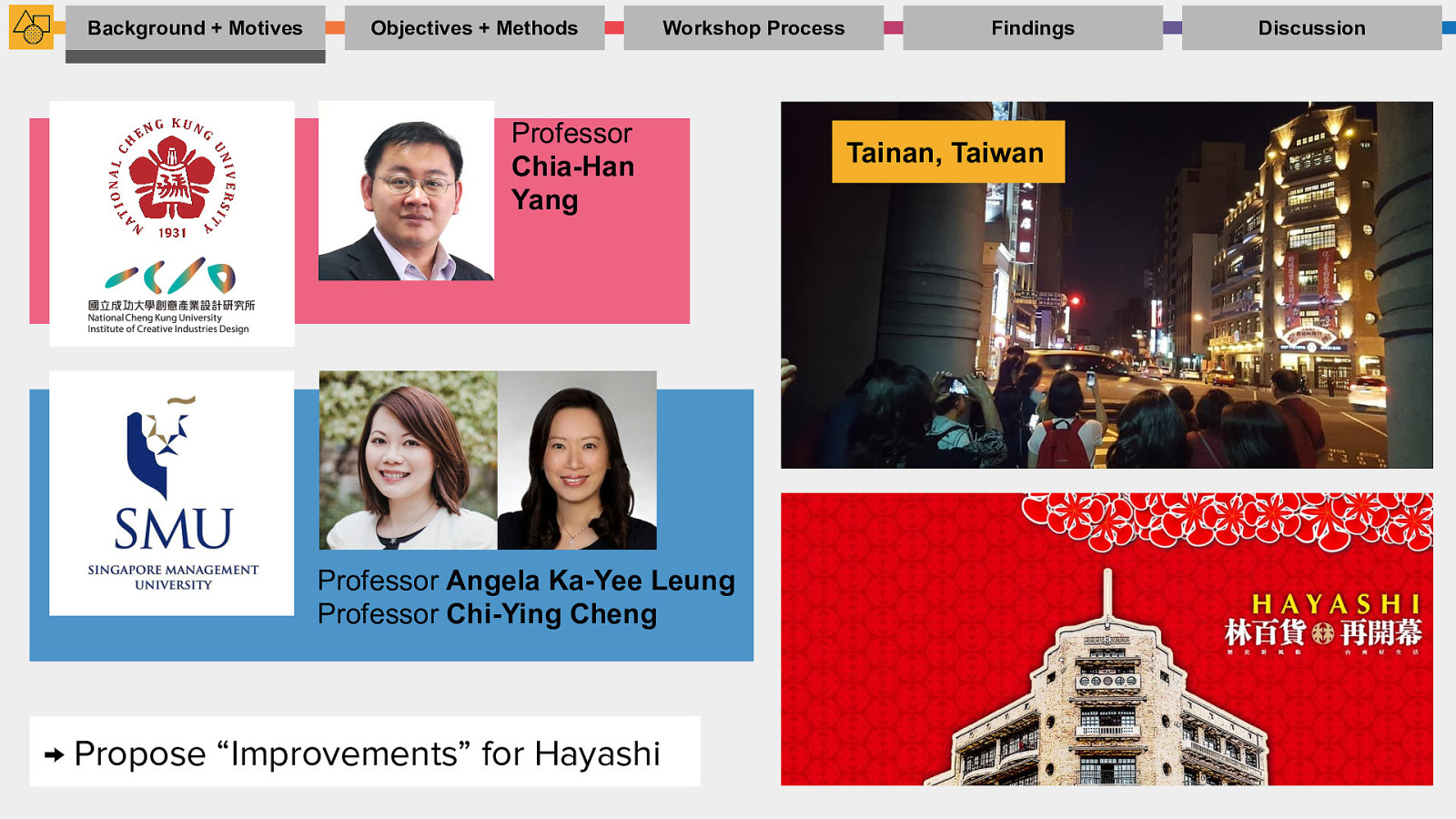
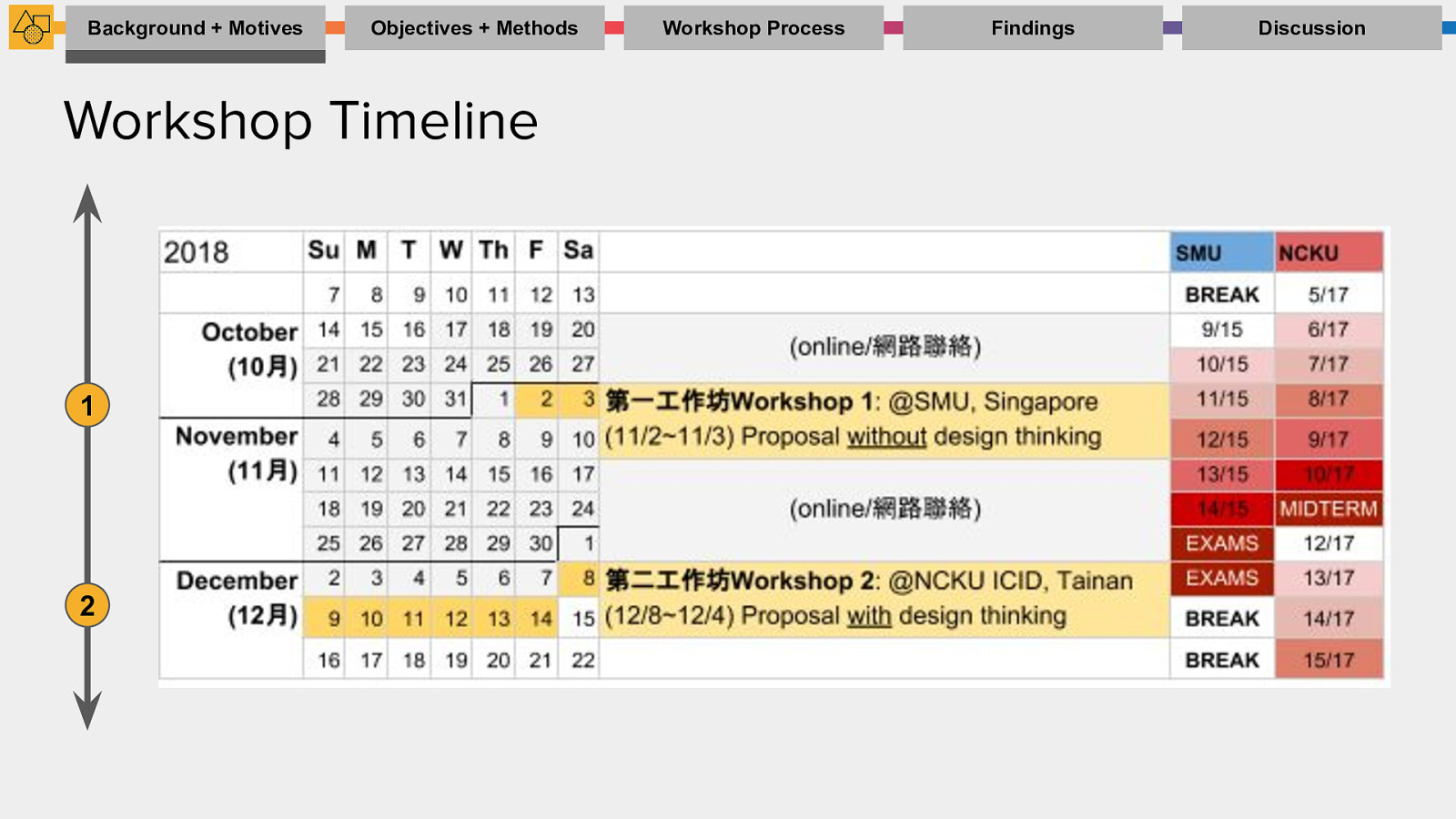
Background + Motives
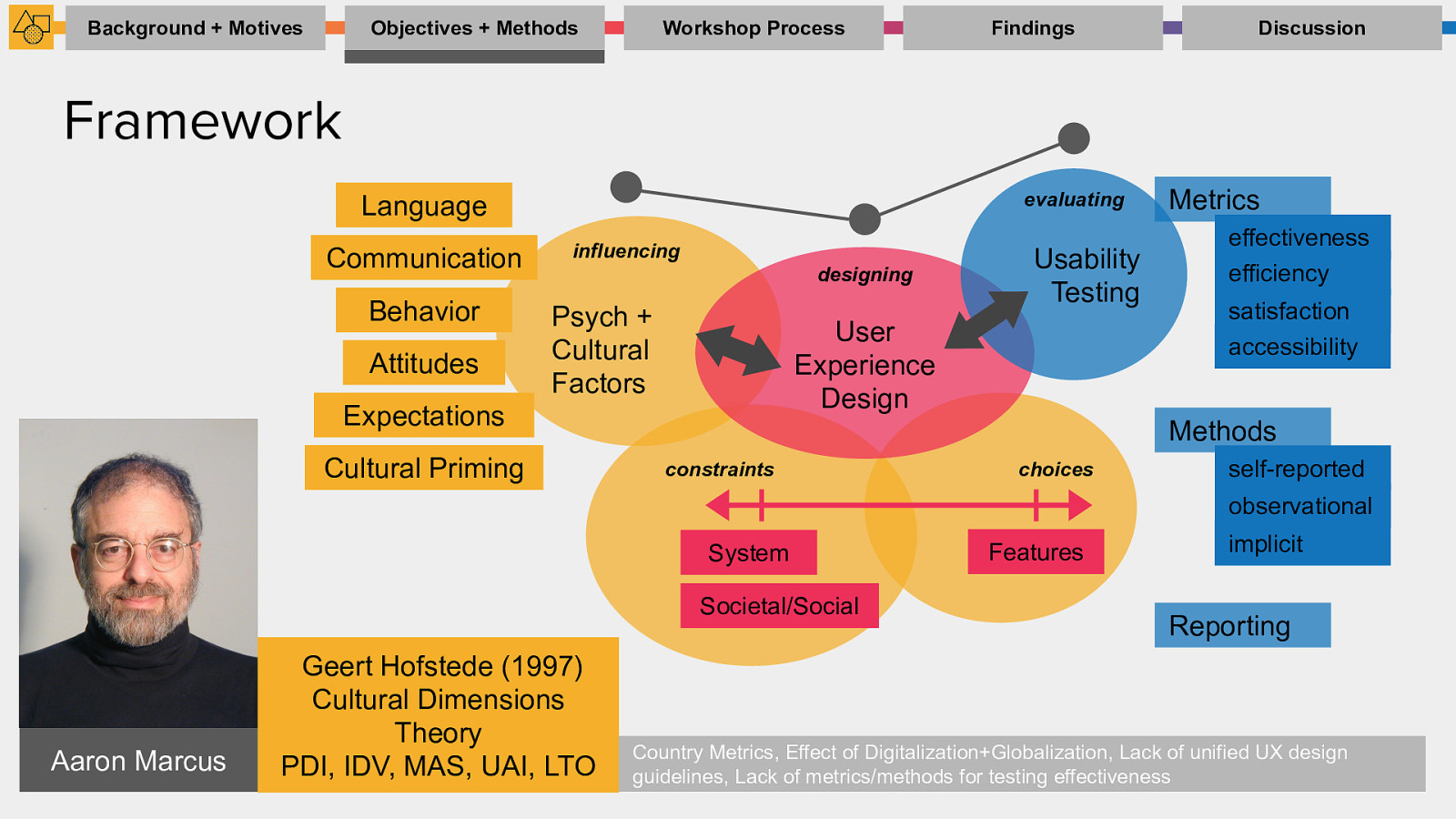
Objectives + Methods
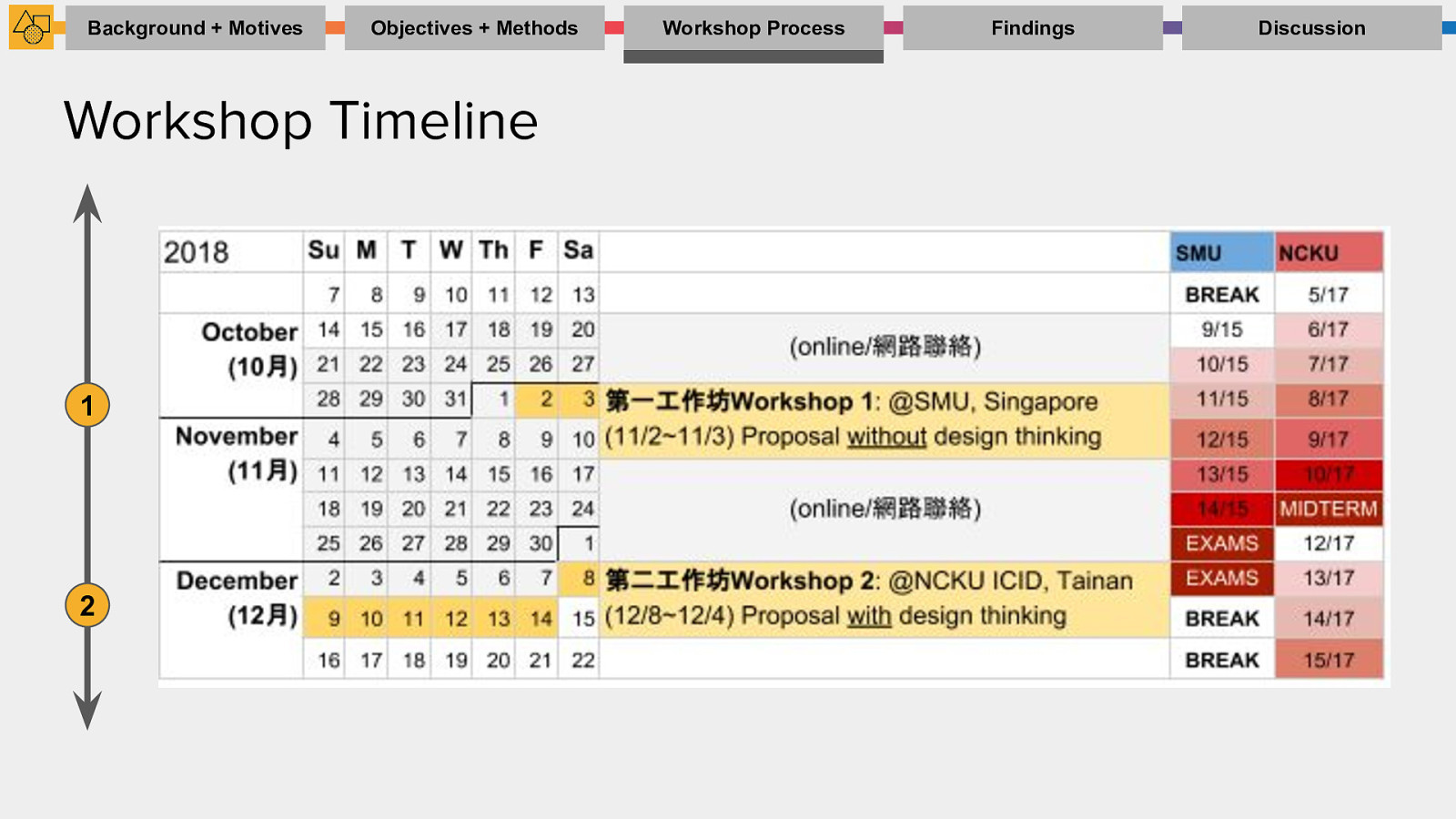
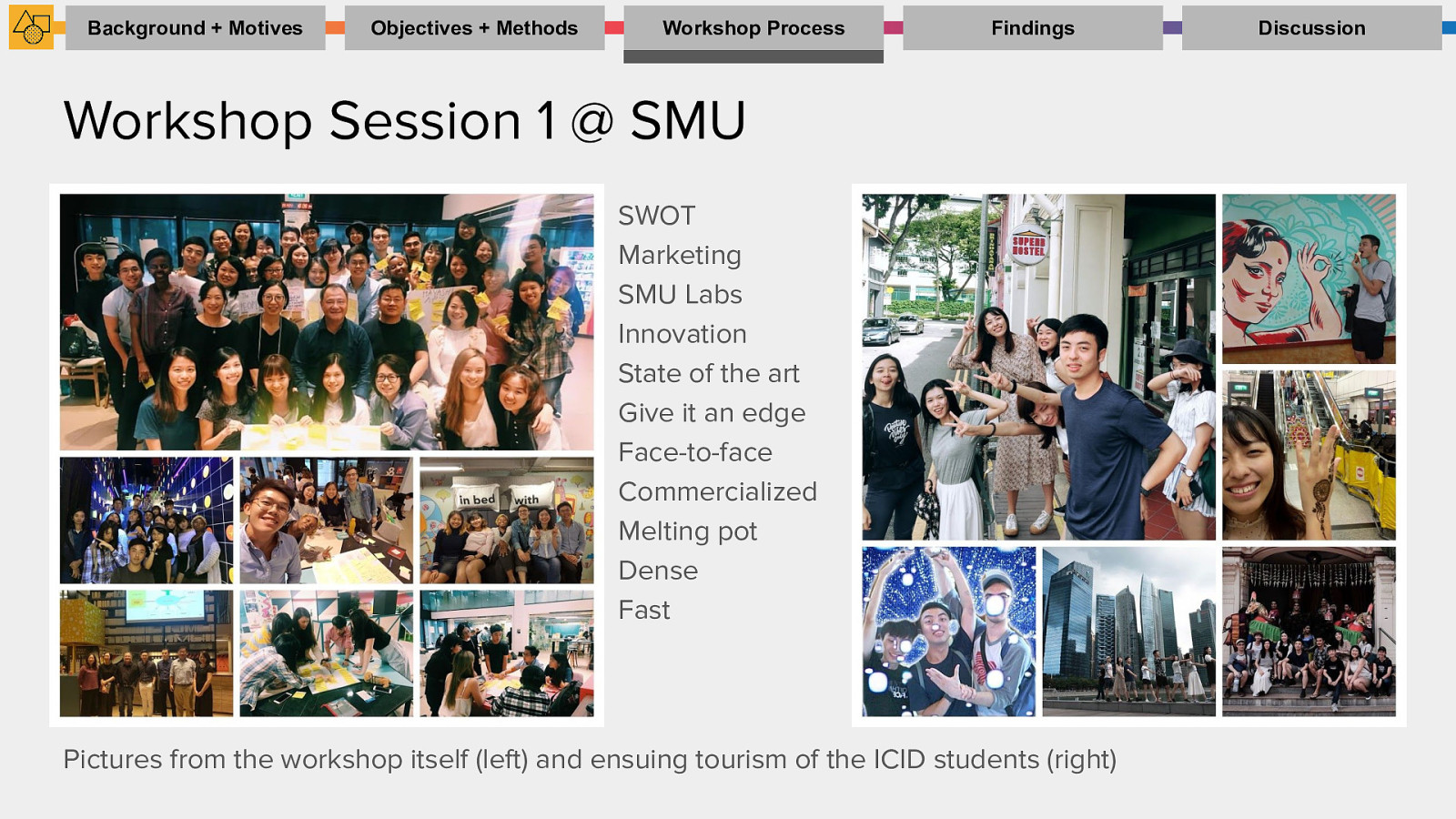
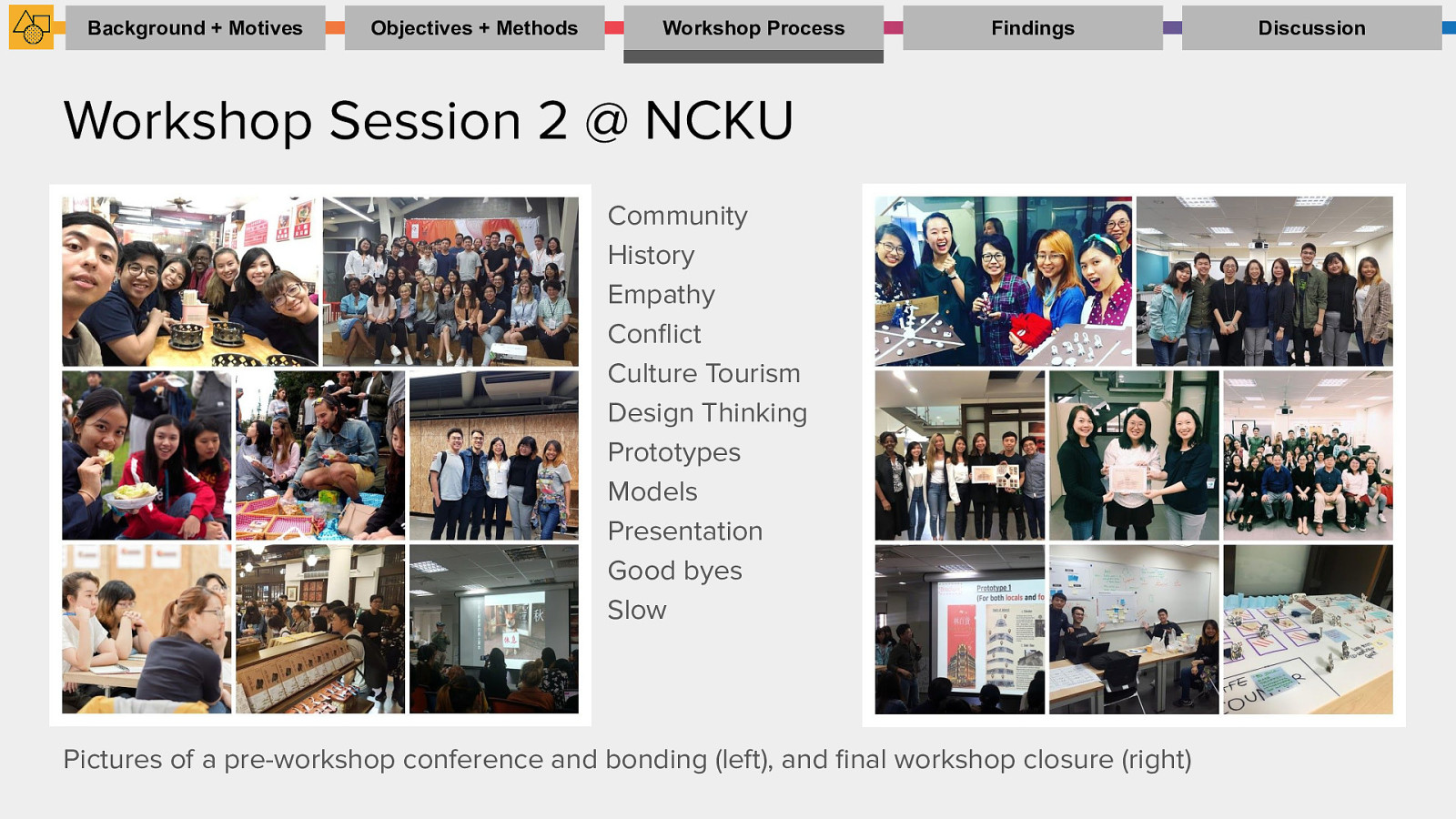
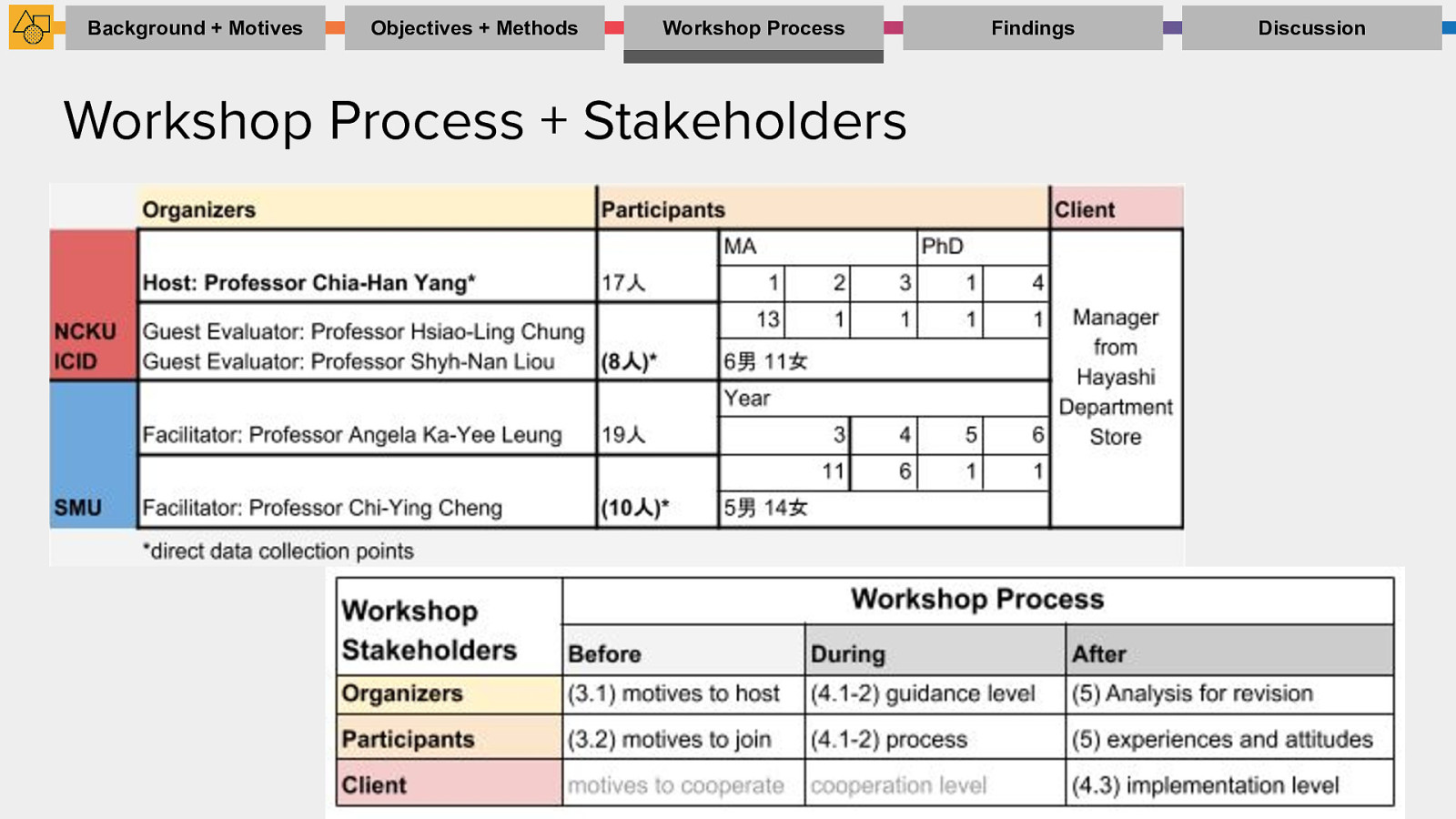
