Why your red team should not be special Well it should be special but not that special @isaiahsarju
A presentation at ShowMeCon 2019 in July 2019 in St. Louis, MO, USA by Isaiah Sarju

Why your red team should not be special Well it should be special but not that special @isaiahsarju

Security consultant, co-owner Revis Solutions Red teamer Me Teacher Anti: nihilism, security theater, wasted time Pro: risk based security Loves islay whiskey @isaiahsarju

It’s not for everyone Why you should have a red team Need more than a pentest Challenge SOC/blue team Fine tune processes, decrease response time There are APTs in your threat model Justify security decisions with evidence @isaiahsarju

Dislike using corporate.* Red teams want to be special Manage own infrastructure Avoid oversight/accountability Believe they are un-hackable Think rules don’t apply to them @isaiahsarju

Naughty AWS Activity Scare Stories Lazy P3nt35t3r5 What’s yours? @isaiahsarju

Why your red team should not be special Shadow IT Hackers can get hacked Lack of empathy @isaiahsarju

What testing is right for us? Red team maturity model What should drive testing? Organizational preparedness? Threats in threat model? @isaiahsarju

This happens when red teams manage their own infrastructure Testing infrastructure Configuration drift Red teams aren’t IT departments Shadow IT Red teams can’t Test And help with remediation And hone skills And build new infrastructure And maintain infrastructure And do security monitoring And … @isaiahsarju

Hackers can get hacked This happens because hackers ≠ good defenders Are they testing or are they hacked? Mentality @isaiahsarju

This happens because hackers can be condescending “Just do _____” Lack of empathy Corporate assets are cumbersome Balance security with usability Don’t understand how hard processes are to follow Red teams need to take their own medicine @isaiahsarju

