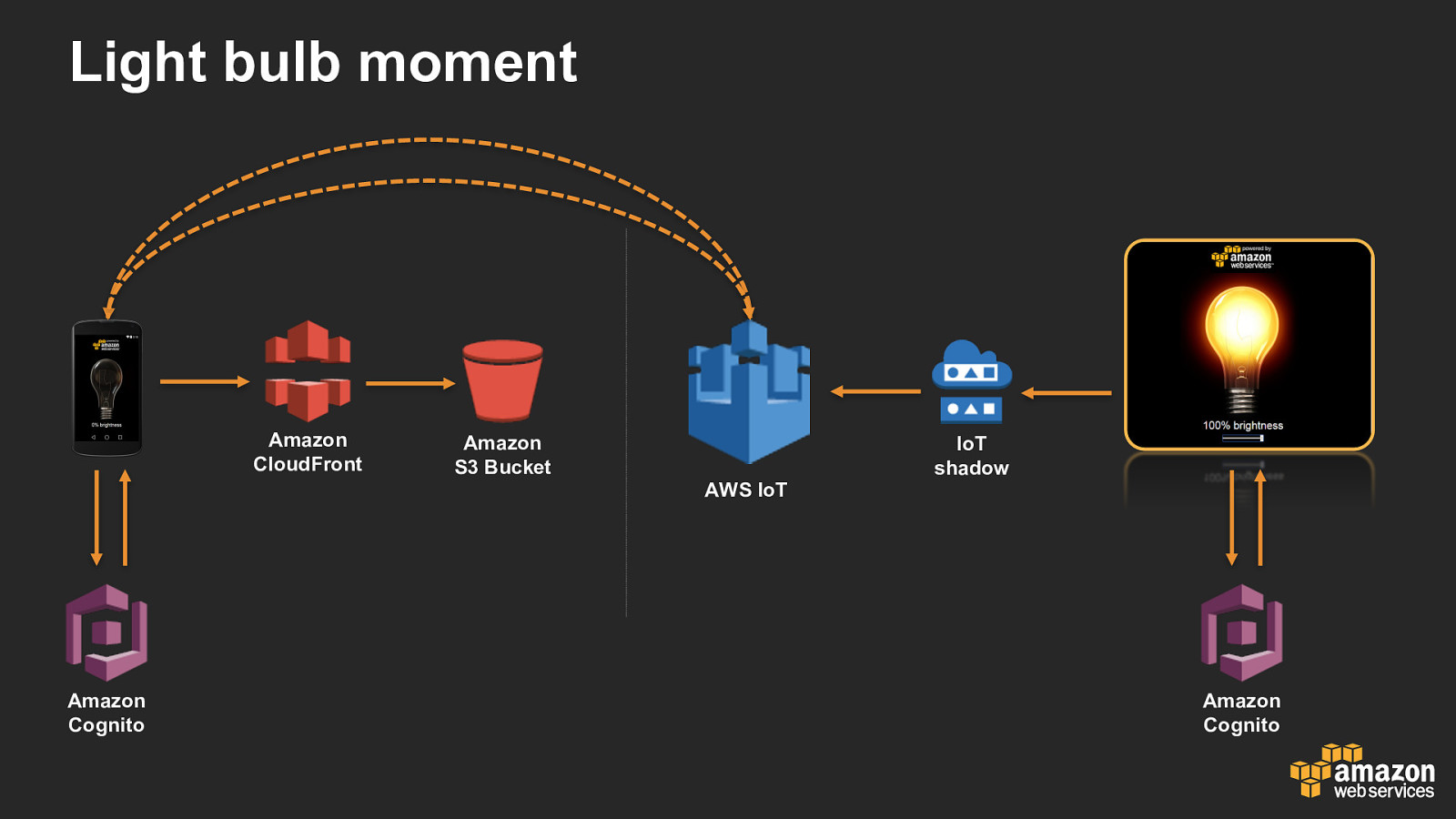
Light bulb moment Amazon CloudFront Amazon S3 Bucket AWS IoT Amazon Cognito IoT shadow Amazon Cognito
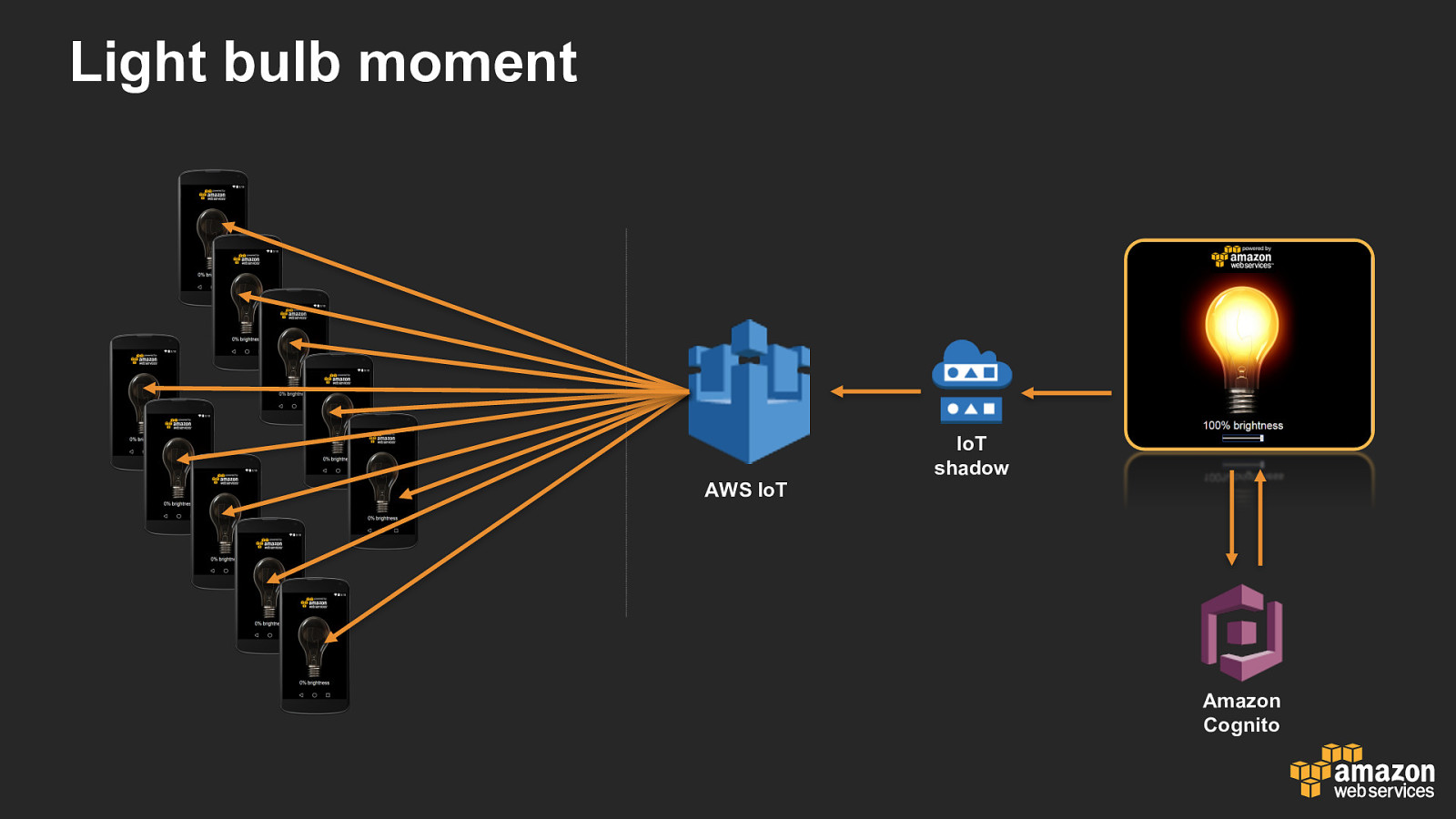
Light bulb moment AWS IoT IoT shadow Amazon Cognito
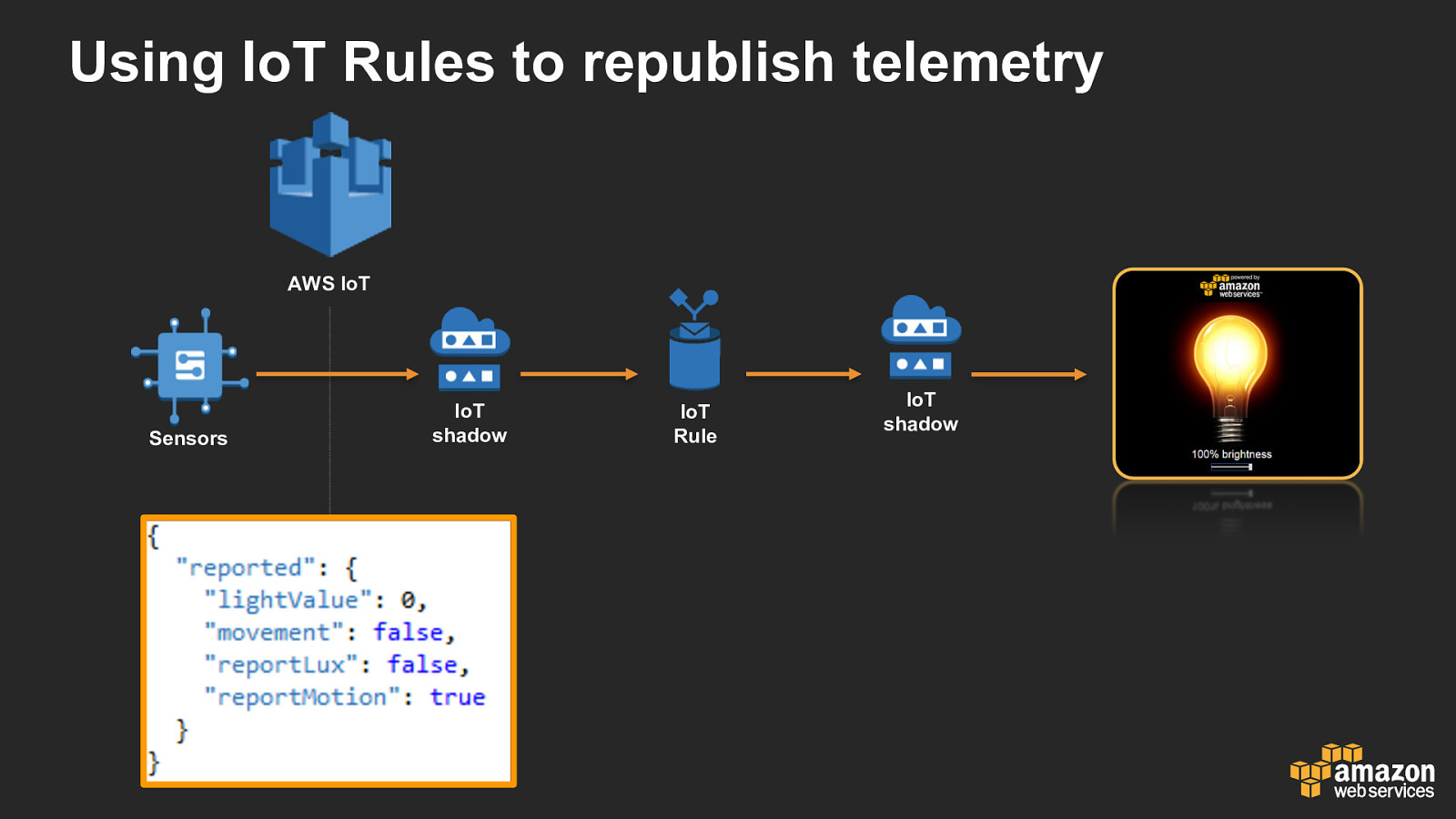
Using IoT Rules to republish telemetry AWS IoT Sensors IoT shadow IoT Rule IoT shadow
