An Accessible Design Framework Enabling designers to proactively embed accessibility considerations into all aspects of their work March 20, 2024
A presentation at CSUN in March 2024 in Anaheim, CA, USA by Karen Hawkins

An Accessible Design Framework Enabling designers to proactively embed accessibility considerations into all aspects of their work March 20, 2024

Meet Karen Hawkins Karen Hawkins, CPACC Connect with me Principal of Accessible Design, Level Access Email LinkedIn Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 2

Get today’s slides Get today’s slides Deck on notist https://noti.st/khawk27 Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 3

MY OBJECTIVE Provide designers with a framework to design with accessibility in mind, as well as check their work or the work of others for accessibility. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 4

Agenda • The framework • Applying the framework • Summary and questions Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 5

The framework Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 6

Definition of “Human Factors” by the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Human Factors is a body of knowledge about human abilities, human limitations, and other human characteristics that are relevant to design. Human Factors engineering is the application of Human Factors information to the design of tools, machines, systems, tasks, jobs, and environments for safe, comfortable, and effective human use. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 7

Definition of “Human Factors” by the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Human Factors is a body of knowledge about human abilities, human limitations, and other human characteristics that are relevant to design. Human Factors engineering is the application of Human Factors information to the design of tools, machines, systems, tasks, jobs, and environments for safe, comfortable, and effective human use. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 8
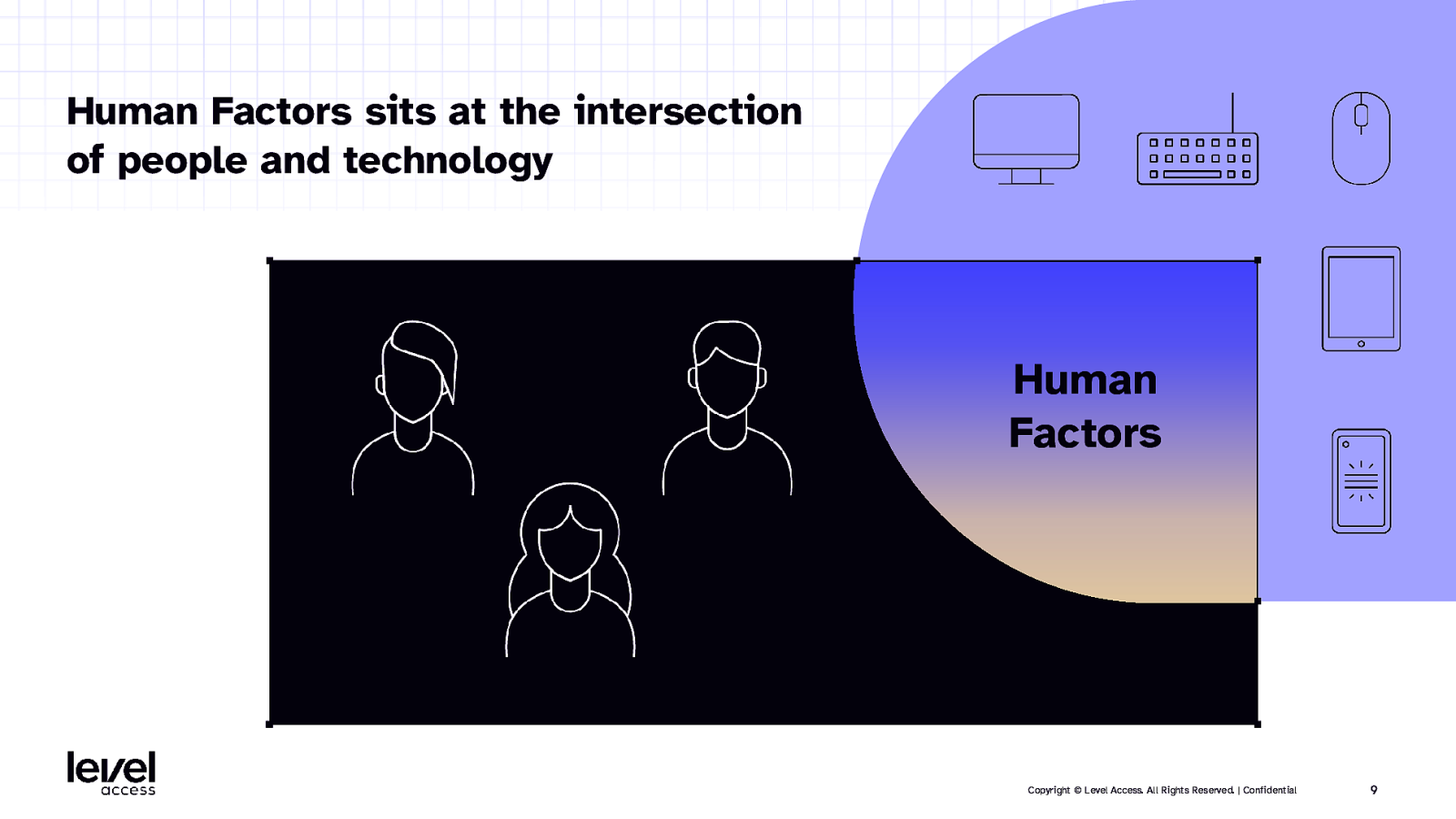
Human Factors sits at the intersection of people and technology Human Factors Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 9
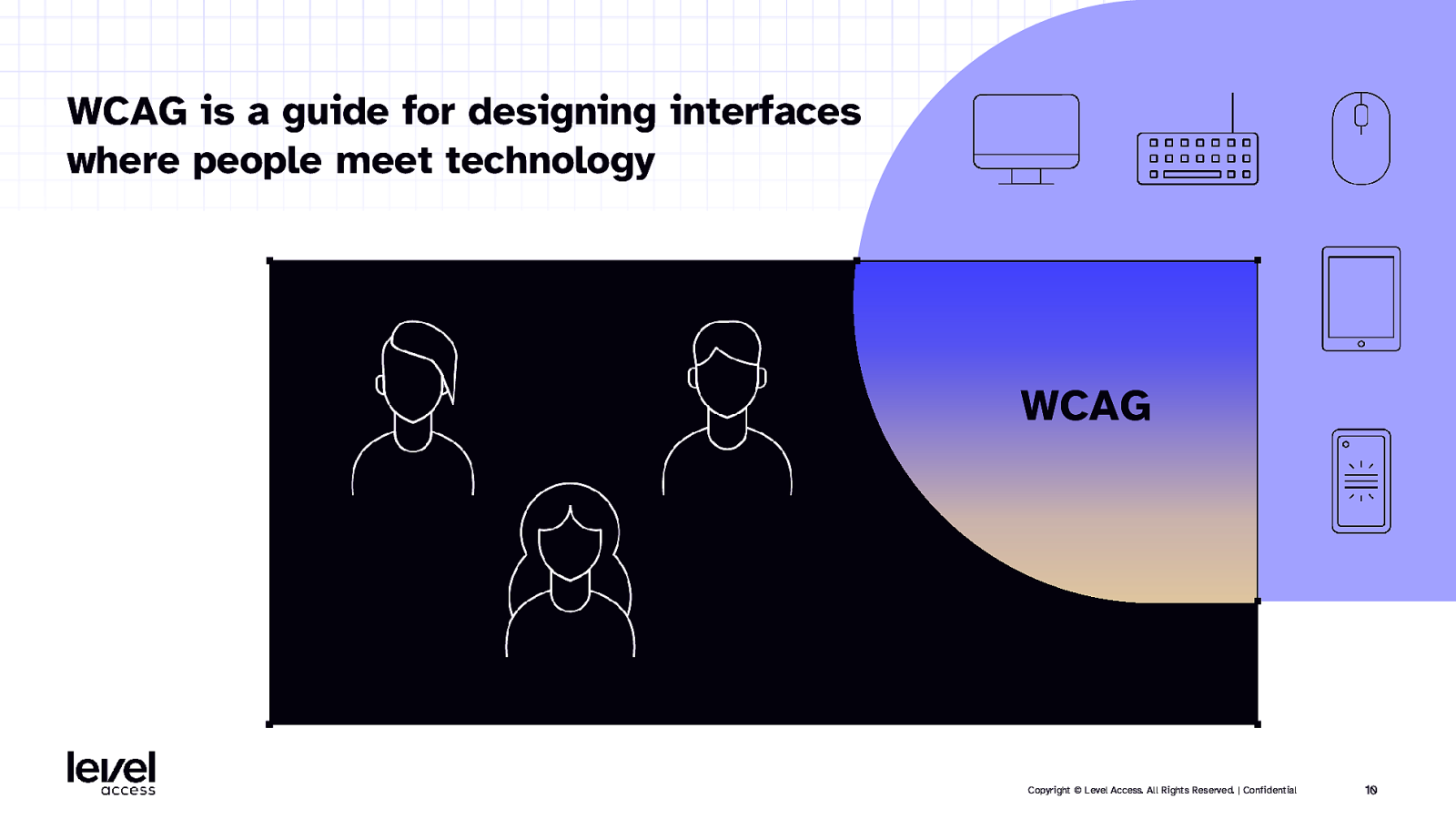
WCAG is a guide for designing interfaces where people meet technology WCAG Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 10