What’s NOT the answer? “Here’s a laptop just like everyone else. Go forth and test” Give them a nice MacBook and say “show me me your worst” Ugh. Security is expensive. Goat sacrifices and crossed fingers are cheaper @isaiahsarju
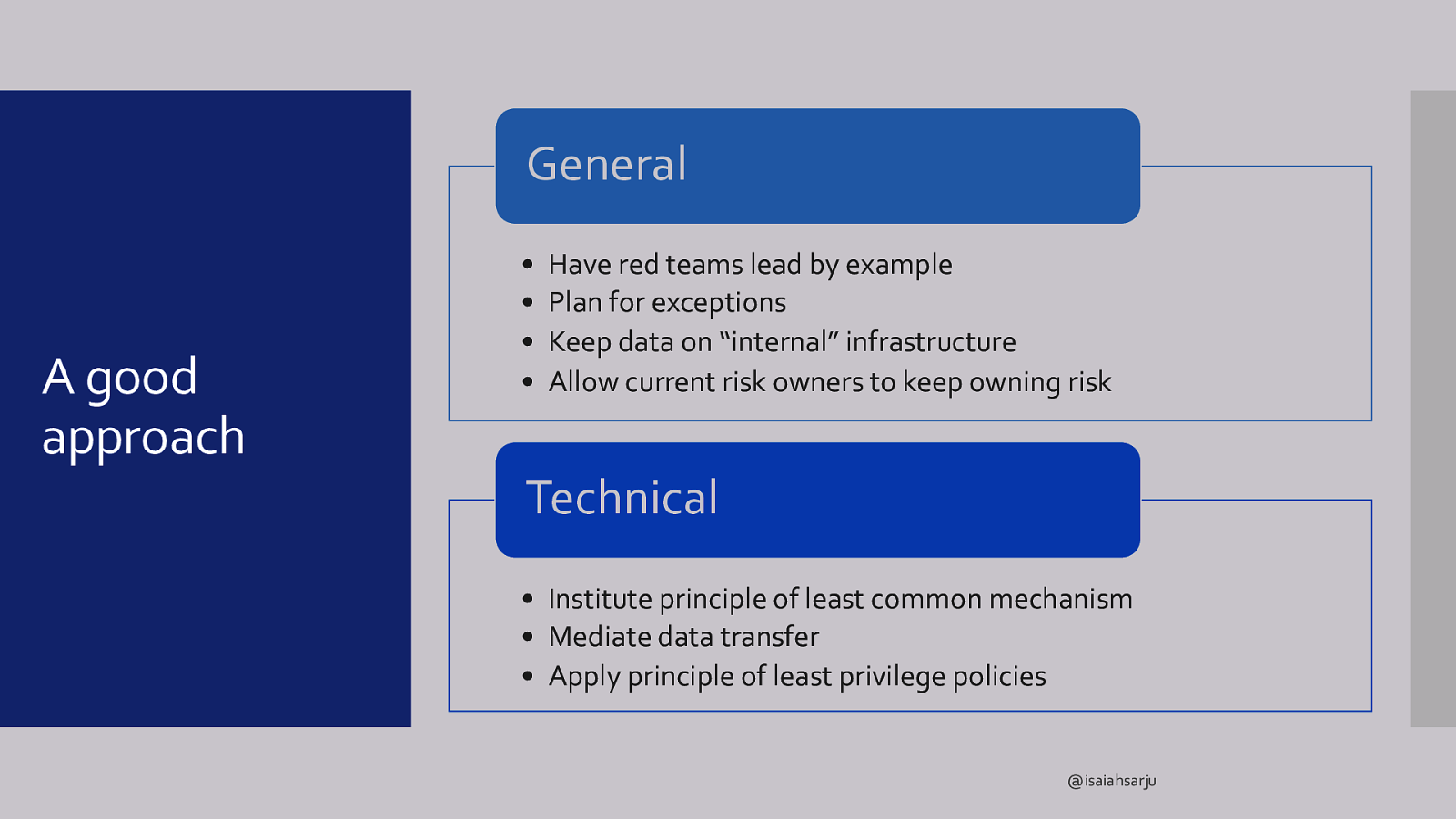
General A good approach • • • • Have red teams lead by example Plan for exceptions Keep data on “internal” infrastructure Allow current risk owners to keep owning risk Technical • Institute principle of least common mechanism • Mediate data transfer • Apply principle of least privilege policies @isaiahsarju