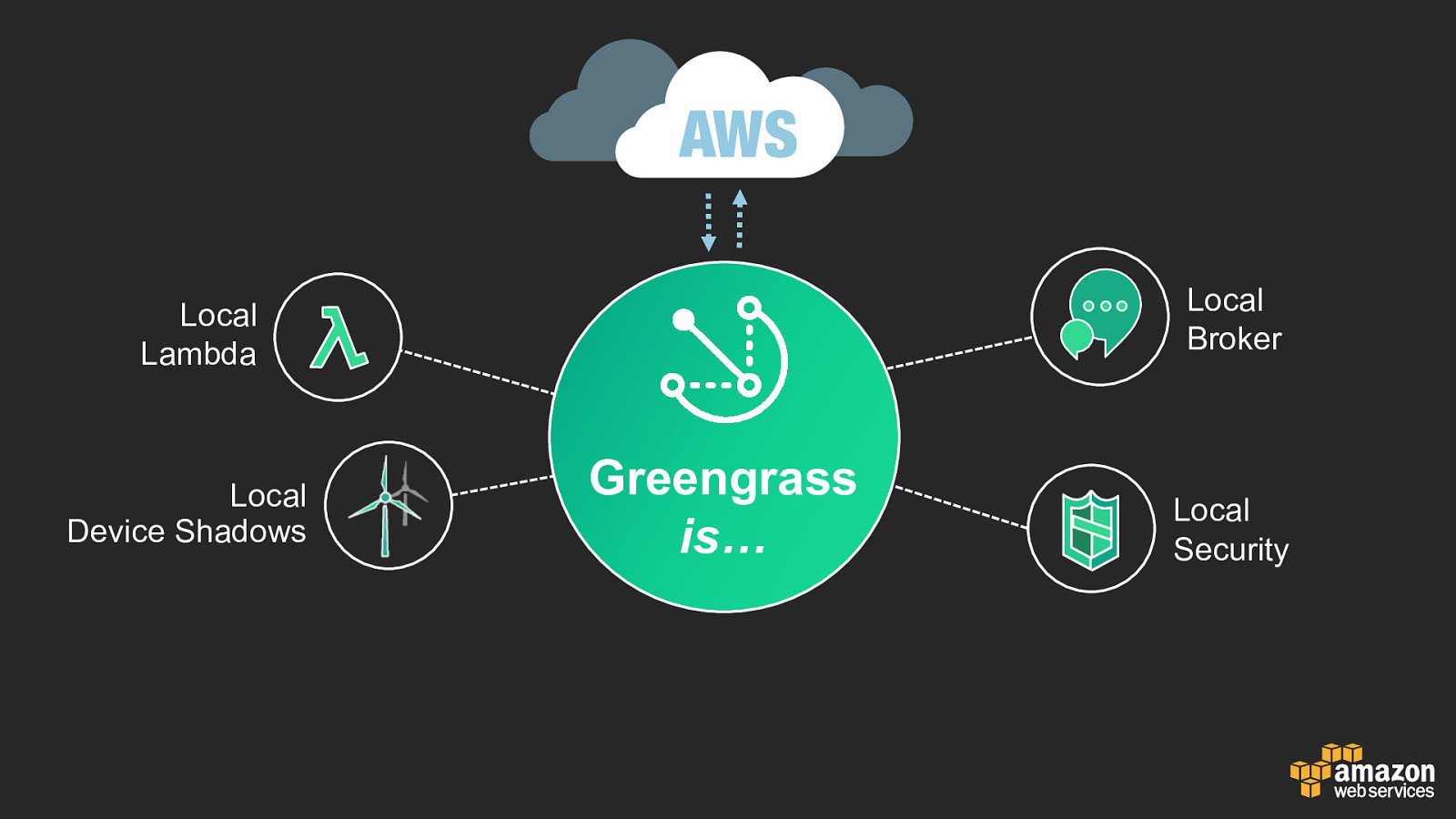
AWS Local Broker Local Lambda Local Device Shadows Greengrass is… Local Security
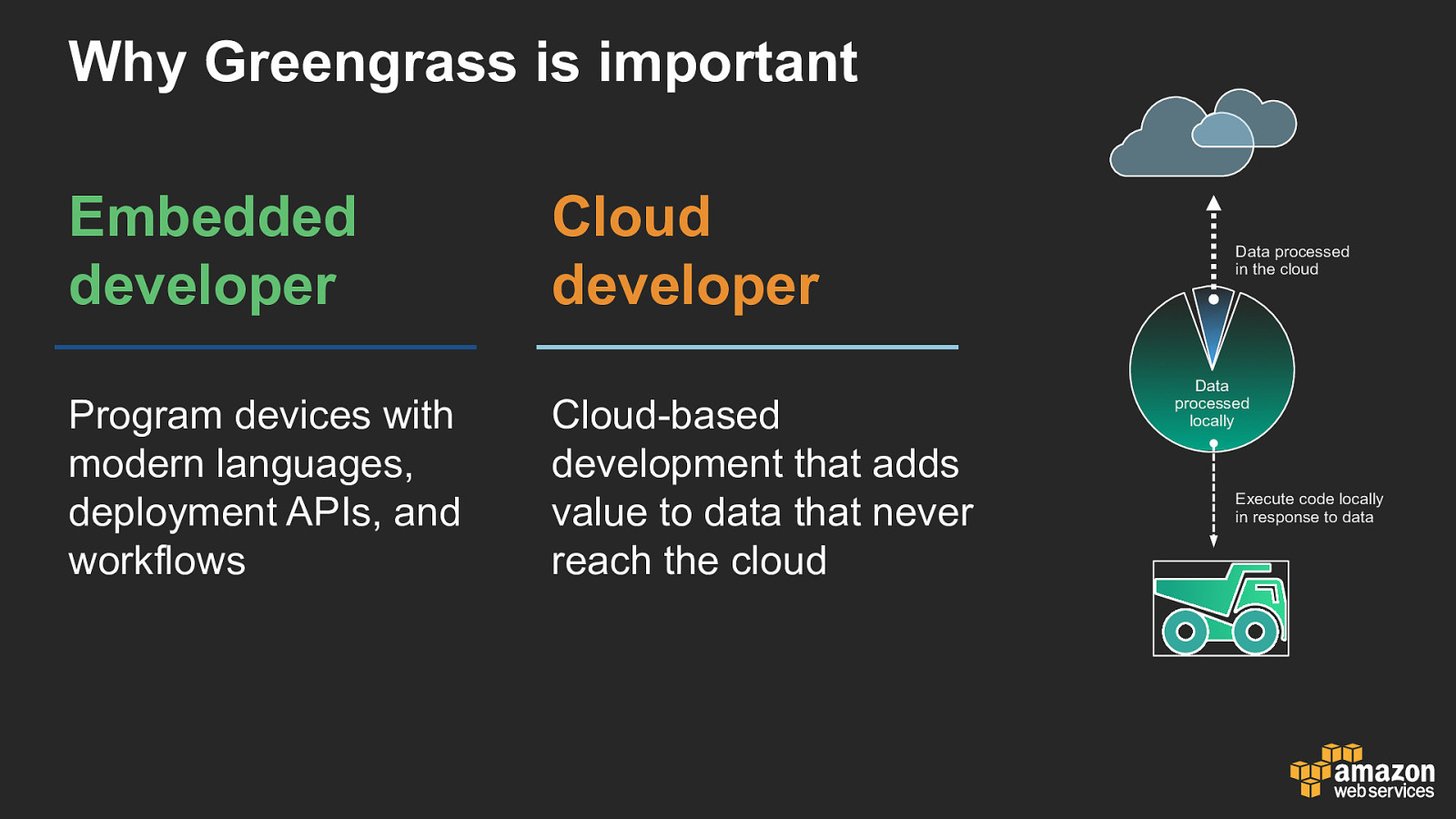
Why Greengrass is important Embedded developer Program devices with modern languages, deployment APIs, and workflows Cloud developer Cloud-based development that adds value to data that never reach the cloud Data