WCAG is perceived to be about people with disabilities and assistive technology Assistive technologies WCAG People with disabilities Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 11
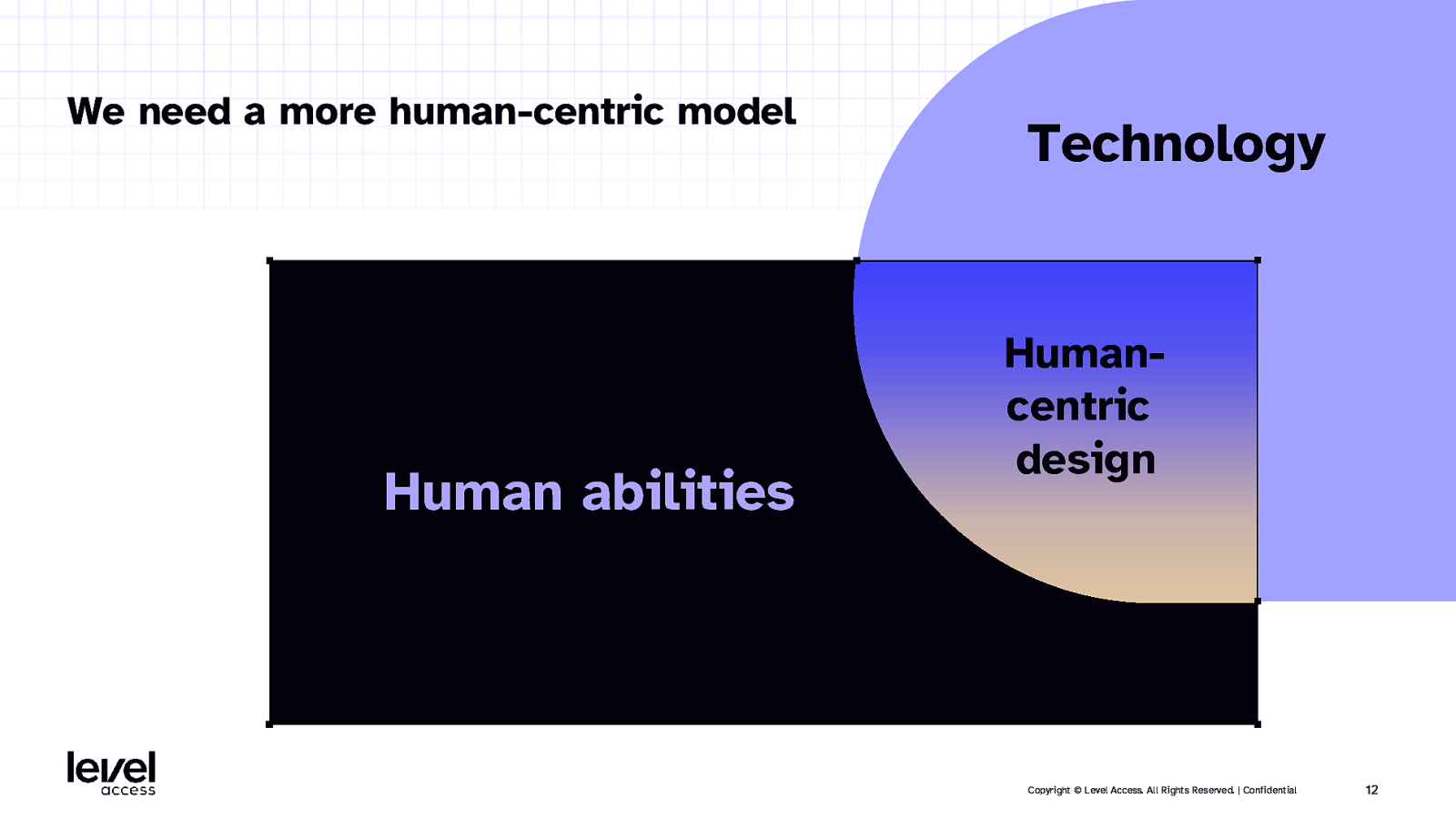
We need a more human-centric model Human abilities Technology Humancentric design Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 12

KEY TAKEAWAY Our scope of design is a system that includes an able yet flawed human, as well as the set of technologies that enable them to execute their desired tasks in digital environments. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 13

KEY TAKEAWAY We need to design for human abilities and limitations, and for technology’s abilities and limitations, all within a given environment or context. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 14