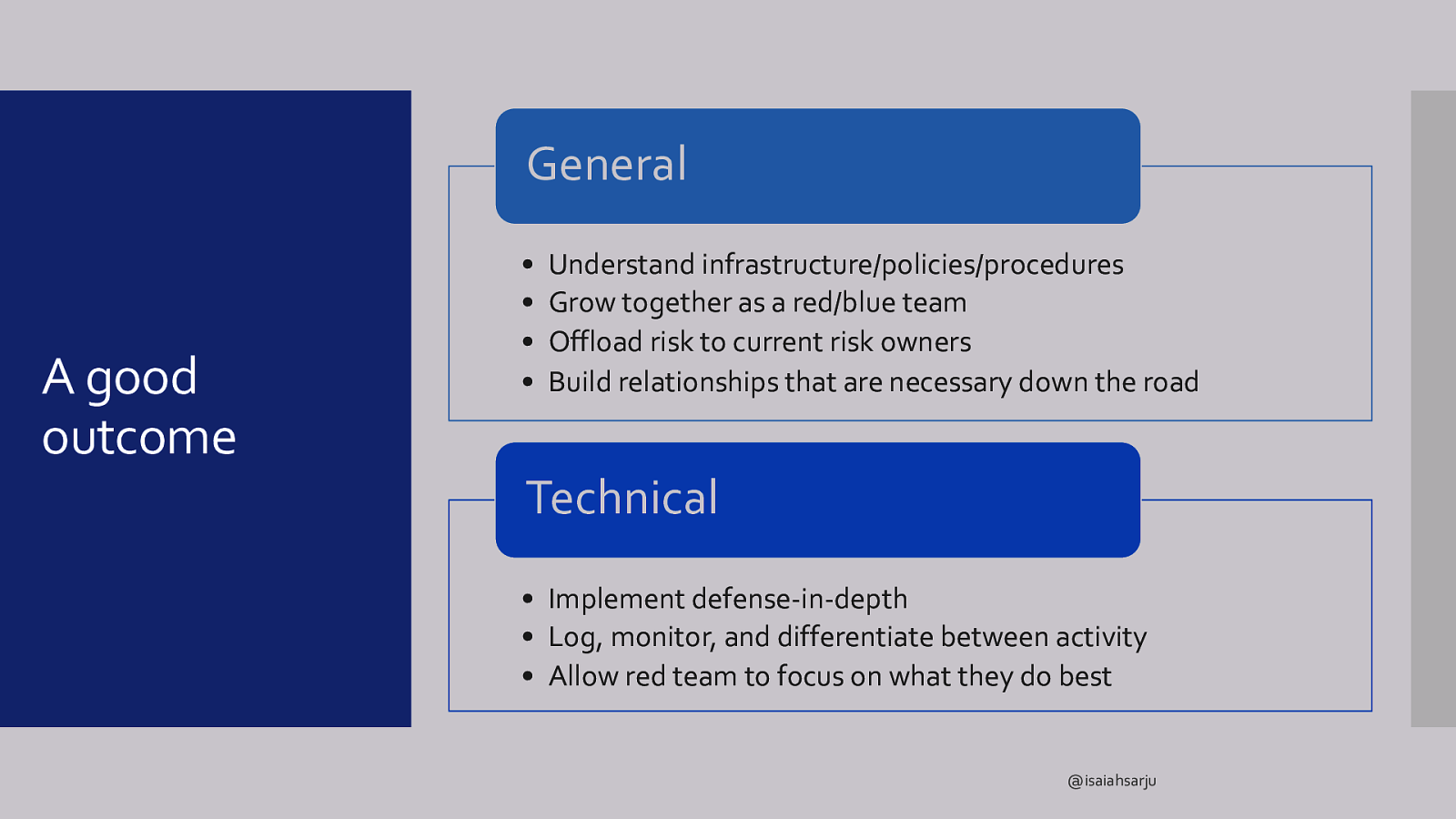
General A good outcome • • • • Understand infrastructure/policies/procedures Grow together as a red/blue team Offload risk to current risk owners Build relationships that are necessary down the road Technical • Implement defense-in-depth • Log, monitor, and differentiate between activity • Allow red team to focus on what they do best @isaiahsarju
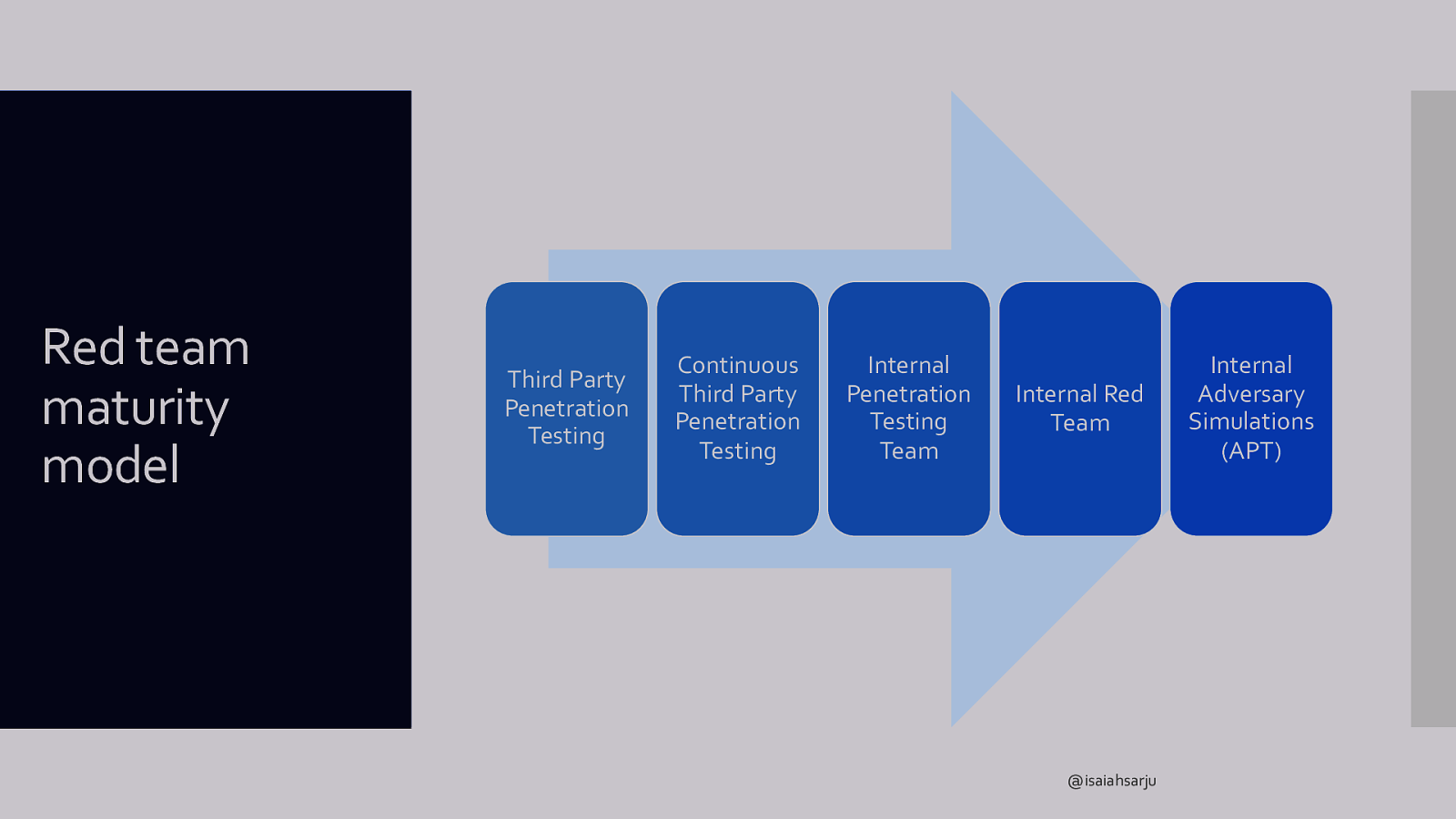
Red team maturity model Third Party Penetration Testing Continuous Third Party Penetration Testing Internal