processed in the cloud Data processed locally Execute code locally in response to data

Benefits of AWS Greengrass Respond to local events quickly Operate offline Simplified device programming Reduce the cost of IoT applications
Greengrass Components Greengrass is software, not hardware (you bring your own) 2 Components that work together: • Greengrass Core • IoT Device SDK
AWS Greengrass Core (GGC) The runtime responsible for Lambda execution, messaging, device shadows, security, and for interacting directly with the cloud
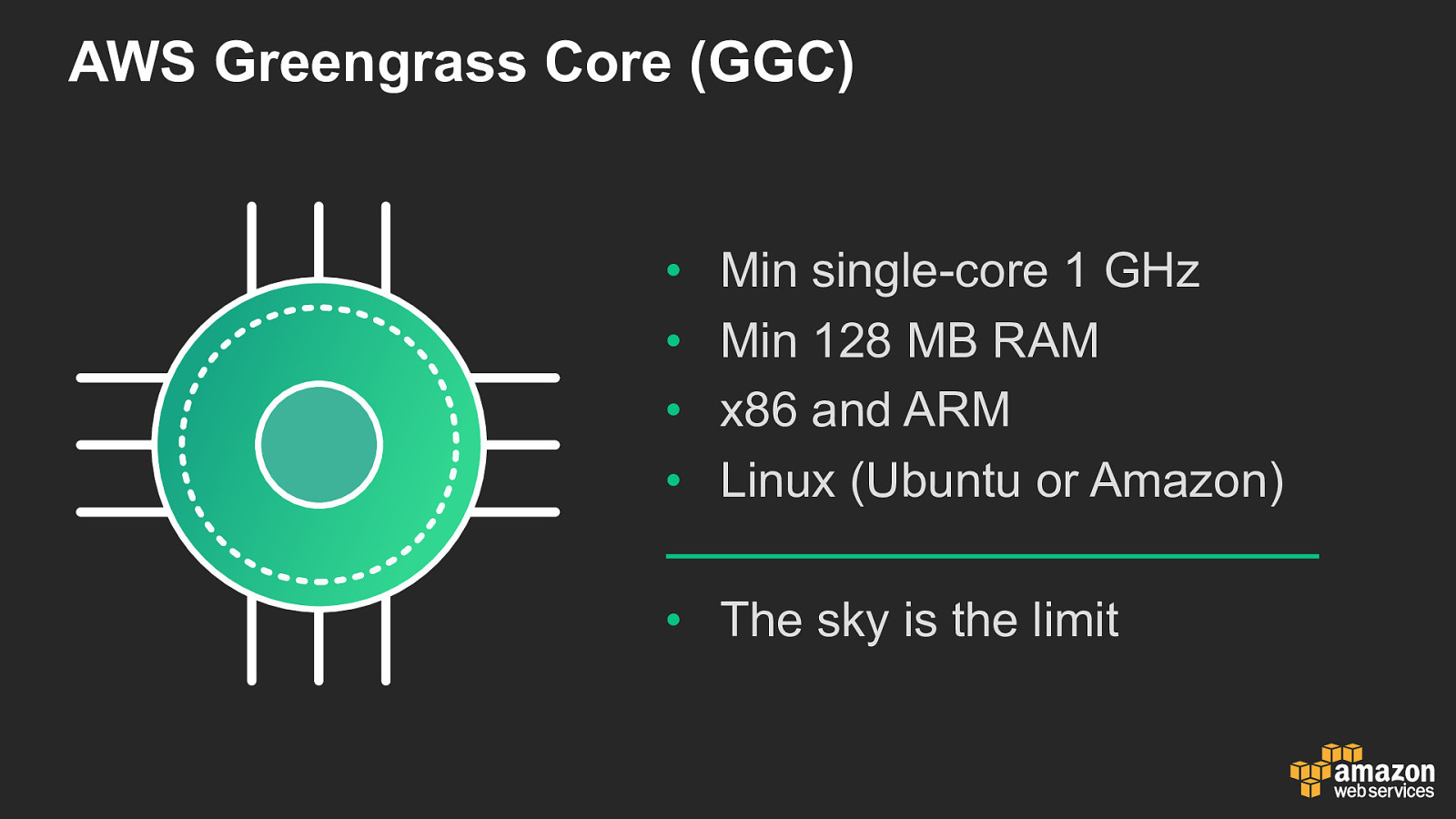
AWS Greengrass Core (GGC) • • • • Min single-core 1 GHz Min 128 MB RAM x86 and ARM Linux (Ubuntu or Amazon) • The sky is the limit
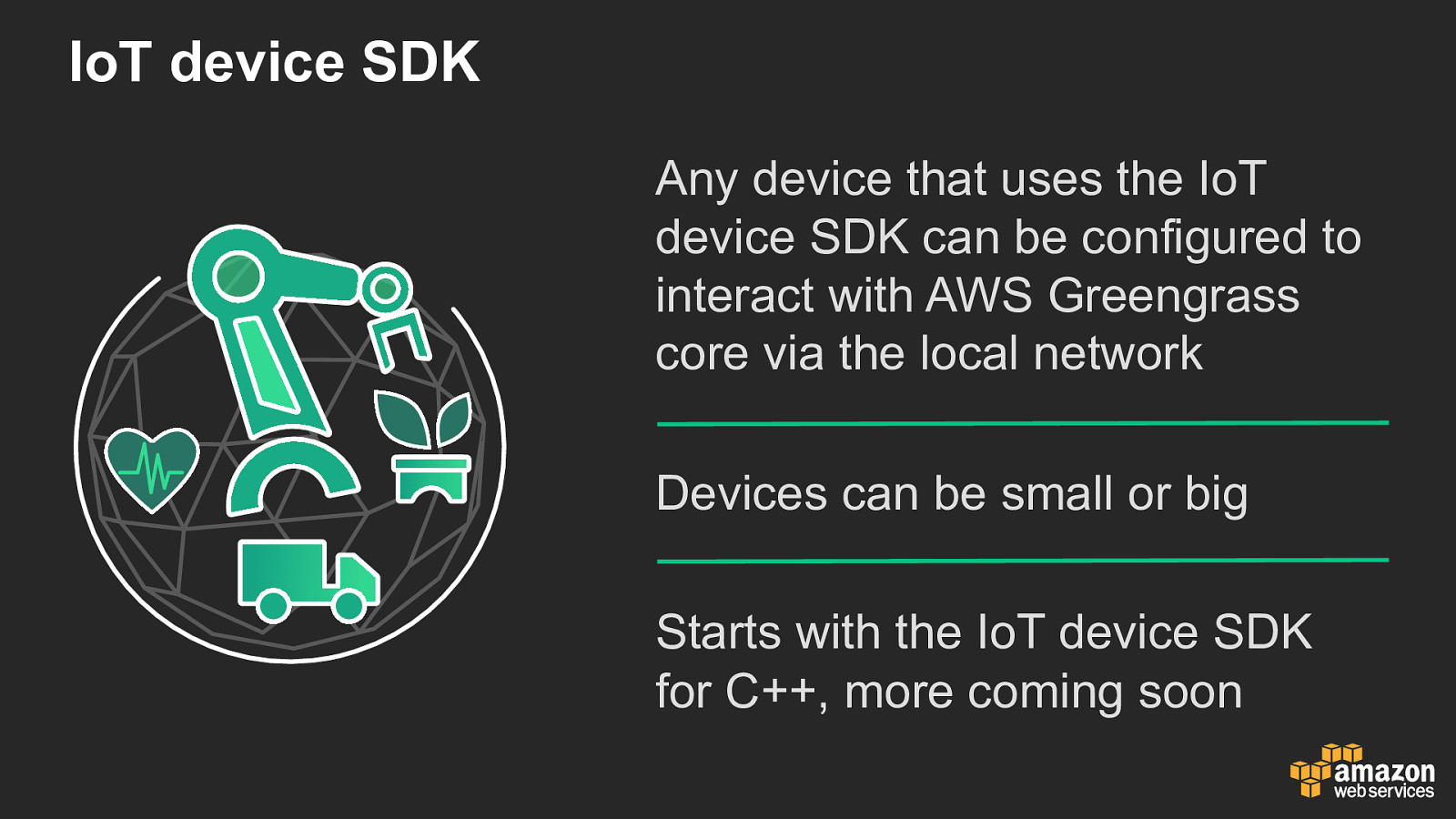