NOTE What’s missing is a focus on the technology. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 15
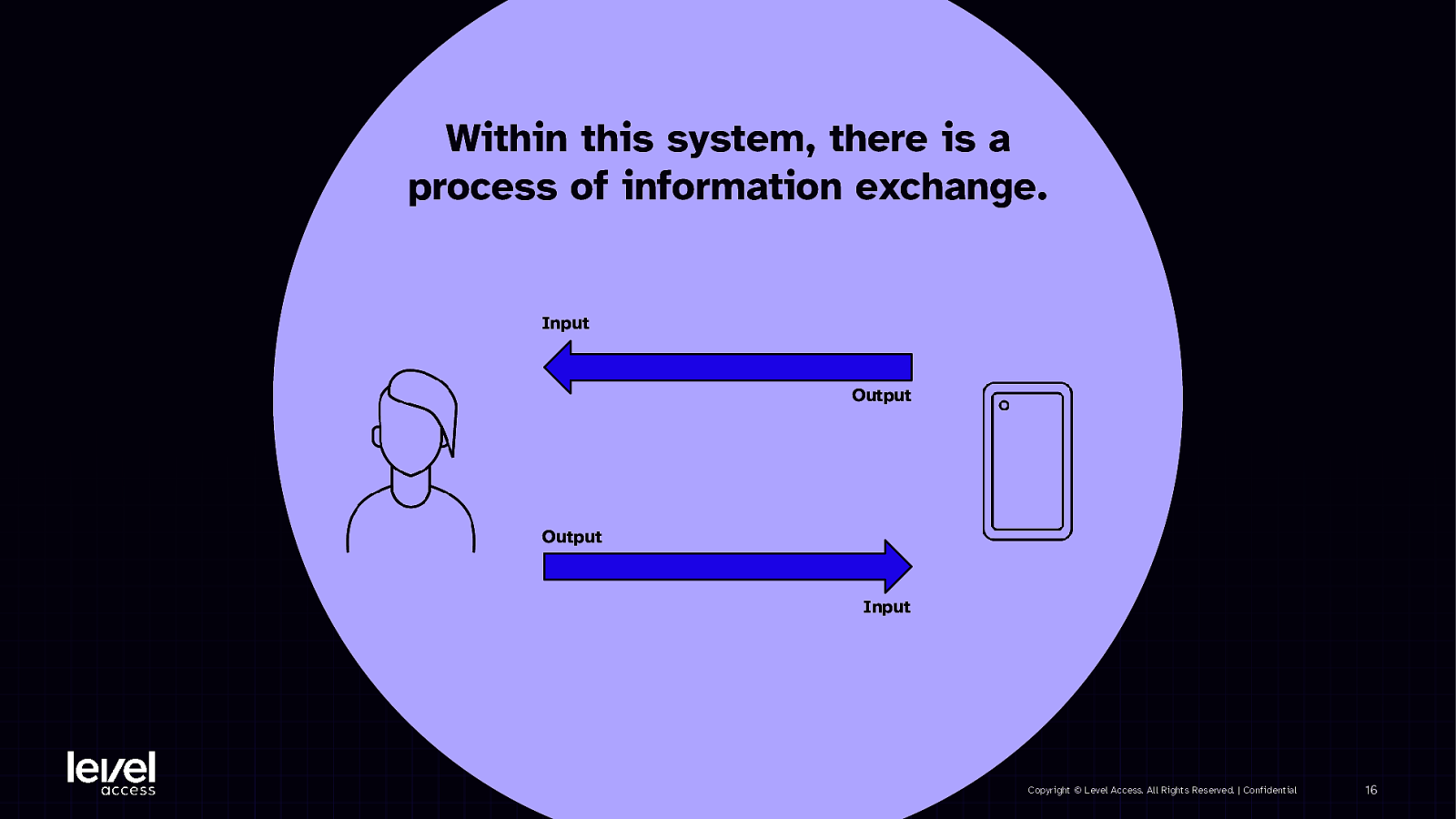
Within this system, there is a process of information exchange. Input Output Output Input Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 16
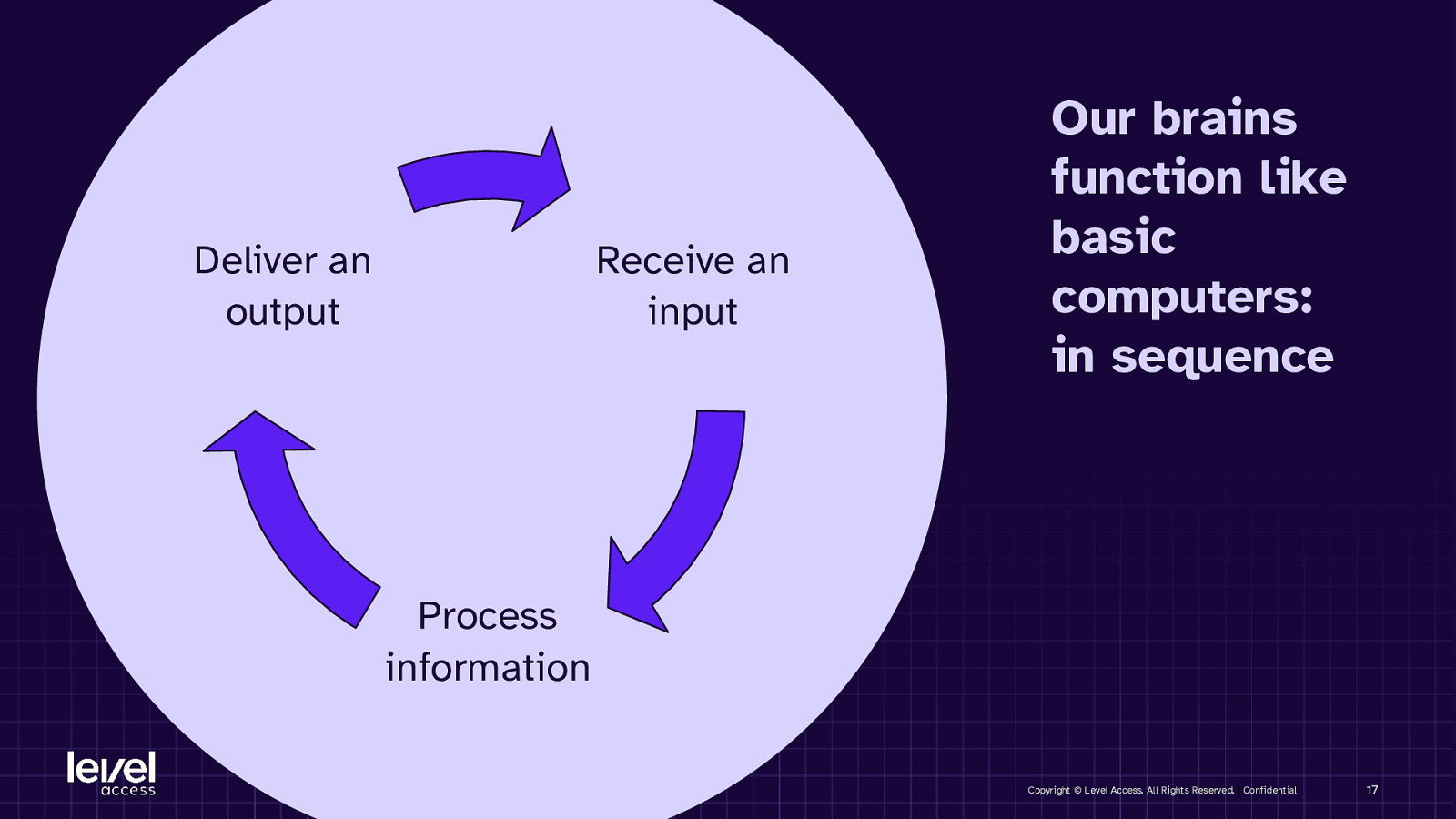
Deliver an output Receive an input Our brains function like basic computers: in sequence Process information Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 17
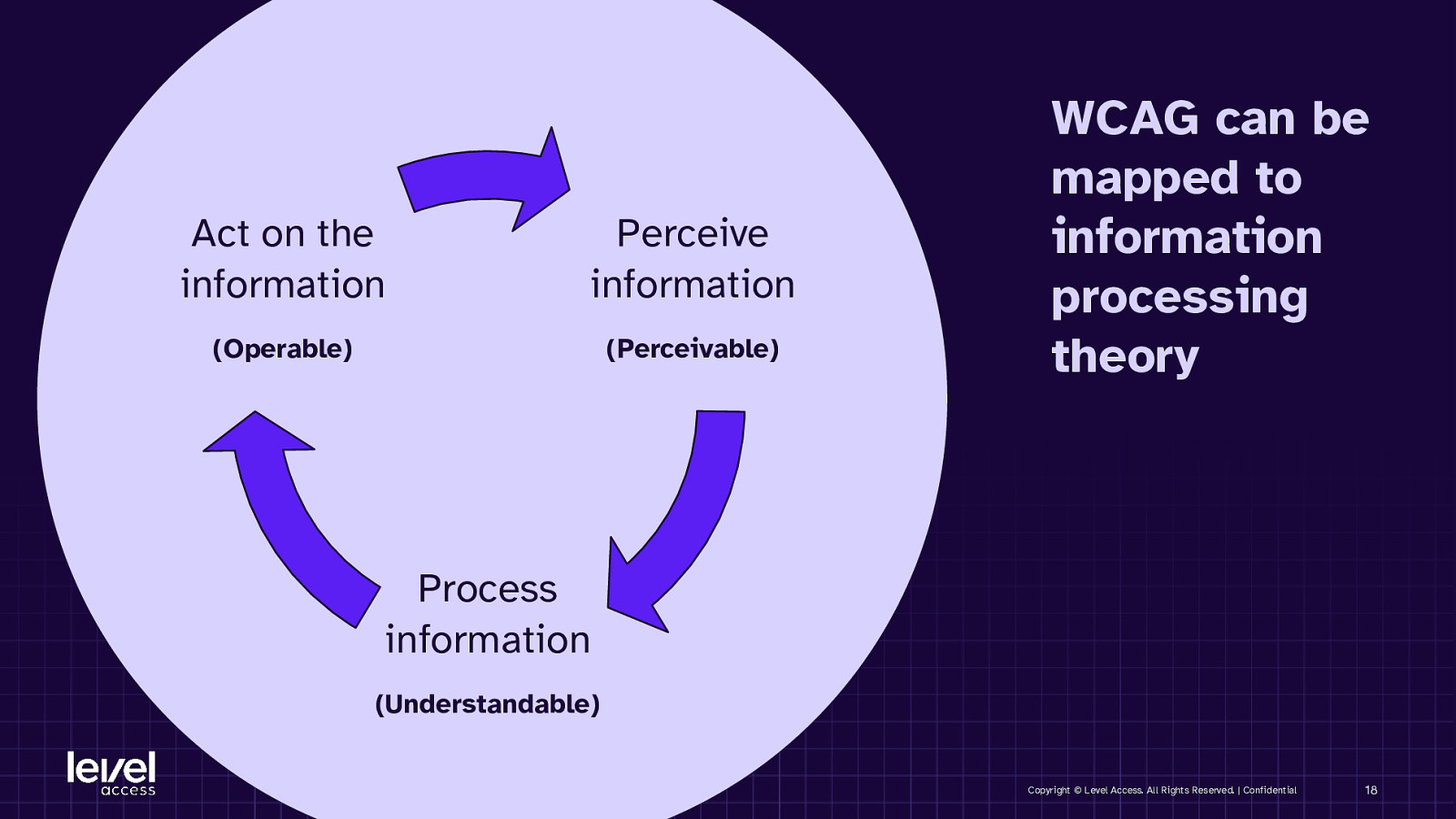
Act on the information Perceive information (Operable) (Perceivable) WCAG can be mapped to information processing theory Process information (Understandable) Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 18