Penetration Testing Team Internal Red Team @isaiahsarju Internal Adversary Simulations (APT)
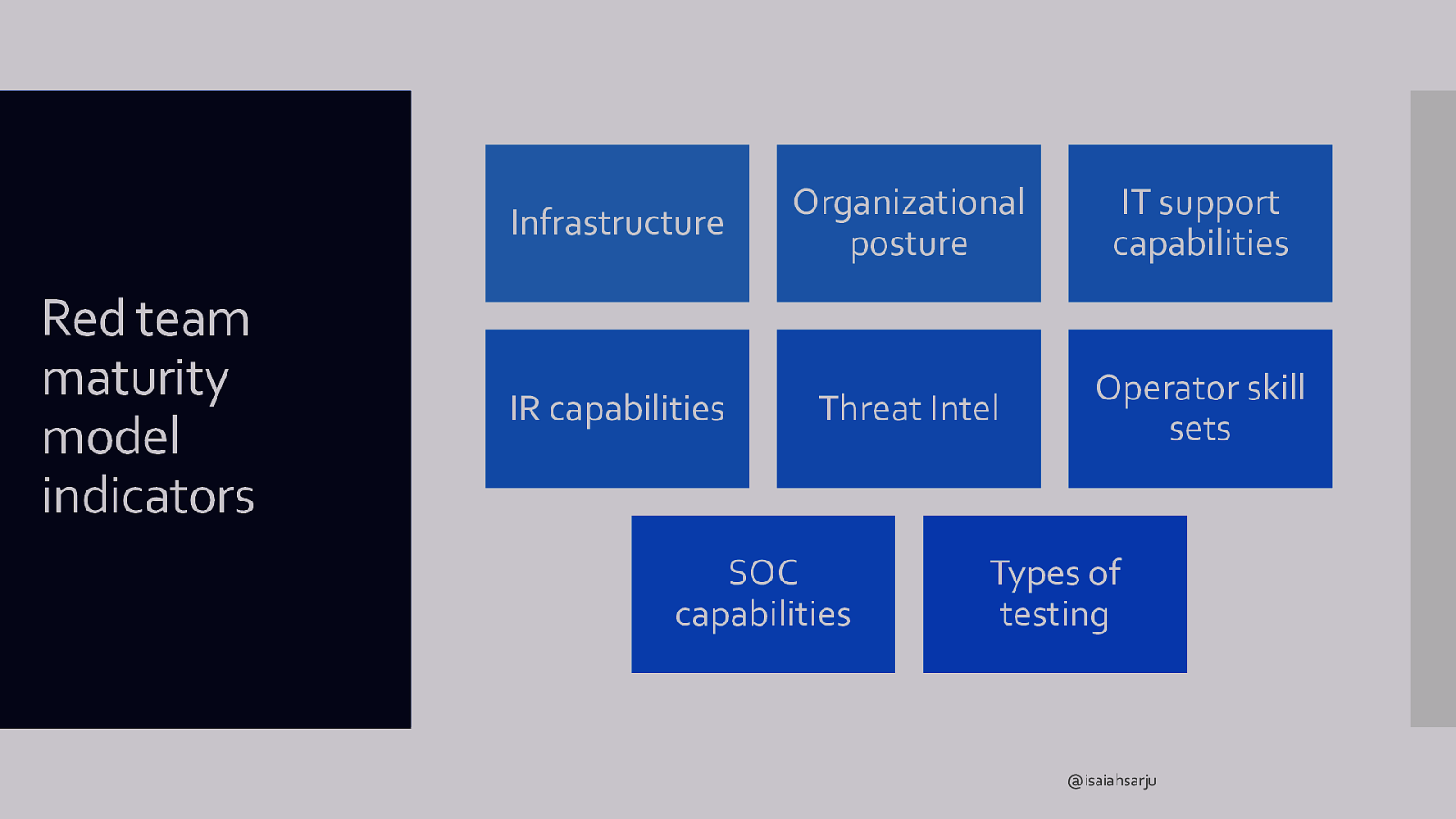
Infrastructure Red team maturity model indicators IR capabilities Organizational posture IT support capabilities Threat Intel Operator skill sets SOC capabilities Types of testing @isaiahsarju
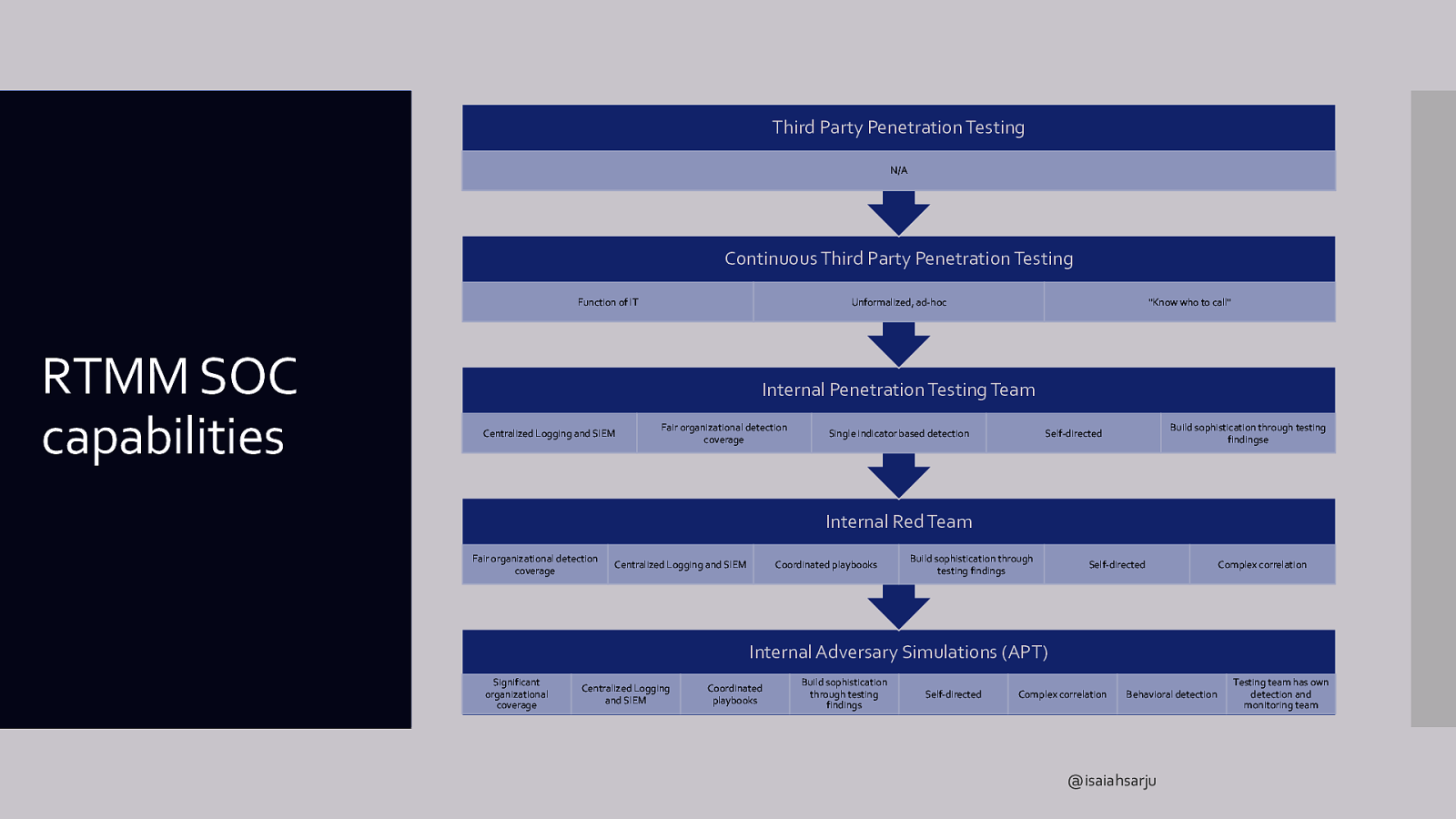
Third Party Penetration Testing N/A Continuous Third Party Penetration Testing Function of IT RTMM SOC capabilities Unformalized, ad-hoc “Know who to call” Internal Penetration Testing Team