IoT device SDK Any device that uses the IoT device SDK can be configured to interact with AWS Greengrass core via the local network Devices can be small or big Starts with the IoT device SDK for C++, more coming soon
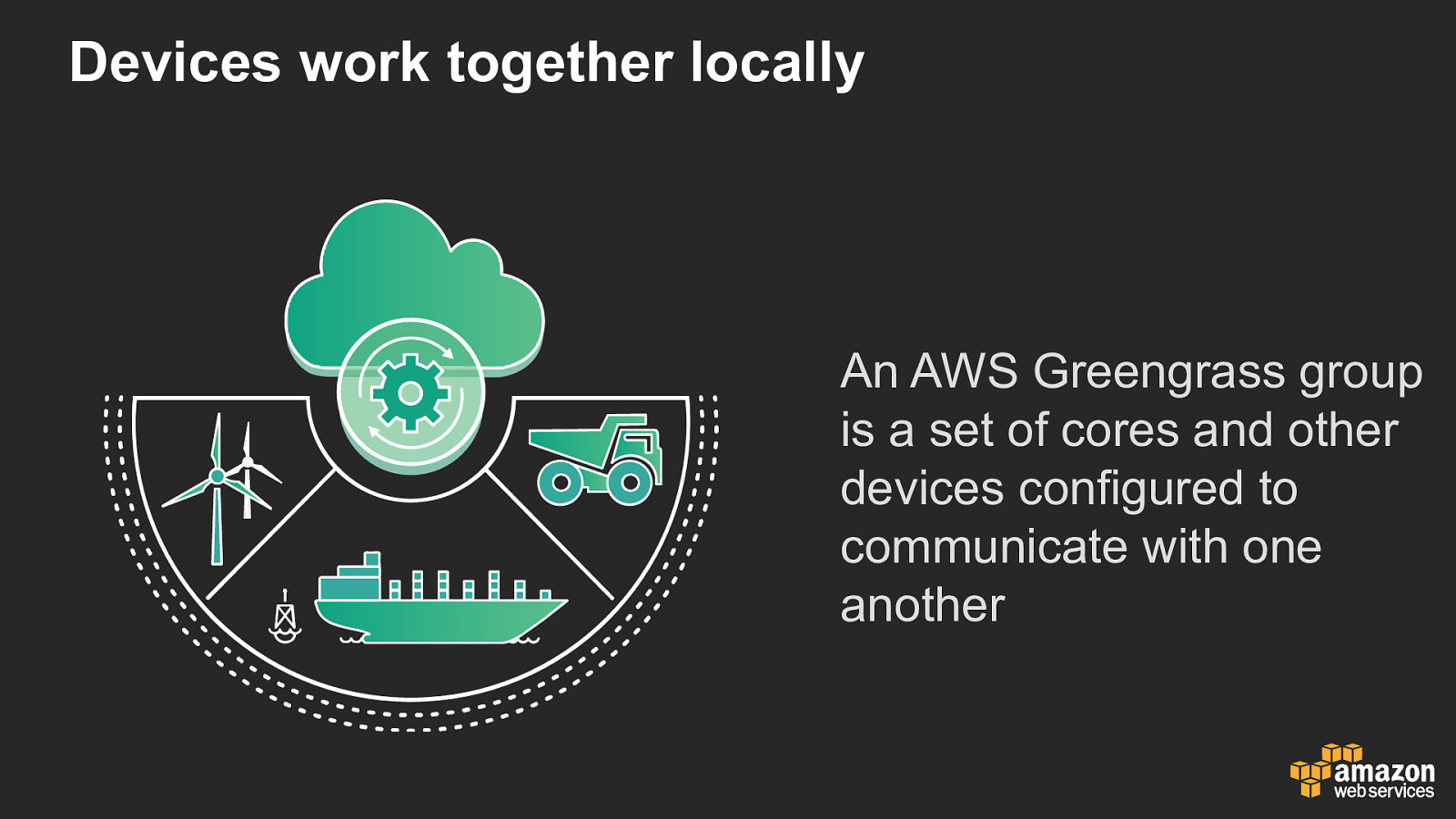
Devices work together locally An AWS Greengrass group is a set of cores and other devices configured to communicate with one another
