Making a Strong Case for Accessibility Todd Libby @toddlibby
A presentation at Beer City Code 2022 in August 2022 in Grand Rapids, MI, USA by Todd Libby

Making a Strong Case for Accessibility Todd Libby @toddlibby

Thank you!

Thank you!
Maine

Arizona



Portland, Maine 🦞 Phoenix, Arizona 🥵 Accessibility Team Lead @ WebstaurantStore Accessibility Engineer @ Centre for Inclusive Design W3C Invited Expert - Accessibility & WCAG3 23 years of developer, design, & accessibility experience ➡︎ Host of the Front End Nerdery Podcast

Making Your Case at Your Organization

Using Data to Advocate

WebAIM Million Report • One million homepages https://webaim.org/projects/million/

WebAIM Million Report • One million homepages • 50.8+ million accessibility errors https://webaim.org/projects/million/

WebAIM Million Report • One million homepages • 50.8+ million accessibility errors • Decreased 1.1% since February 2021 https://webaim.org/projects/million/

WebAIM Million Report • 887 to 955 elements per home page
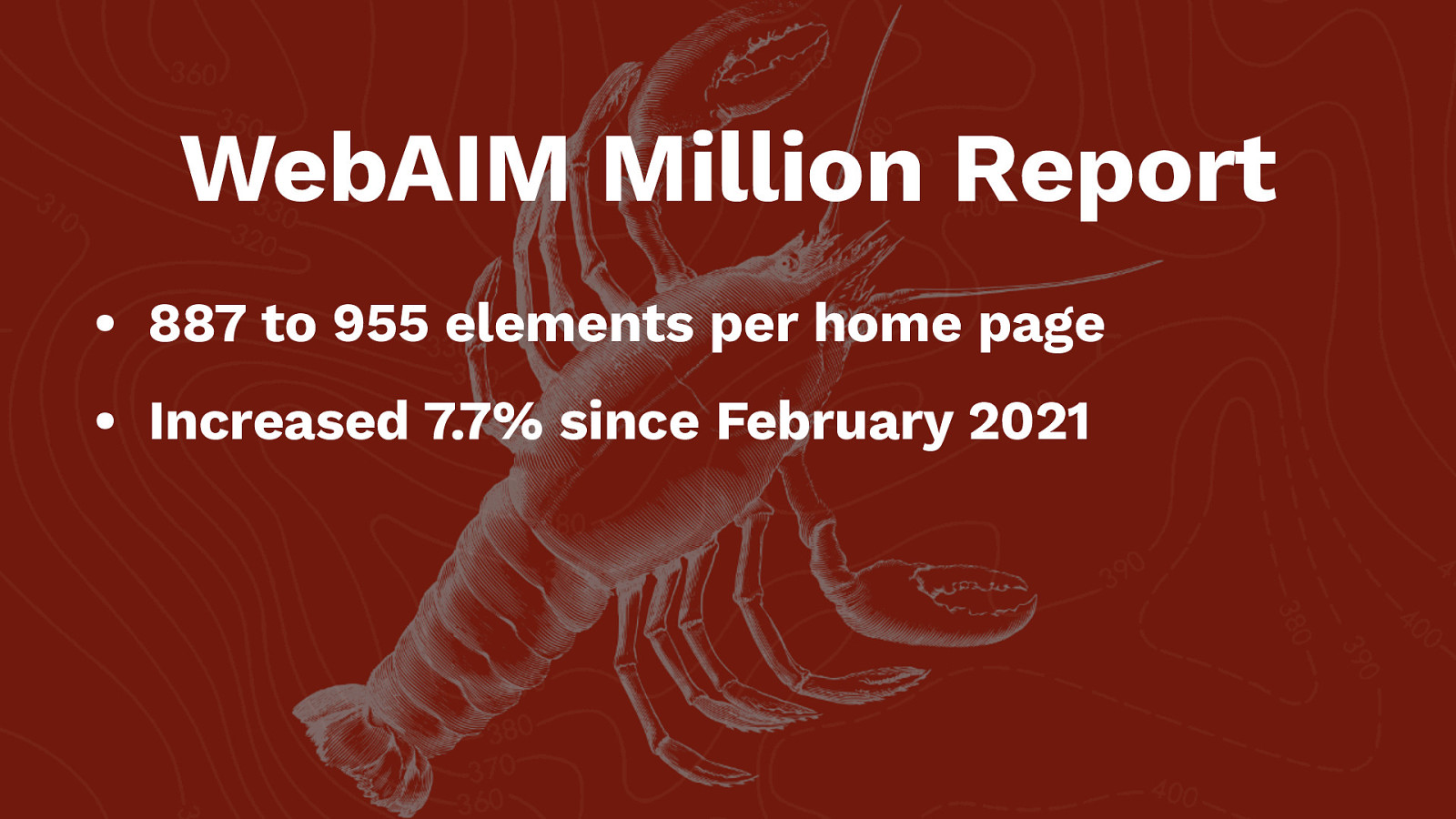
WebAIM Million Report • 887 to 955 elements per home page • Increased 7.7% since February 2021
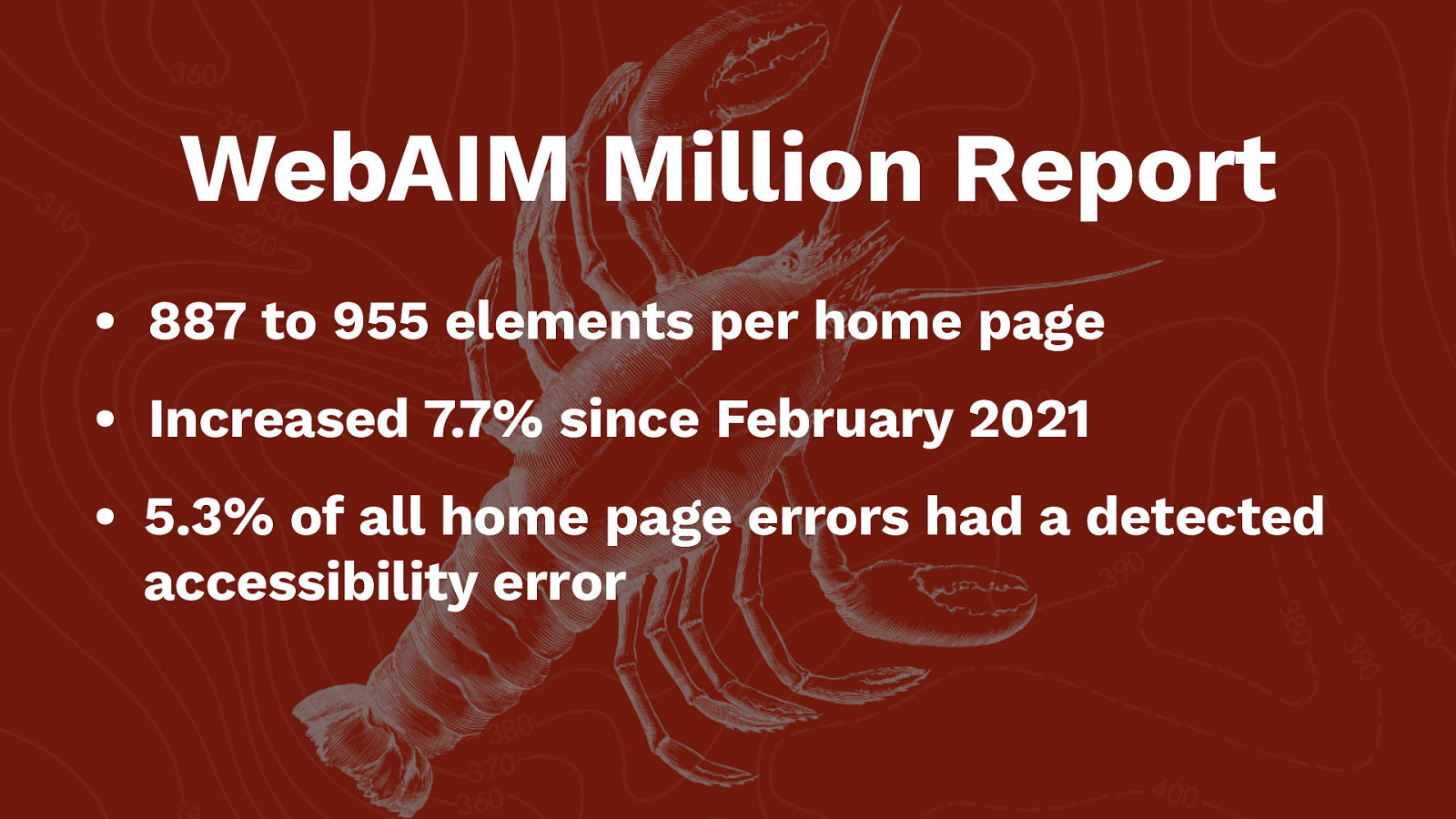
WebAIM Million Report • 887 to 955 elements per home page • Increased 7.7% since February 2021 • 5.3% of all home page errors had a detected accessibility error