KEY TAKEAWAY Ask yourself: - Is the user able to get all the relevant information? - Is the information easy to understand? - How can the user act on that information? Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 19
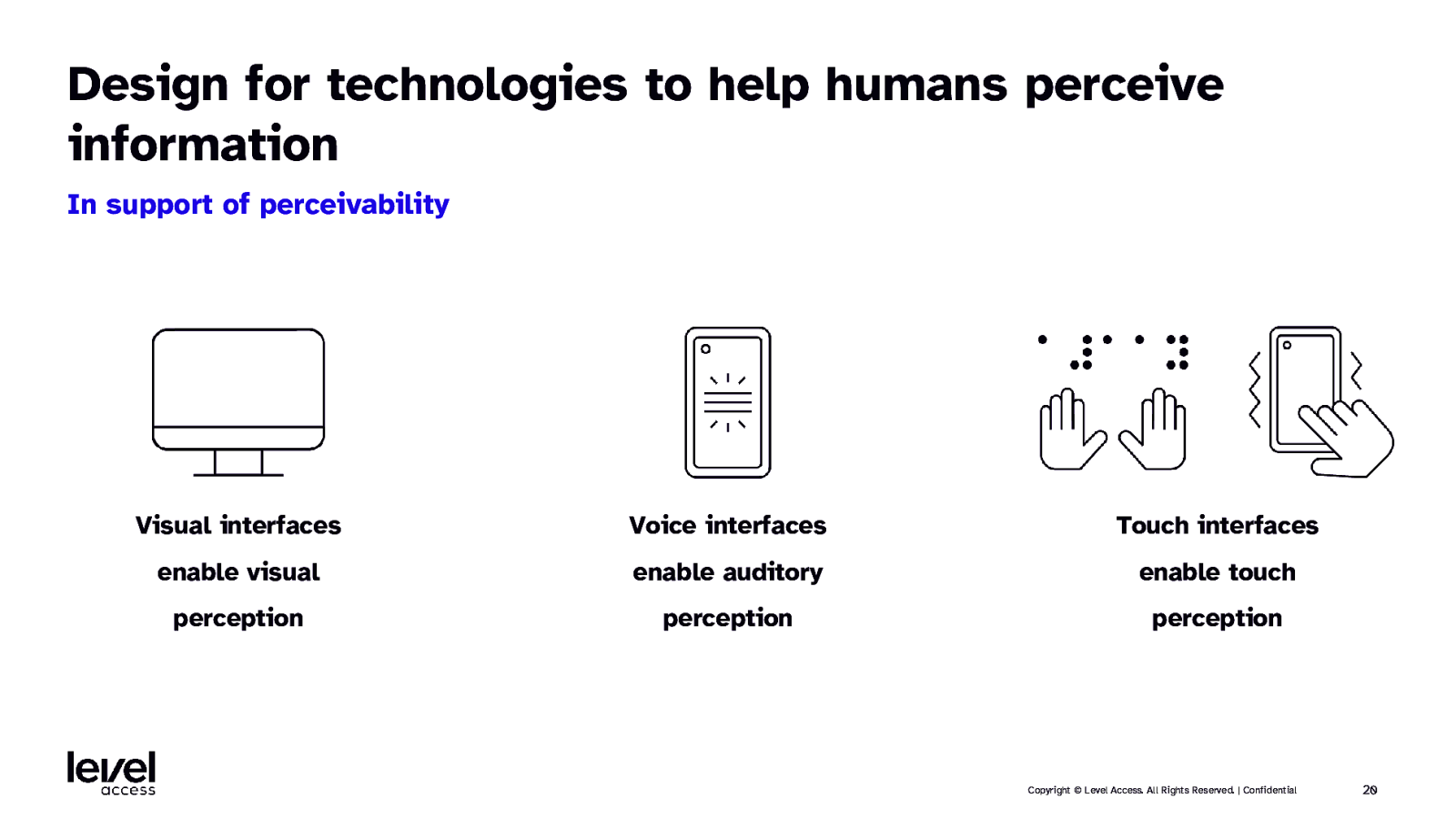
Design for technologies to help humans perceive information In support of perceivability Visual interfaces Voice interfaces Touch interfaces enable visual enable auditory enable touch perception perception perception Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 20

Design for technologies to help humans take action In support of operability Pointers Keyboard interfaces Motion Speech recognition Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 21
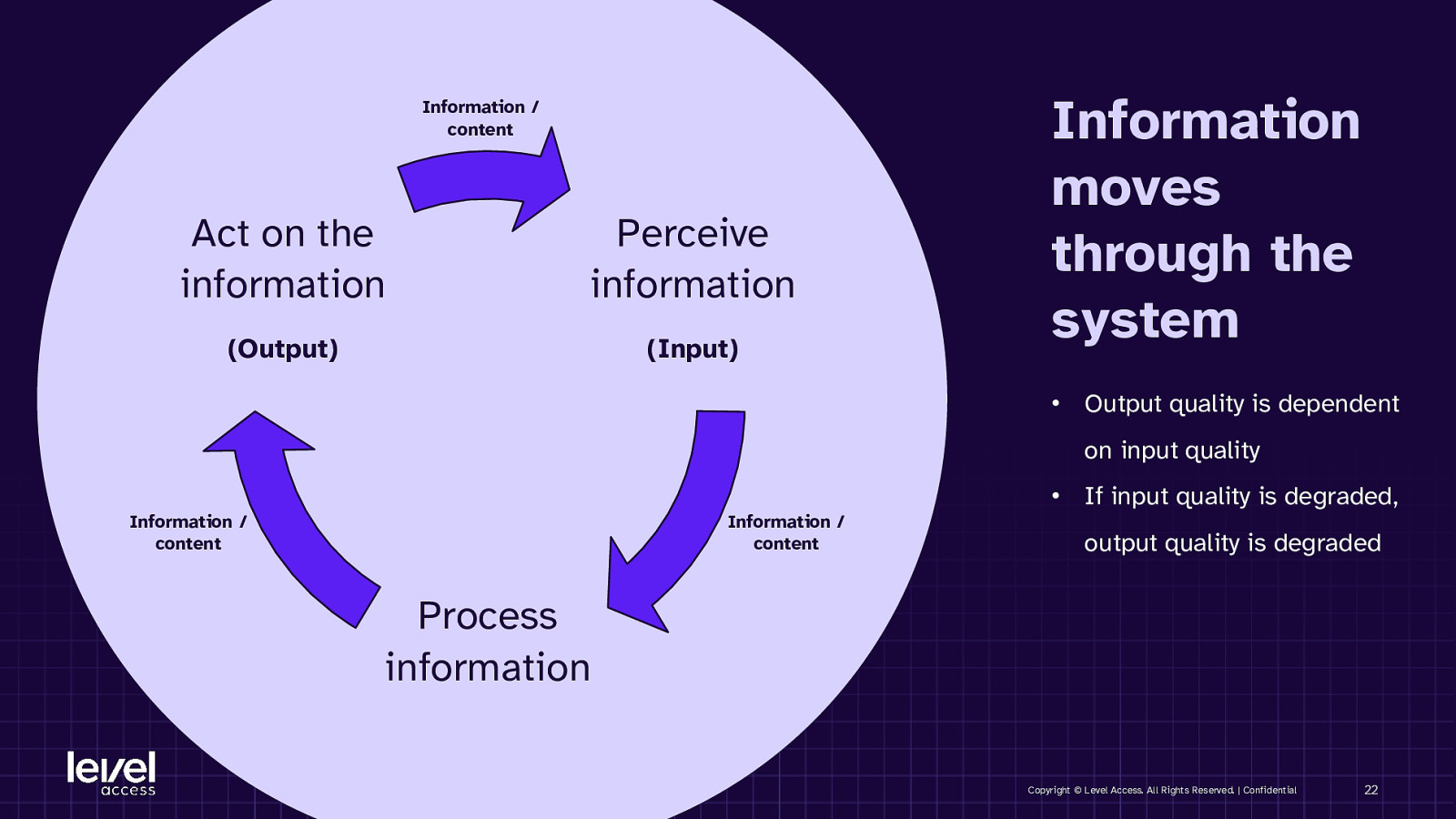
Information / content Act on the information Perceive information (Output) (Input) Information moves through the system • Output quality is dependent on input quality • If input quality is degraded, Information / content Information / content output quality is degraded Process information Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 22