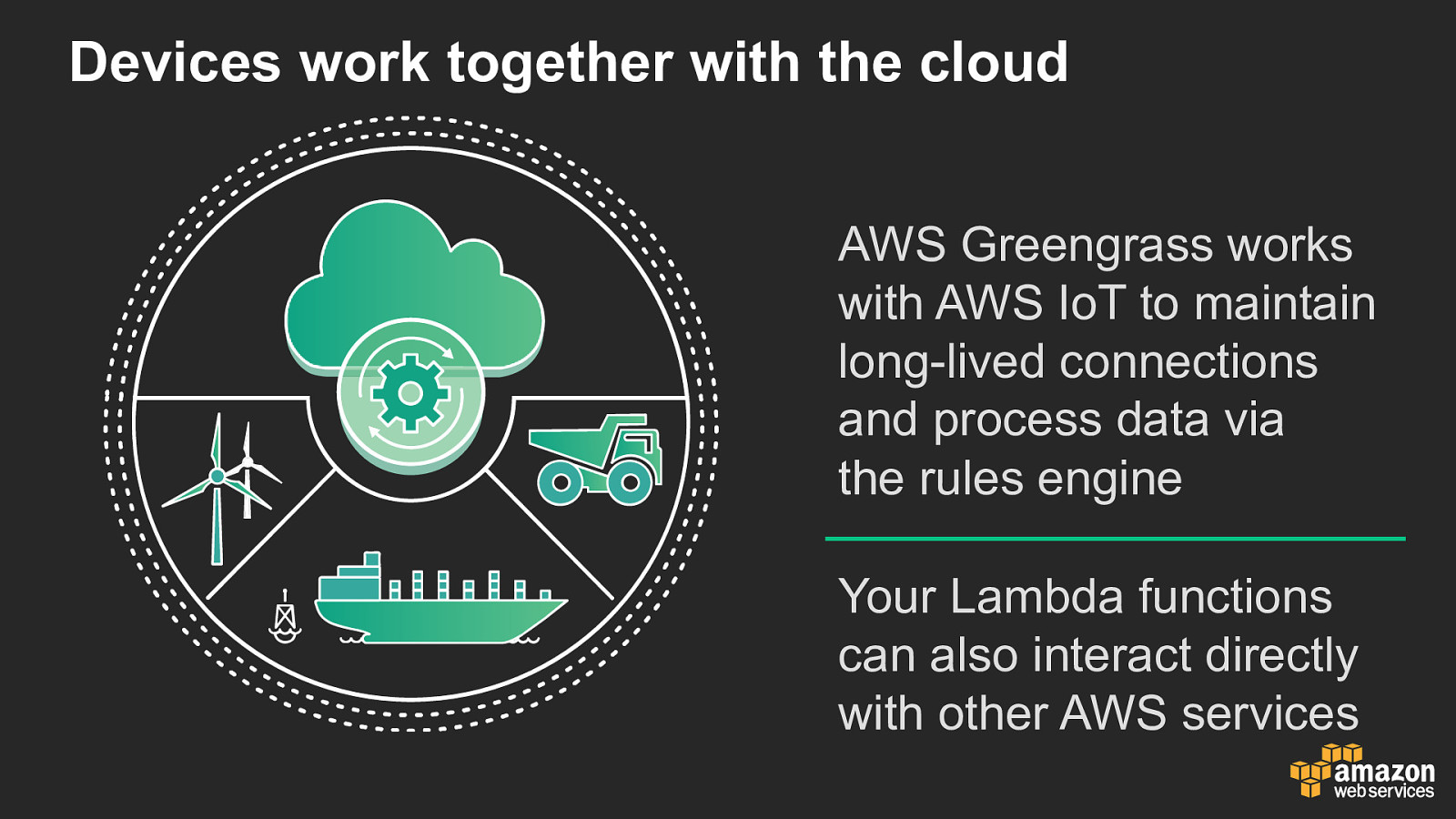
Devices work together with the cloud AWS Greengrass works with AWS IoT to maintain long-lived connections and process data via the rules engine Your Lambda functions can also interact directly with other AWS services
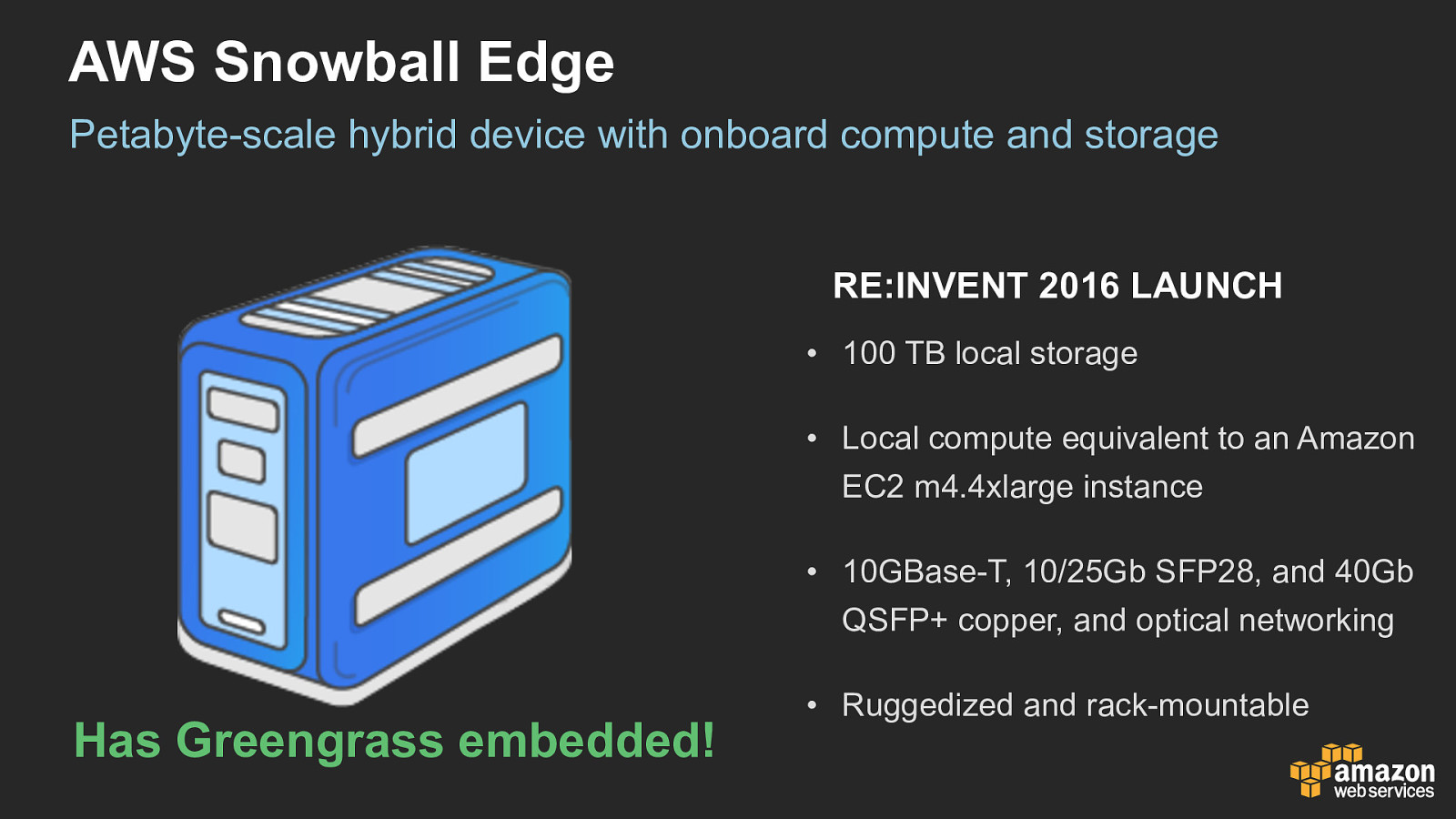