96.8% had WCAG 2 failures

What are the failures?

Low Contrast of Text

1.1:1 color contrast ratio g (Contrast ran es from 1:1 to 21:1)

SC 1.4.3 Contrast (Minimum)(Level AA) “The visual presentation of text and images of text has a contrast ratio of at least 4.5 to 1” https://www.w3.org/WAI/WCAG21/Understanding/contrast-minimum.html

Missing Alternative Text


<img src=“/path/to/img/lobster.png”> 🚫 <img src=“/path/to/img/lobster.png” alt=“”> ✅ <img src=“/path/to/img/lobster.png” alt=“Todd’s lobster roll, hot butter, and blueberry soda.”> ✅

• Low contrast text • Missing alternative text of images • Empty links • Missing form input labels • Empty buttons • Missing document language

96.5% of all errors
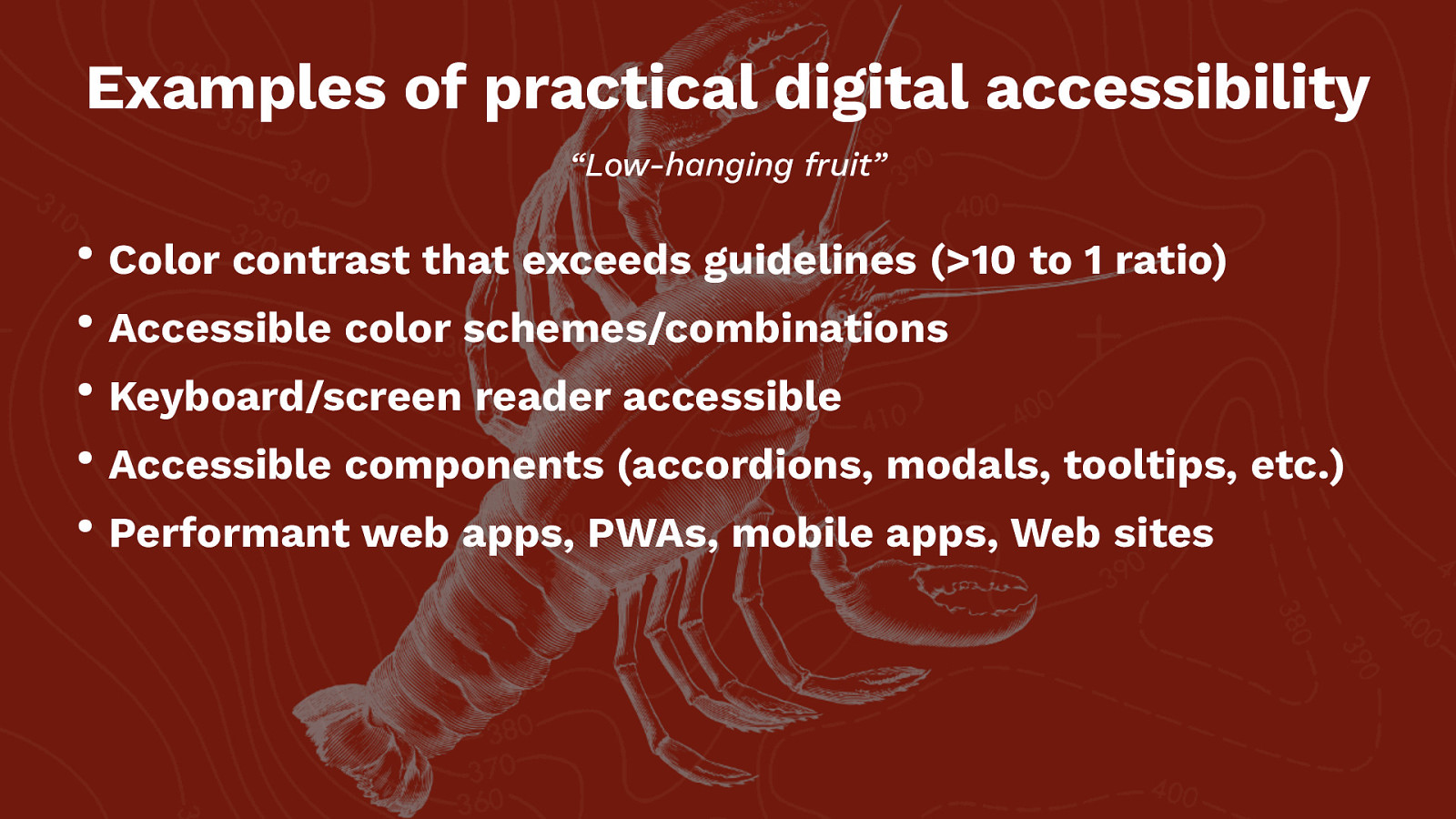
Examples of practical digital accessibility “Low-hanging fruit” • Color contrast that exceeds guidelines (>10 to 1 ratio) • Accessible color schemes/combinations • Keyboard/screen reader accessible • Accessible components (accordions, modals, tooltips, etc.) • Performant web apps, PWAs, mobile apps, Web sites