KEY TAKEAWAY It’s the quality of the content that’s important to help people understand it. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 23

KEY TAKEAWAY Content can be thought of as a technology that enables the understandability of the system. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 24

KEY TAKEAWAY Content needs to be thoughtfully designed so it can move through the system quickly and efficiently. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 25

Design for technologies to help humans understand In support of understandability High quality content Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 26
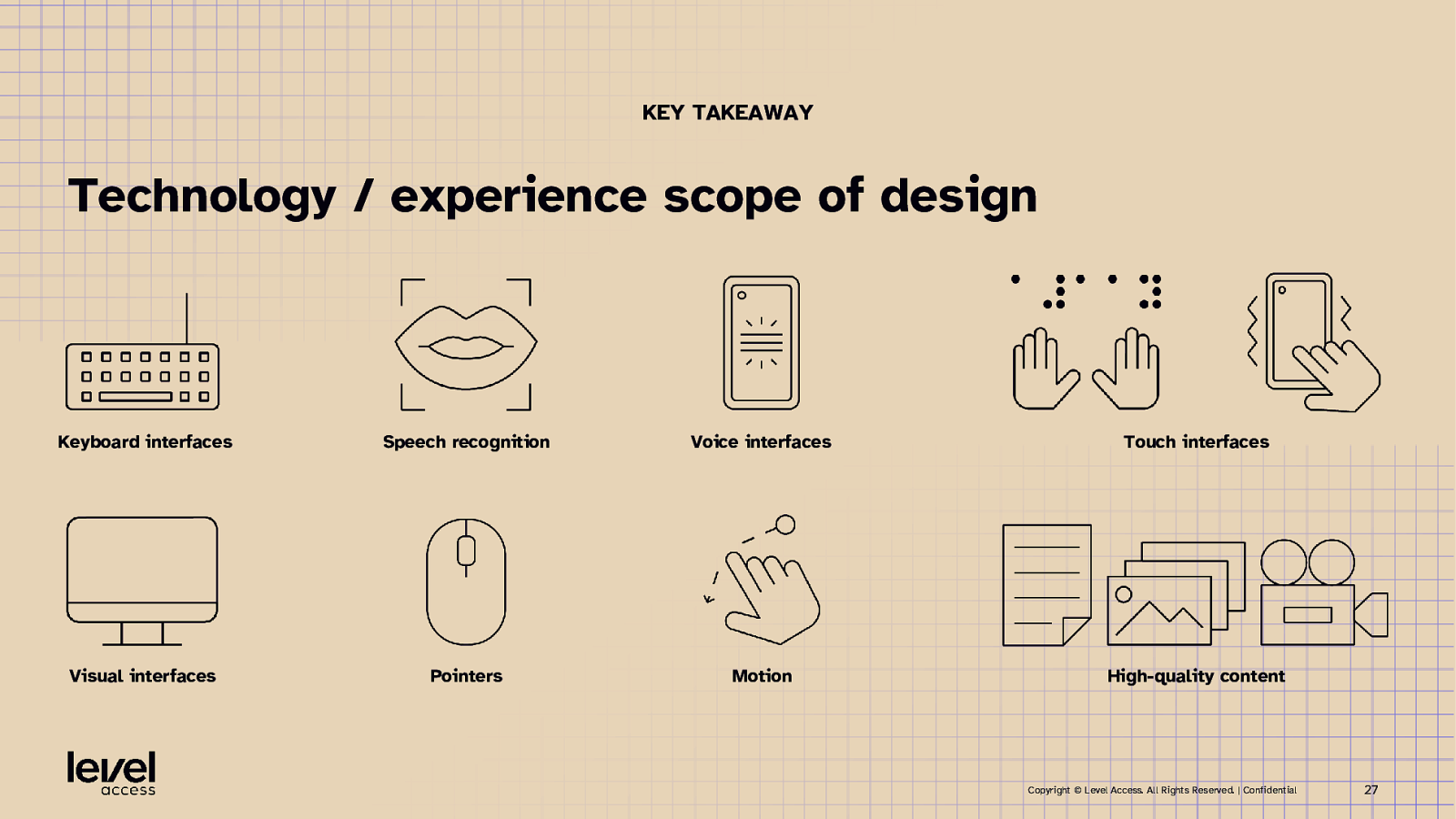
KEY TAKEAWAY Technology / experience scope of design Keyboard interfaces Speech recognition Voice interfaces Touch interfaces Visual interfaces Pointers Motion High-quality content Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 27

MY GOALS FOR THIS FRAMEWORK Adoption and Stickiness Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 28