AWS Snowball Edge Petabyte-scale hybrid device with onboard compute and storage RE:INVENT 2016 LAUNCH • 100 TB local storage • Local compute equivalent to an Amazon EC2 m4.4xlarge instance • 10GBase-T, 10/25Gb SFP28, and 40Gb QSFP+ copper, and optical networking Has Greengrass embedded! • Ruggedized and rack-mountable
How to get started today http://aws.amazon.com/Greengrass Sign up for limited preview

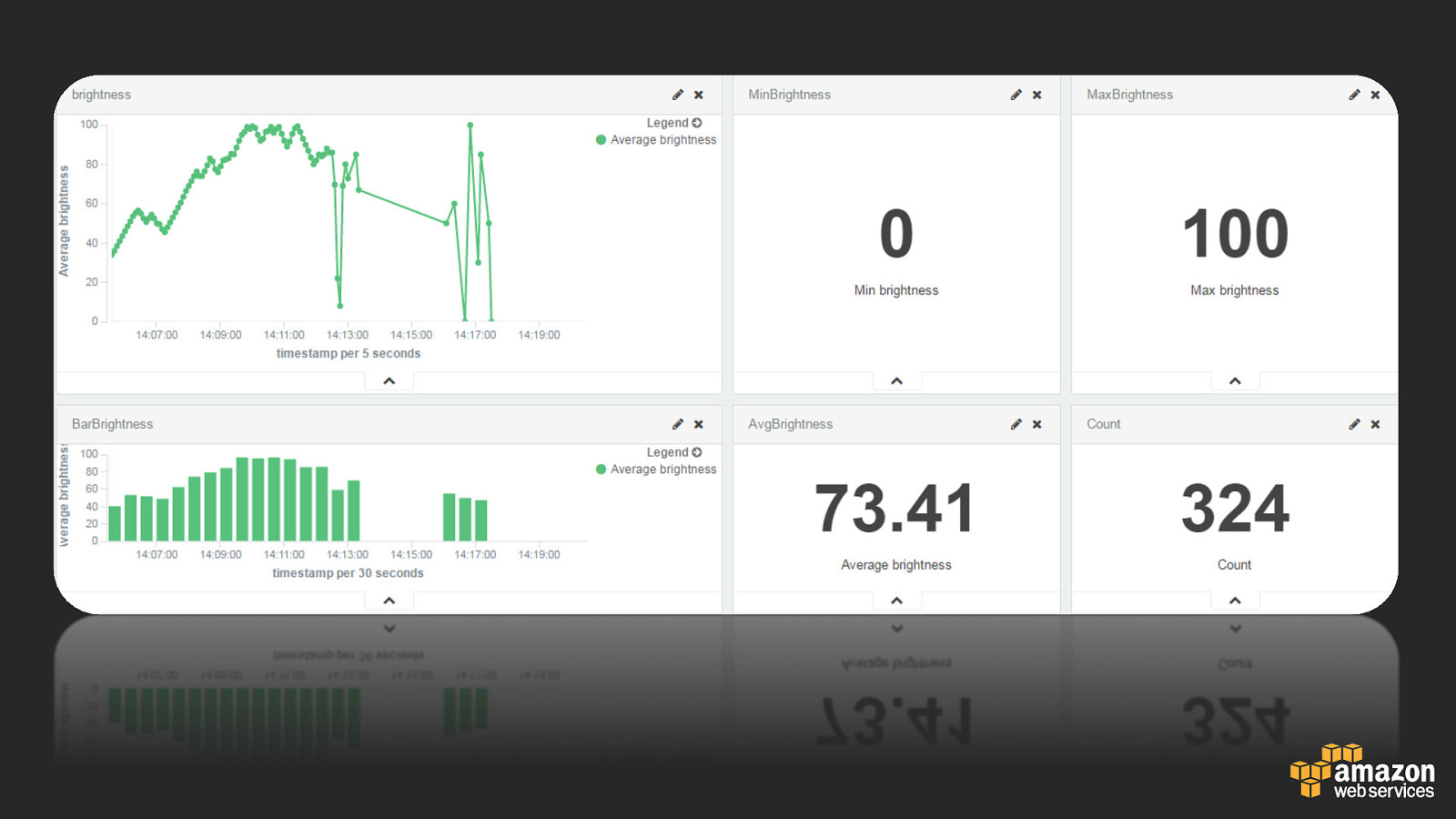
Demo: Color Cube Demo bit.ly/nyclight01
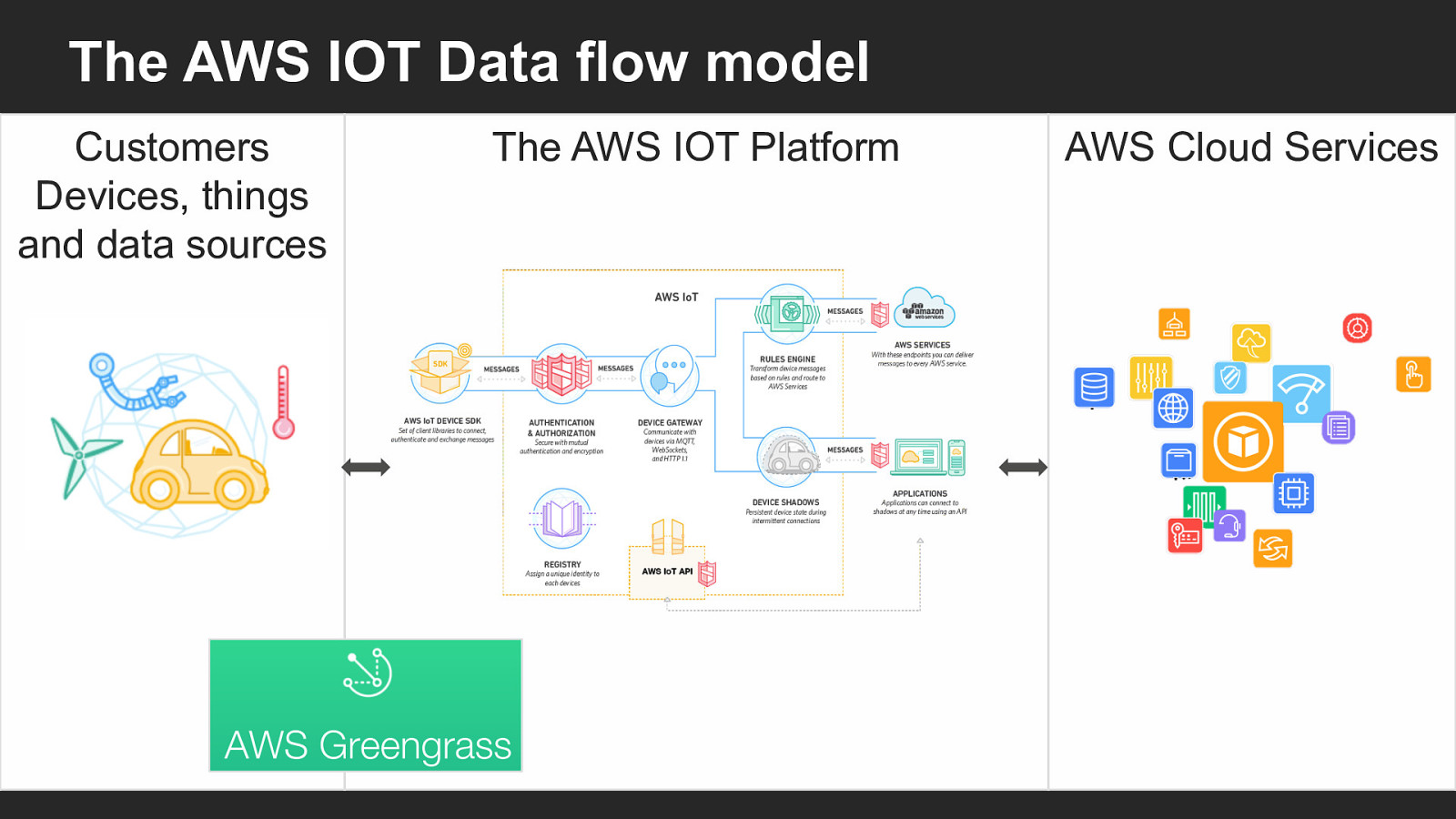
The AWS IOT Data flow model Customers Devices, things and data sources The AWS IOT Platform AWS Cloud Services

Chris Munns munns@amazon.com @chrismunns https://www.flickr.com/photos/theredproject/3302110152/

? https://secure.flickr.com/photos/dullhunk/202872717/