More Examples of practical digital accessibility • Scrollable interactive content • Alternative text on images where necessary (infographics, charts, graphs) • Accessible when viewing mobile phone screen (glare from sun) • Other situational disabilities • Broken arm • Child on lap

Disability is just Blind, Deaf, or Paralysis. Right?


Learning / Cognitive ADHD / ADD Fibromyalgia / Arthritis Tremors / Parkinson’s Migraine Headaches / Photophobia

Excuses

“The client doesn’t have the budget for it.”

“We’ll get to it after launch.”

“Why do we even need to make this thing accessible?”

“Why do we even need to make this thing accessible?” “There is no time to do this.”

“Why do we even need to make this thing accessible?” “There is no time to do this.” “We don’t have disabled users.”

“Why do we even need to make this thing accessible?” “There is no time to do this.” “We don’t have disabled users.” “The people that use our product are not disabled.”

“It’s a huge waste of time.”




Buy-In

Buy-In How do I et buy-in from stakeholders, clients, collea ues? g g • Support trickles down from C-suite & top level to managers, teams, and individuals.

Buy-In How do I et buy-in from stakeholders, clients, collea ues? • Support trickles down from C-suite & top level to managers, teams, and individuals. g g • Do this from the start. Low maintenance is needed, because of accessible designs and clean code.

Buy-In How do I et buy-in from stakeholders, clients, collea ues? • Support trickles down from C-suite & top level to managers, teams, and individuals. • Do this from the start. Low maintenance is needed, because of accessible designs and clean code. g g • Cite instances from the lawsuits that have been won against major corporations (Domino’s Pizza, Target, Bank of America).

Buy-In How do I et buy-in from stakeholders, clients, collea ues? • Support trickles down from C-suite & top level to managers, teams, and individuals. • Do this from the start. Low maintenance is needed, because of accessible designs and clean code. • Cite instances from the lawsuits that have been won against major corporations (Domino’s Pizza, Target, Bank of America). g g • Live testing with disabled users recorded on video.