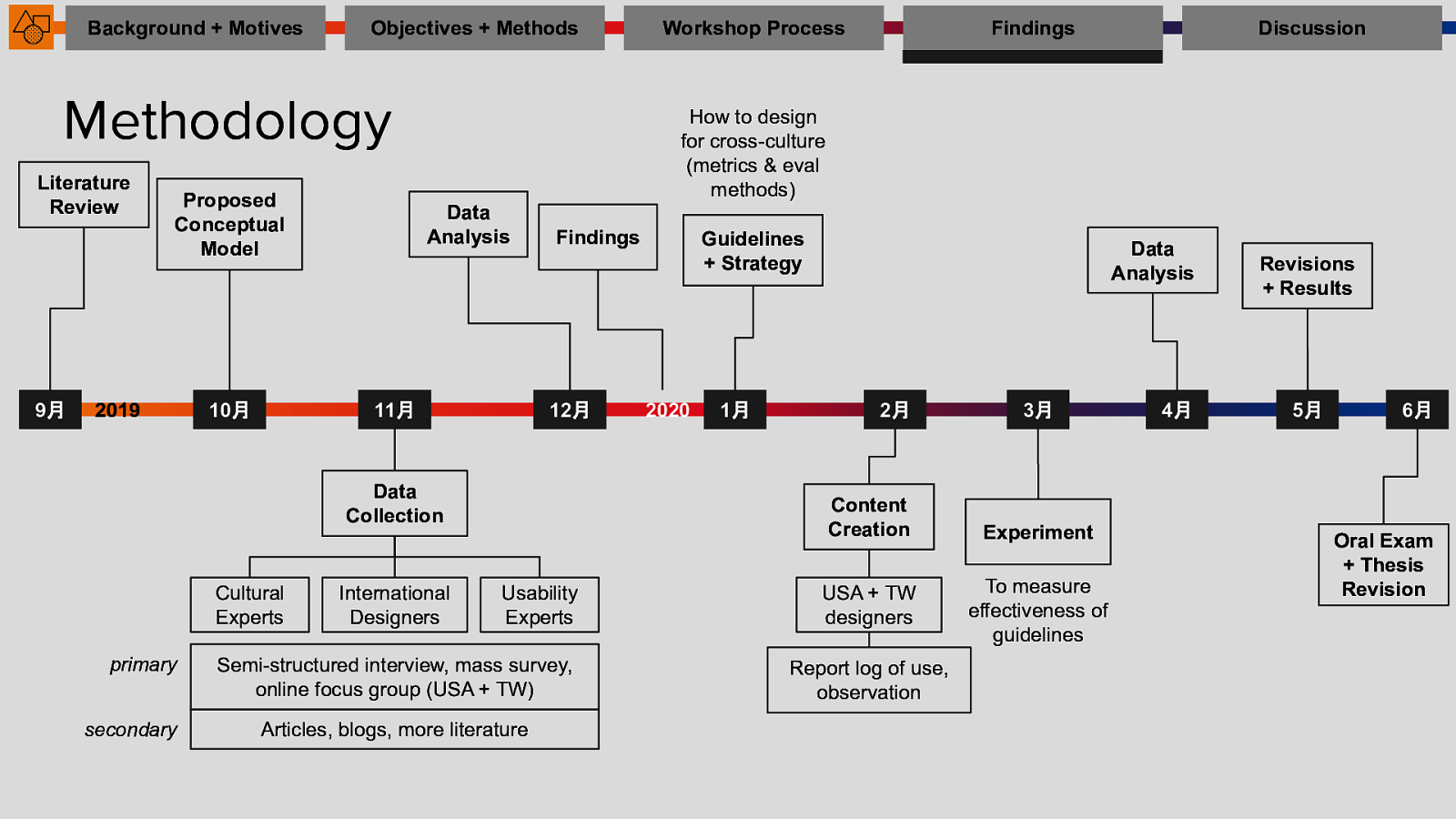
Workshop Process
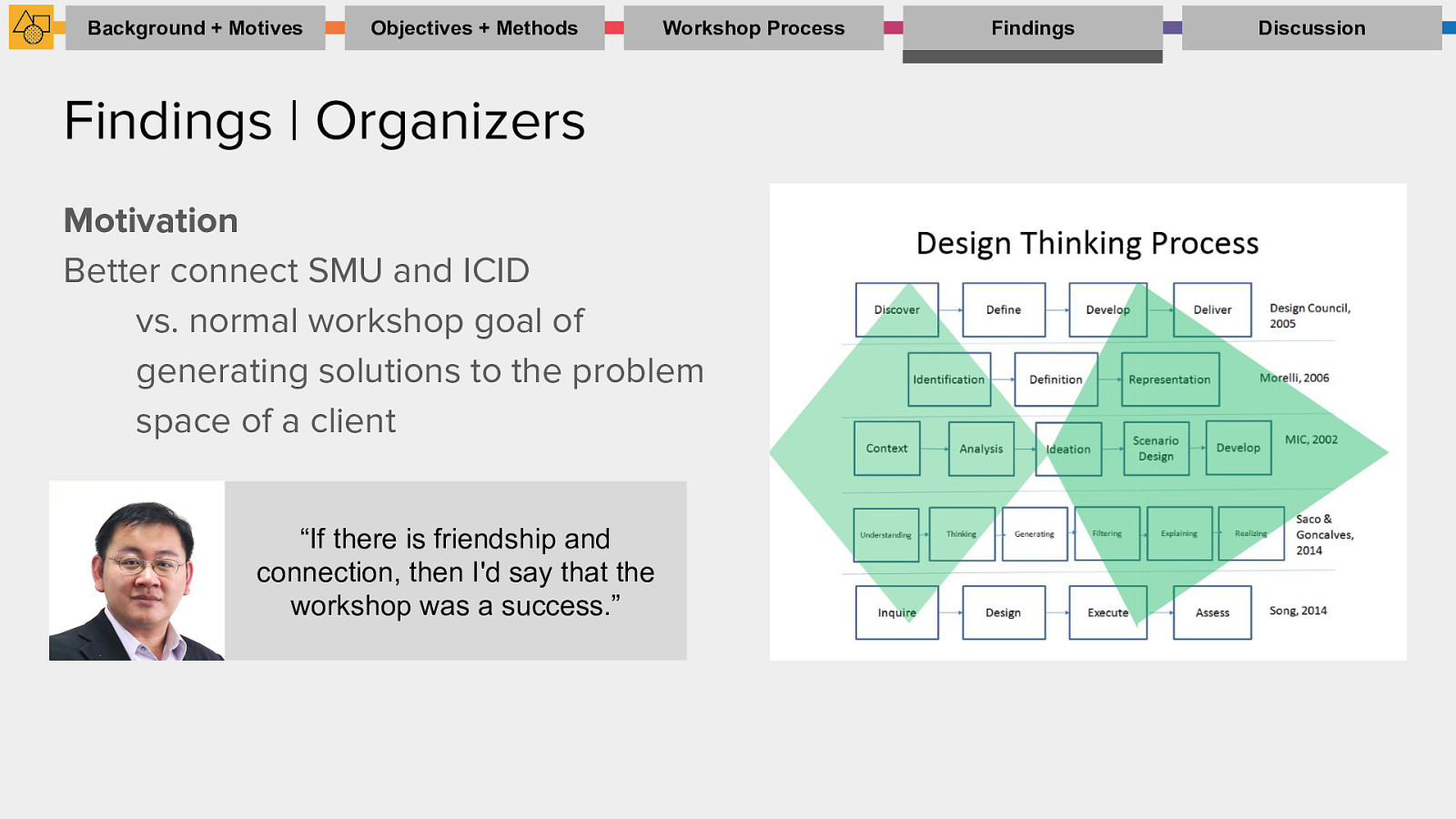
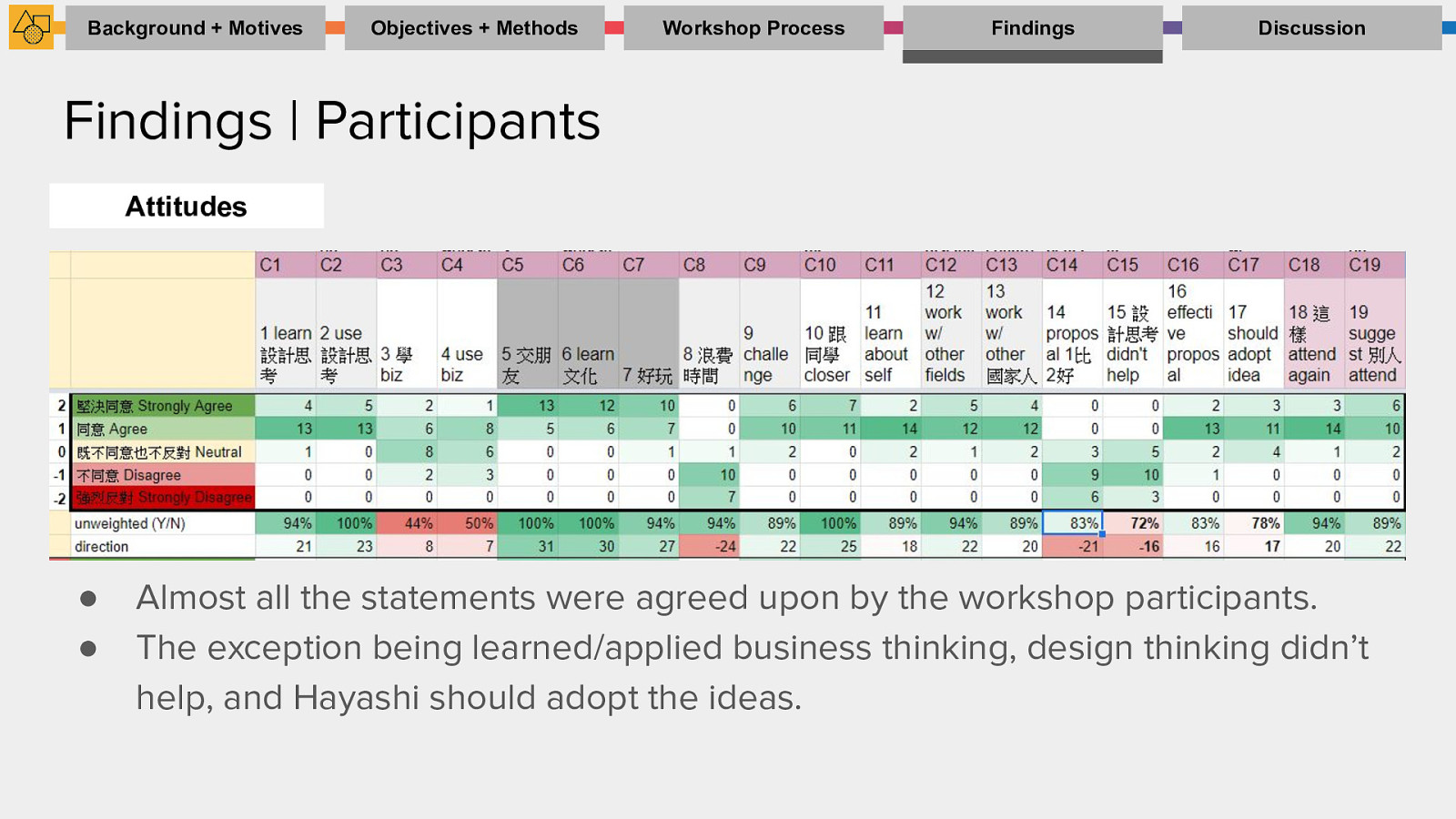
Findings
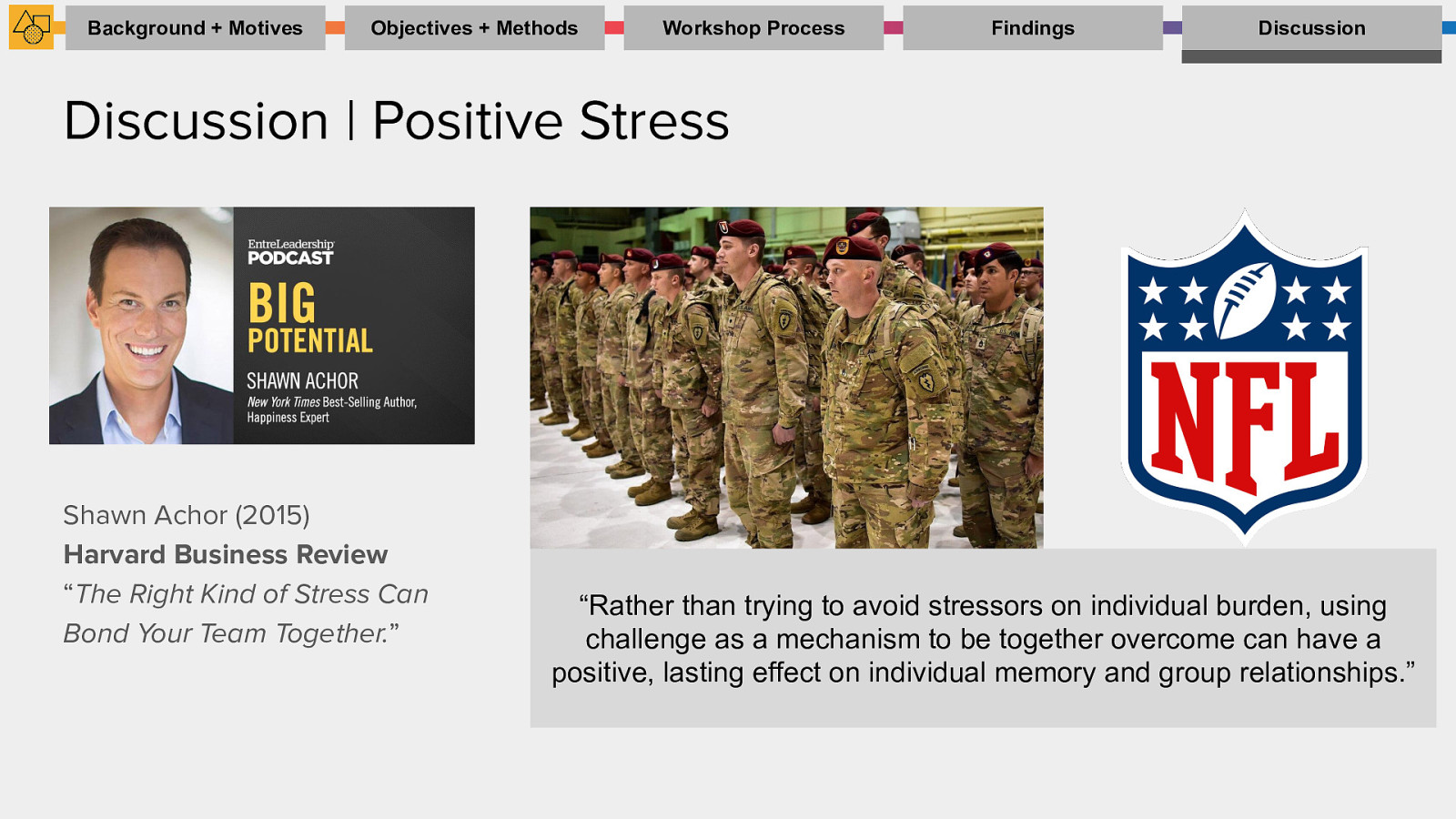
Discussion
References Psych+Culture
UX Design (focused on culture)
Usability
● The weirdest people in the world? [Jun 2010] J. Henrich, S. J. Heine, A. Norenzayan ● We agree it’s WEIRD, but is it WEIRD enough? [July 2010] gregdowney ● Language socialization in theory and practice [Feb 2007] S. R. Schecter, R. Bayley ● Argument in Support and Against of Hofstede Work [July 2010] A. E. Safi ● Alternative Cross-Cultural Theories: Why Still Hofstede? [Dec 2018] M. Zainuddin, I. Yasin, I. Arif, A. B. Abdul Hamid ● Building Upon Interaction Gestalt Research [2016] S.Reinhard
● Cross-Cultural UX Design (SIGGRAPH Asia 2013) [Nov 2013] Aaron Marcus ● Crosscurrents: cultural dimensions and global Web user-interface design [July 2000] Aaron Marus, E. W. Gould ● Cross-Cultural User-Experience Design (Diagrams Conference; from p.16) [June 2006] Aaron Marcus ● Cross-Cultural User Experience Design Helping Product Designers to Consider Cultural Differences [Aug 2015] F. Lachner, C. V. Saucken, F. Mueller, U. Lindemann ● Cross-Cultural Design and the Role of UX [2019] J. Shen ● Understanding Design Systems and Patterns [2018] D. G. Fitzpatrick ● Global/Intercultural User Interface Design [2007] Aaron Marcus ● Laws of UX [Feb 2018] Jon Yablonski
● Developing the Usability Testing Protocol [Dec 2017] E. Geisen & J. R. Bergstrom ● ISO/IEC 25062:2006 (INCITS 354) SQuaRE CIF for usability testing reports ● Usability of Multiple Devices for Assessment in Psychological Research: Salience of Reasons Underlying Usability [Jan 2019] D. Raccanello, M. Brodino, M. Pasini, R. Burro ● Measuring Perceived Usability: The CSUQ, SUS, and UMUX [Jan 2018] J. R. Lewis ● Tough Sell: Selling User Experience [Feb 2011] M. Vaughan ● New ISO Standards for Usability, Usability Reports and Usability Measures [2016] N. Bevan, J. Carter J. Earthy, T. Geis, S. Harker ● Development of a Comprehensive Usability Testing and Analysis Protocol for Ergonomic Product Design [Aug 2009] W. Lee, K. Jung, H. You ● Usability.gov [May 2019] US Dept of Health & Human Services ● Usability Testing Basics TechSmith ● Usability Testing in a nutshell [Aug 2018] M. Thalagala