FRAMEWORK REQUIREMENTS
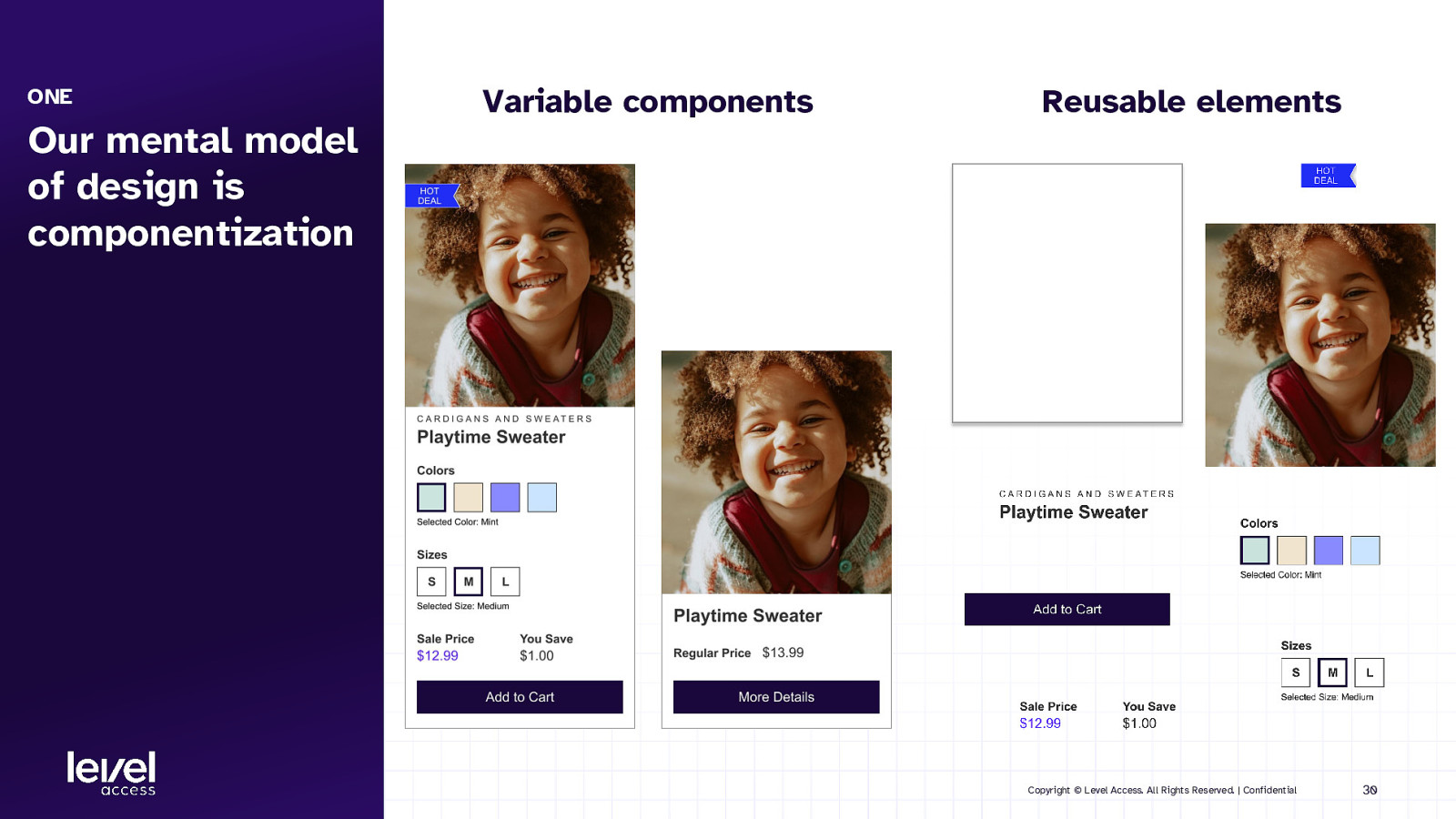
ONE Variable components Reusable elements Our mental model of design is componentization Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 30
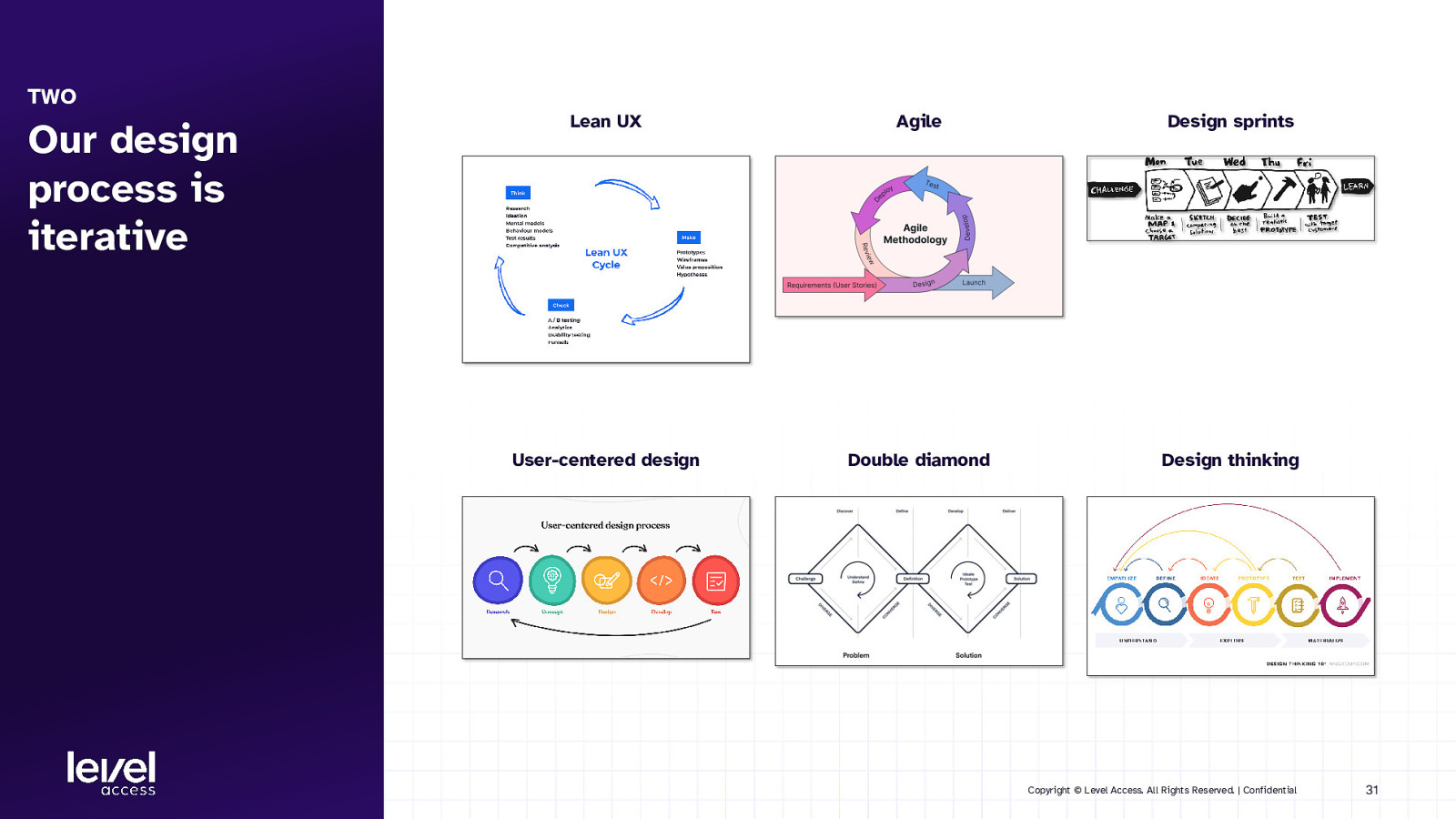
TWO Our design process is iterative Lean UX Agile Design sprints User-centered design Double diamond Design thinking Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 31

NOTE What’s missing from an accessibility standpoint is rigor in that iteration. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 32

KEY TAKEAWAY Appropriately design the features and functionality against which the realized page will be tested. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 33
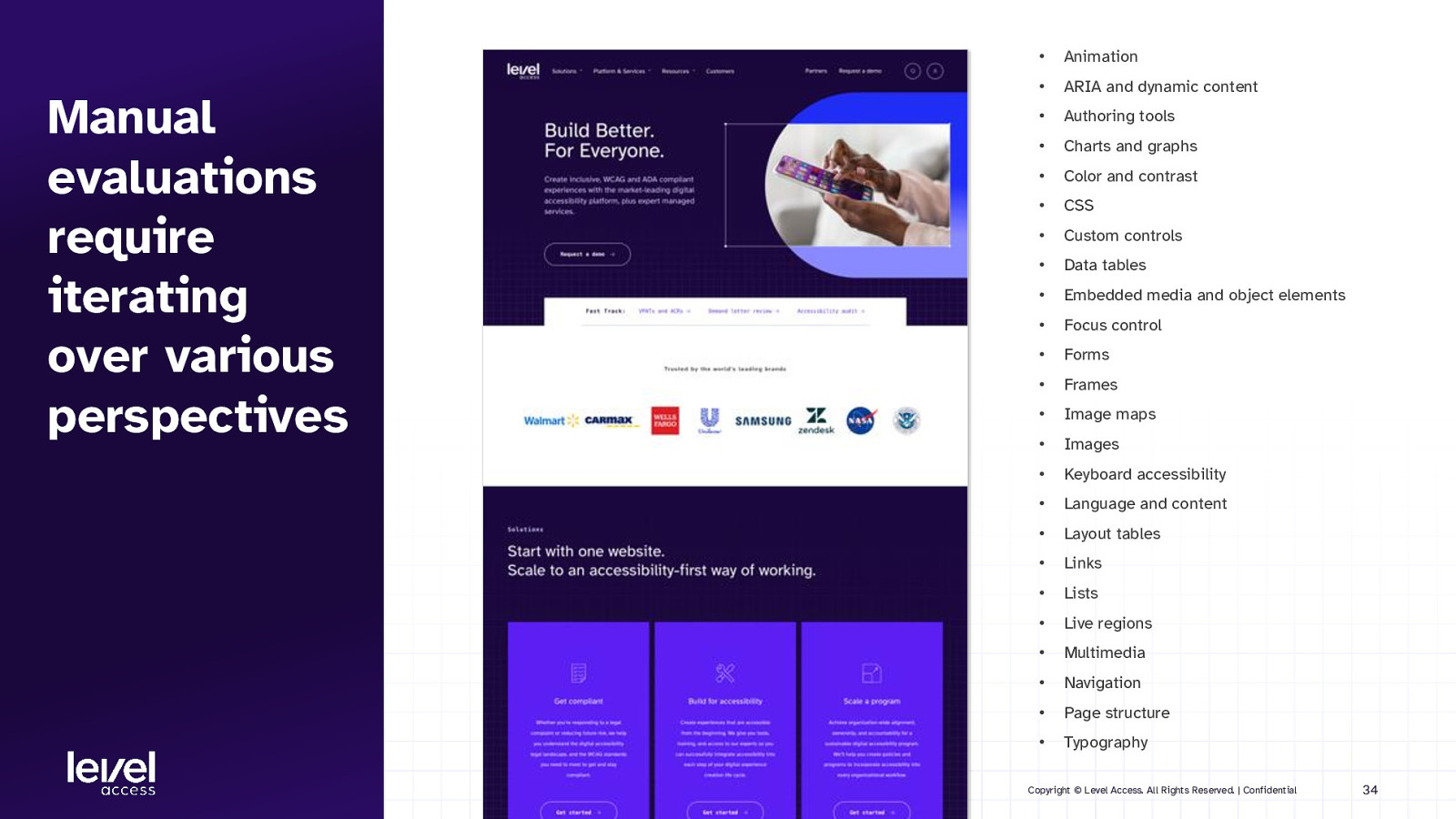
Manual evaluations require iterating over various perspectives • Animation • ARIA and dynamic content • Authoring tools • Charts and graphs • Color and contrast • CSS • Custom controls • Data tables • Embedded media and object elements • Focus control • Forms • Frames • Image maps • Images • Keyboard accessibility • Language and content • Layout tables • Links • Lists • Live regions • Multimedia • Navigation • Page structure • Typography Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 34