$8 Trillion Worldwide of disposable income of individuals with disabilities https://www.triplepundit.com/story/2022/investing-disability-inclusion/741416

$490 Billion Disposable income of individuals with disabilities in the U.S. https://diverseabilitymagazine.com/2018/09/buying-power-people-disabilities/

Advocates

Organization Advocates Teams or individuals that advocate in your or anization g • Having a person throughout each department or a team focused on accessibility as a liaison.

Organization Advocates Teams or individuals that advocate in your or anization • Having a person throughout each department or a team focused on accessibility as a liaison. g • Someone that can answer questions and work with others to practice the guidelines and work with others to make accessible products.

Organization Advocates Teams or individuals that advocate in your or anization • Having a person throughout each department or a team focused on accessibility as a liaison. • Someone that can answer questions and work with others to practice the guidelines and work with others to make accessible products. g • Help set up documentation and tooling, serve as an intermediary between departments.

Assessment

Assessment Assess the product and the proficiency within the or anization g • Gauging where the product(s) are as far as how inclusive and accessible they are is a key priority.

Assessment Assess the product and the proficiency within the or anization • Gauging where the product(s) are as far as how inclusive and accessible they are is a key priority. g • What is the current state of the product, website, or mobile application?

Assessment Assess the product and the proficiency within the or anization • Gauging where the product(s) are as far as how inclusive and accessible they are is a key priority. • What is the current state of the product, website, or mobile application? g • Getting the general idea of the level of knowledge that teams and people in the company currently have.

Assessment Assess the product and the proficiency within the or anization • Gauging where the product(s) are as far as how inclusive and accessible they are is a key priority. • What is the current state of the product, website, or mobile application? • Getting the general idea of the level of knowledge that teams and people in the company currently have. g • How versed are they in guidelines (WCAG) and practices?

Assessment Assess the product and the proficiency within the or anization • Gauging where the product(s) are as far as how inclusive and accessible they are is a key priority. • What is the current state of the product, website, or mobile application? • Getting the general idea of the level of knowledge that teams and people in the company currently have. • How versed are they in guidelines (WCAG) and practices? g • How much training do you have and will you need?

Training

Training Maintainin A Written Record • Of all accessibility training done g • It should meet requirements that apply to the organization

Training Maintainin A Written Record • Of all accessibility training done • It should meet requirements that apply to the organization g • Great way to keep data on all training done in organization

Training Maintainin A Written Record • Of all accessibility training done • It should meet requirements that apply to the organization • Great way to keep data on all training done in organization g • Record the training and who trained and when it was completed

Training Maintainin A Written Record • Of all accessibility training done • It should meet requirements that apply to the organization • Great way to keep data on all training done in organization g • Record the training and who trained and when it was completed • If there is no inter-organizational training use orgs that do training.

Training Maintainin A Written Record • Of all accessibility training done • It should meet requirements that apply to the organization • Great way to keep data on all training done in organization • Record the training and who trained and when it was completed • If there is no inter-organizational training use orgs that do training. • Deque • TPGi g • WebAIM

Guidelines

Guidelines Consistent implementation • Design systems ensure accessibility and inclusivity and the understanding of code better

Guidelines Consistent implementation • Design systems ensure accessibility and inclusivity and the understanding of code better • Accessible components reduce time to implement

Guidelines Consistent implementation • Design systems ensure accessibility and inclusivity and the understanding of code better • Accessible components reduce time to implement ffi • Testing procedures implemented so people can do jobs well and e ciently

Guidelines Consistent implementation • Design systems ensure accessibility and inclusivity and the understanding of code better • Accessible components reduce time to implement • Testing procedures implemented so people can do jobs well and e ffi • Document guidelines in a collaborative manner using tools ciently

Standards

Standards Guidelines from different countries • American Disabilities Act (ADA), the Air Carrier Access Act (ACAA), and the Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) - United States • Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act, DOJ issues guidance for website accessibility - (U.S. Government)