Centralized Logging and SIEM Fair organizational detection coverage Single indicator based detection Build sophistication through testing findingse Self-directed Internal Red Team Fair organizational detection coverage Centralized Logging and SIEM Coordinated playbooks Build sophistication through testing findings Self-directed Complex correlation Internal Adversary Simulations (APT) Significant organizational coverage Centralized Logging and SIEM Coordinated playbooks Build sophistication through testing findings Self-directed Complex correlation Behavioral detection @isaiahsarju Testing team has own detection and monitoring team
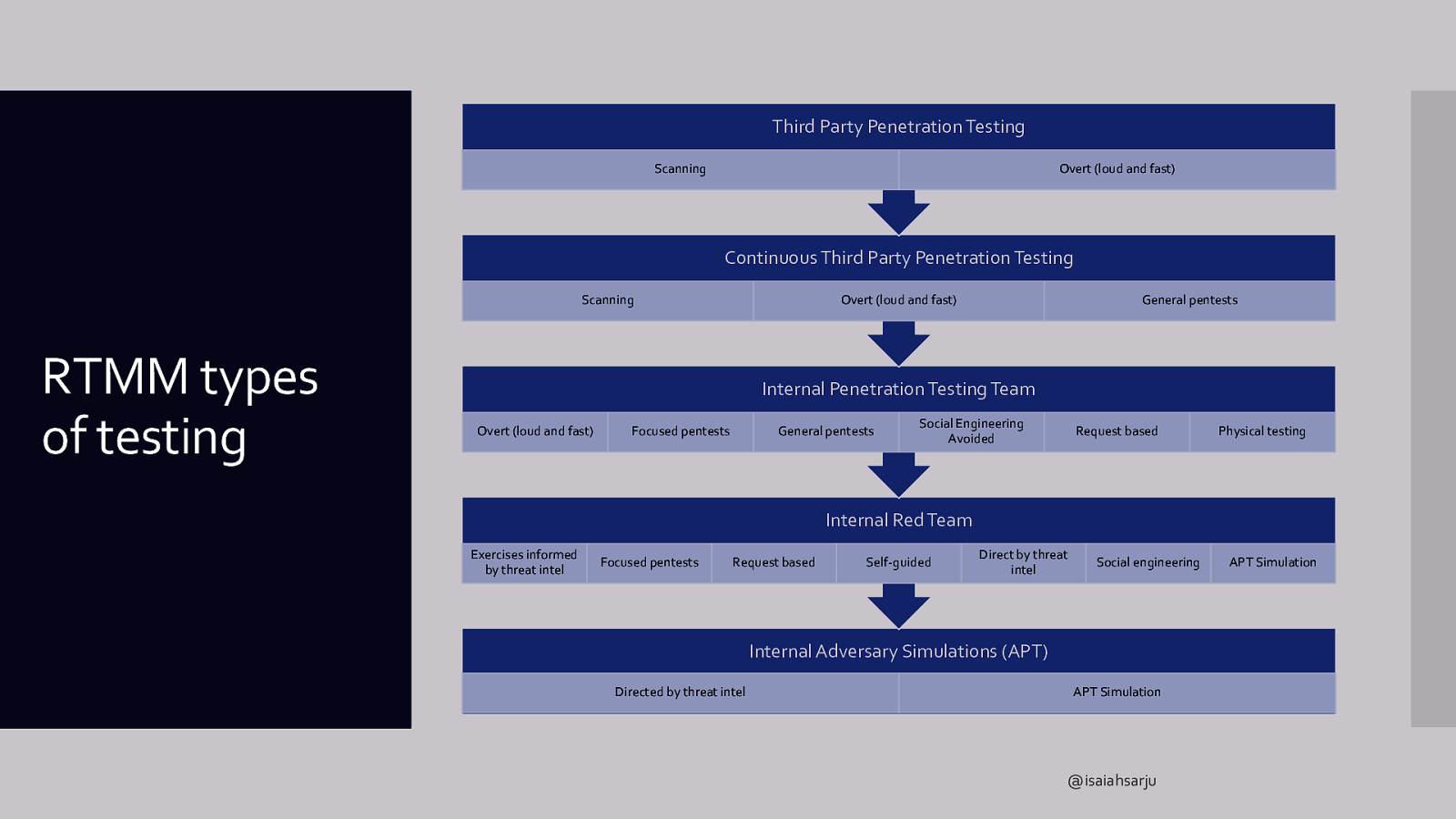
Third Party Penetration Testing Scanning Overt (loud and fast) Continuous Third Party Penetration Testing Scanning RTMM types of testing Overt (loud and fast) General pentests Internal Penetration Testing Team Overt (loud and fast) Focused pentests General pentests Social Engineering Avoided Request based Physical testing Internal Red Team Exercises informed by threat intel Focused pentests Request based Self-guided Direct by threat intel Social engineering Internal Adversary Simulations (APT) Directed by threat intel APT Simulation @isaiahsarju APT Simulation
Folks Why tie RTMM to staff preparedness vs actual threats? Aren’t Ready @isaiahsarju

May be unpopular. Especially with operators Wrap this up Red teams need to take a dose their own medicine Red teams can lead by example and build positive relationships Future Research: “Map” RTMM to ATT&CK @isaiahsarju

Info @isaiahsarju all over The Internet https://github.com/isaiahsarju/presentations @isaiahsarju

Questions? @isaiahsarju