KEY TAKEAWAY To cover the full set of accessibility requirements, you need to comb over your designs multiple times, each time with a different perspective: - Can they perceive all pertinent information? - Can they understand all the information? - Can they execute the actions they want to take? Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 35
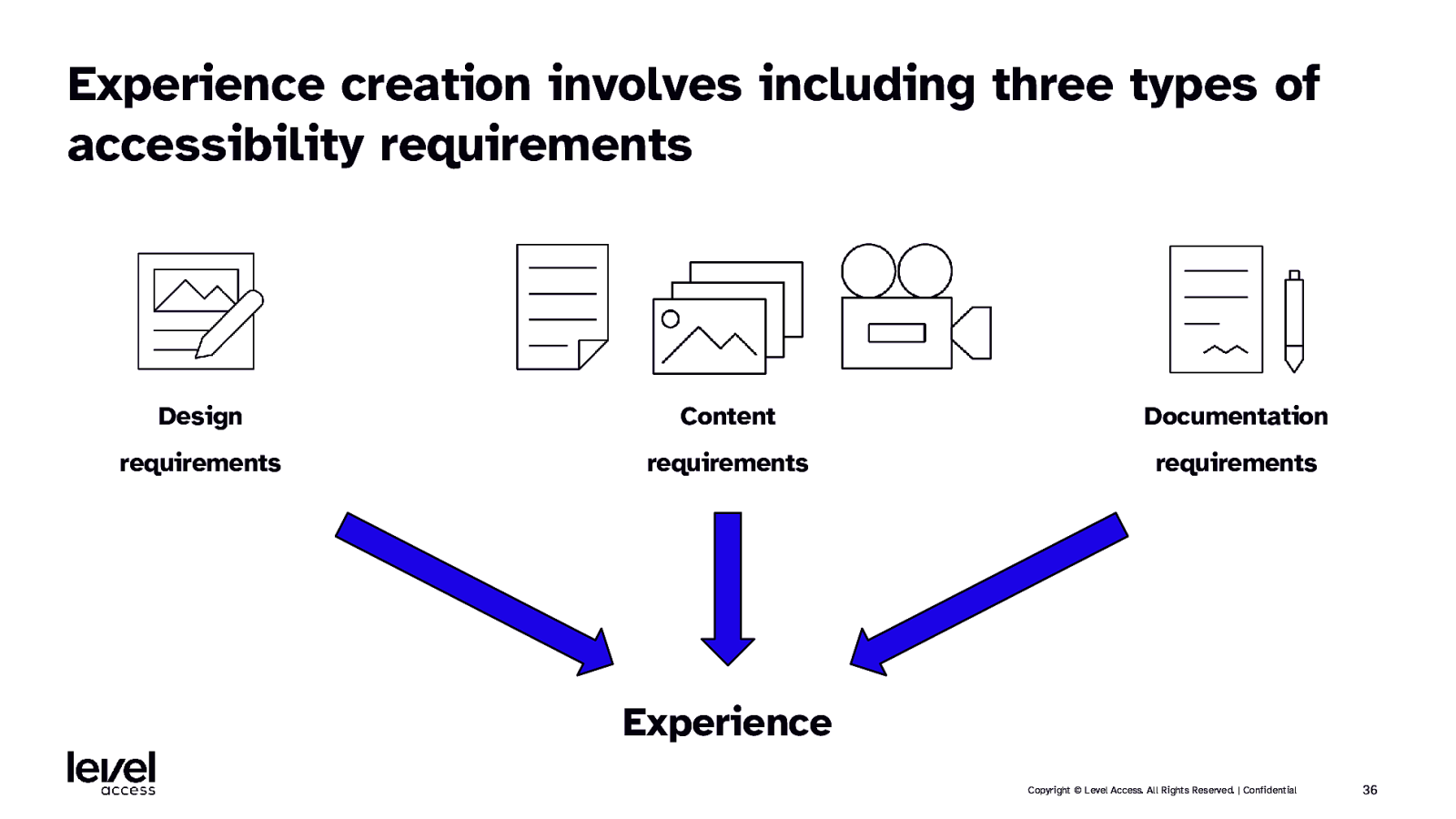
Experience creation involves including three types of accessibility requirements Design Content Documentation requirements requirements requirements Experience Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 36
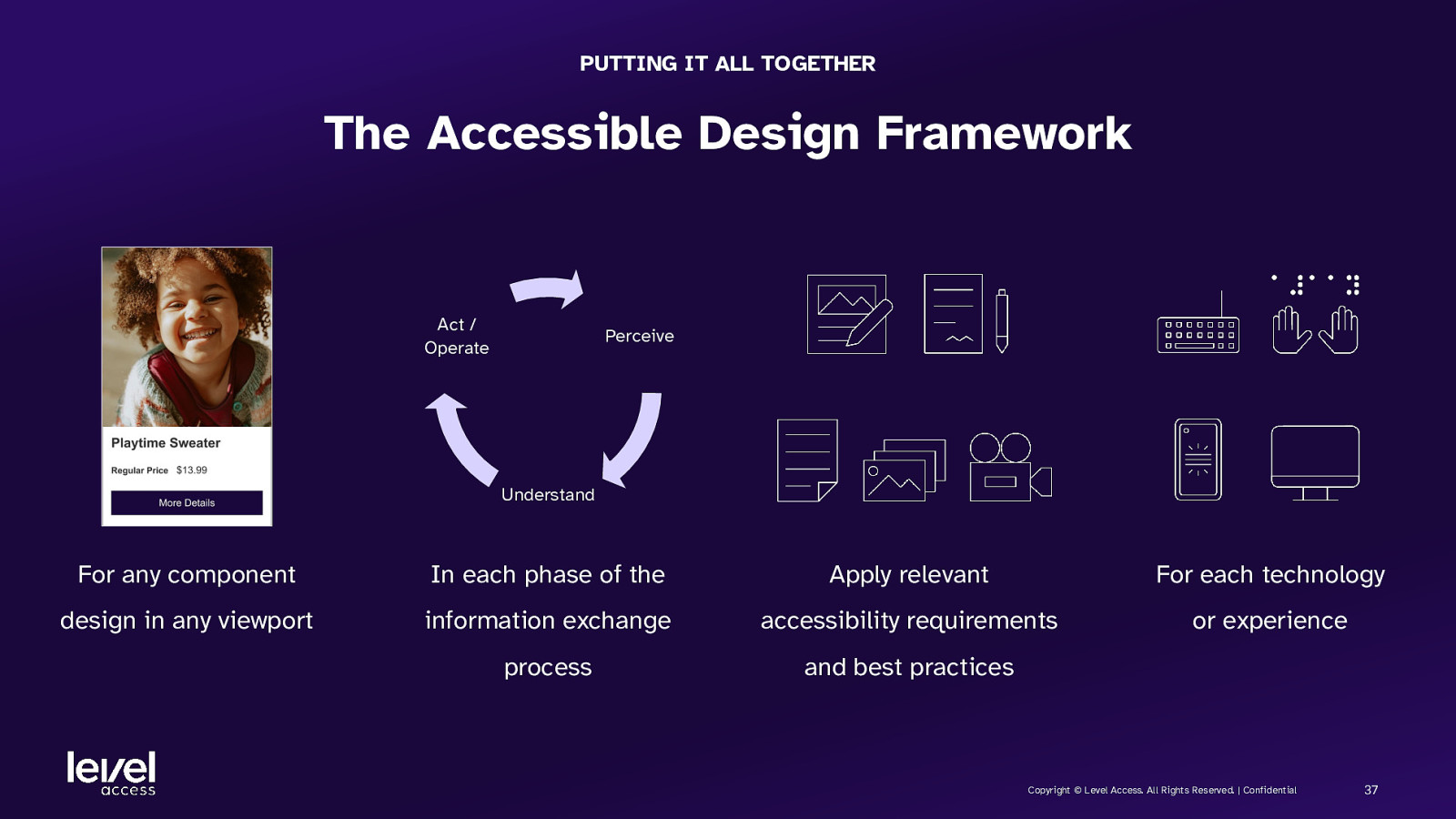
PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER The Accessible Design Framework Act / Operate Perceive Understand For any component In each phase of the Apply relevant For each technology design in any viewport information exchange accessibility requirements or experience process and best practices Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 37