Standards Guidelines from different countries • American Disabilities Act (ADA), the Air Carrier Access Act (ACAA), and the Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) - United States • Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act, DOJ issues guidance for website accessibility - (U.S. Government) • Accessible Canada Act (ACA), Accessibilities for Ontario’s with Disabilities Act (AODA) - Canada

Standards Guidelines from different countries • American Disabilities Act (ADA), the Air Carrier Access Act (ACAA), and the Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) - United States • Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act, DOJ issues guidance for website accessibility - (U.S. Government) • Accessible Canada Act (ACA), Accessibilities for Ontario’s with Disabilities Act (AODA) - Canada • Web Accessibility Directive which updated EN 301 549, European Accessibility Act - European Union

Standards Guidelines from different countries • American Disabilities Act (ADA), the Air Carrier Access Act (ACAA), and the Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) - United States • Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act, DOJ issues guidance for website accessibility - (U.S. Government) • Accessible Canada Act (ACA), Accessibilities for Ontario’s with Disabilities Act (AODA) - Canada • Web Accessibility Directive which updated EN 301 549, European Accessibility Act - European Union • Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) - Internationally

Standards Guidelines from different countries • American Disabilities Act (ADA), the Air Carrier Access Act (ACAA), and the Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) - United States • Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act, DOJ issues guidance for website accessibility - (U.S. Government) • Accessible Canada Act (ACA), Accessibilities for Ontario’s with Disabilities Act (AODA) - Canada • Web Accessibility Directive which updated EN 301 549, European Accessibility Act - European Union • Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) - Internationally • Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CPRD) • Article 9 • Article 21

Testing

Use Cases/Testing Hirin disabled people g • Test & record cases where disabled users are using the product

Use Cases/Testing Hirin disabled people • Test & record cases where disabled users are using the product g • Present to C-suite & top level people to colleagues/teams

Use Cases/Testing Hirin disabled people • Test & record cases where disabled users are using the product • Present to C-suite & top level people to colleagues/teams • Outsource testing with companies: g • Fable

Use Cases/Testing Hirin disabled people • Test & record cases where disabled users are using the product • Present to C-suite & top level people to colleagues/teams • Outsource testing with companies: • Fable • Hire disabled people! g • Teaching and advocating. They have the lived experiences.

Accessibility Overlays

“We use an accessibility overlay. We’re okay.”


AccessiBe Audioeye Equalweb Facil’iti Usablenet Userway Many, many more!

Overlays will get you sued.

!==

So what do we do?

Maintenance

Maintenance Accessibility is never done • Automated testing wherever possible with new releases or changes

Maintenance Accessibility is never done • Automated testing wherever possible with new releases or changes • Screen reader analysis before every release

Maintenance Accessibility is never done • Automated testing wherever possible with new releases or changes • Screen reader analysis before every release • Annual audits

Maintenance Accessibility is never done • Automated testing wherever possible with new releases or changes • Screen reader analysis before every release • Annual audits • User testing

Maintenance Accessibility is never done • Automated testing wherever possible with new releases or changes • Screen reader analysis before every release • Annual audits • User testing • Accessibility is never done! Keep moving forward!

Maintenance Accessibility is never done • Automated testing wherever possible with new releases or changes • Screen reader analysis before every release • Annual audits • User testing • Accessibility is never done! Keep moving forward! • Like the web, accessibility is always evolving


“…our industry as a whole thinks less and less about accessibility (not that we ever had an A game on the subject), and talks less and less about progressive enhancement, preferring to chase the ephemeral goal posts of overengineered solutions to non-problems.” Jeffrey Zeldman - https://www.zeldman.com/2019/12/01/bluebeanieday2019/
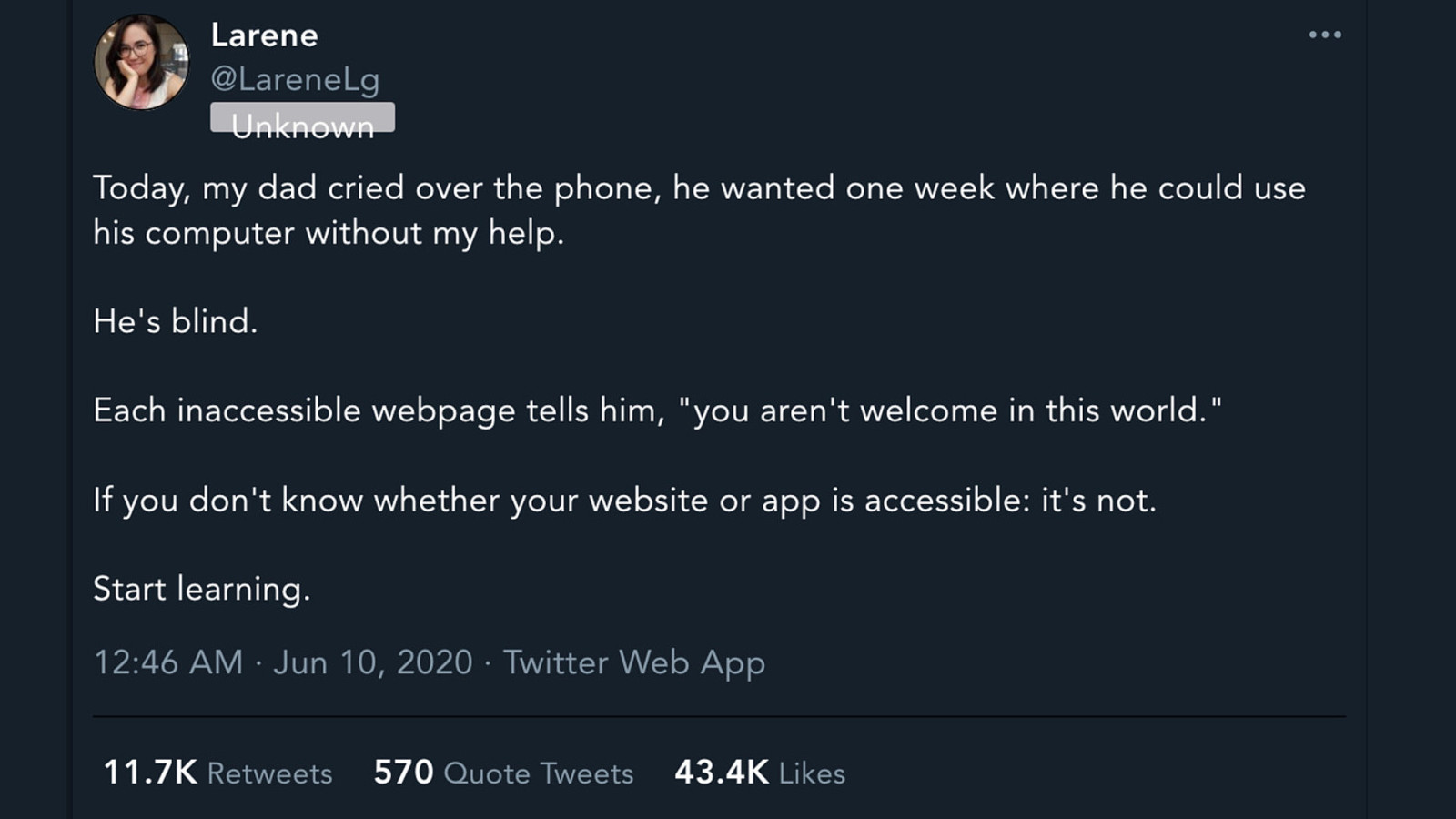

Design and develop for people not like yourself and keep that in mind when throwing words like “inclusive” and “accessible” around.

A11y is a right. NOT a privilege. https://cottonbureau.com/products/a11y-is-a-right#/5254640/

“The power of the Web is in its universality. Access by everyone regardless of disabilities an essential aspect.” — Sir Tim Berners Lee https://www.w3.org/standards/webdesign/accessibility

Links https://toddl.dev/slides/ @toddlibby on Twitter LinkedIn - 🦞 Todd Libby

Thank you!