Applying the framework Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 38
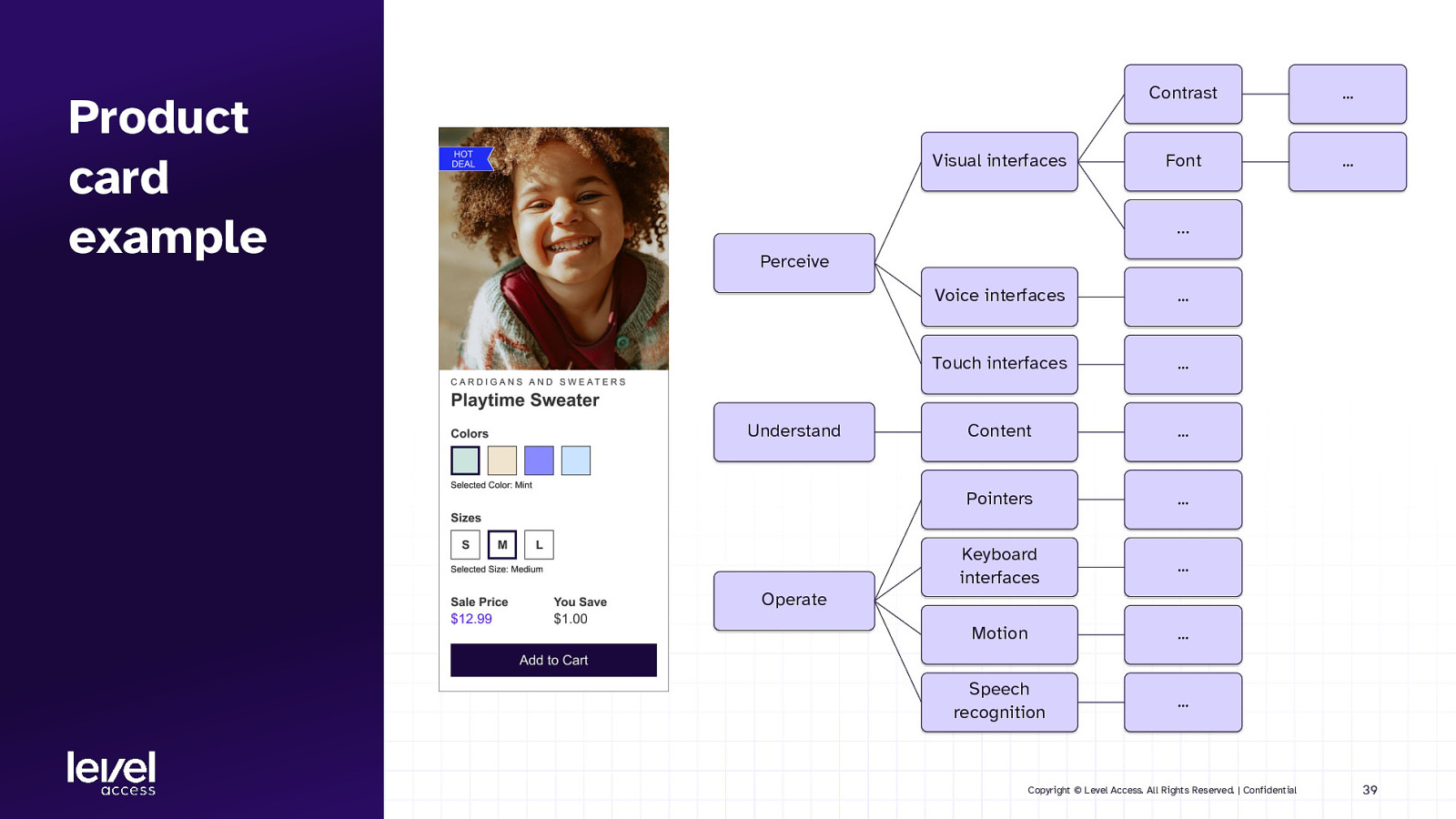
Product card example Visual interfaces Contrast … Font … … Perceive Understand Voice interfaces … Touch interfaces … Content … Pointers … Keyboard interfaces … Motion … Speech recognition … Operate Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 39
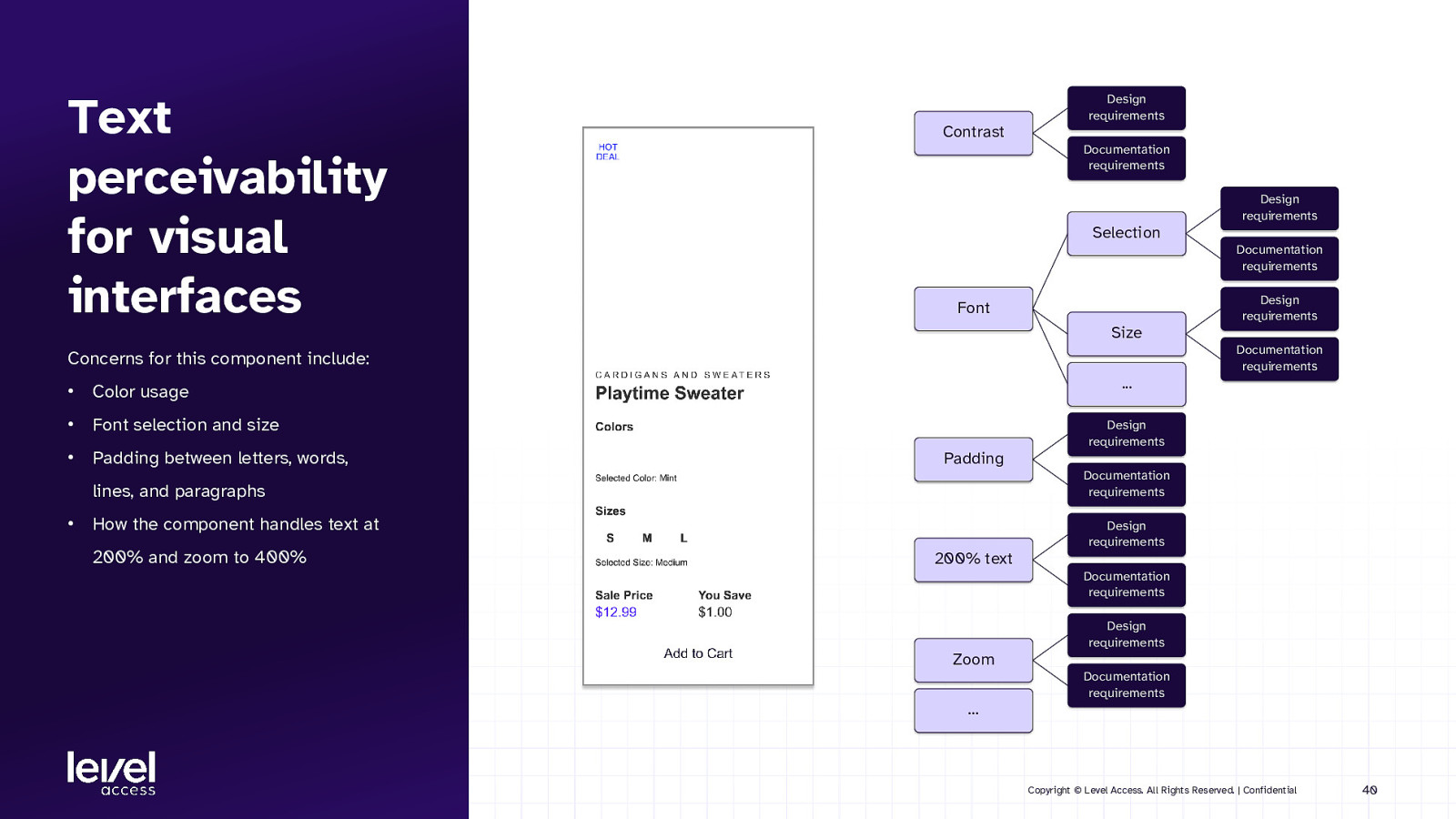
Text perceivability for visual interfaces Design requirements Contrast Documentation requirements Design requirements Selection Documentation requirements Design requirements Font Size Documentation requirements Concerns for this component include: • Color usage • Font selection and size • Padding between letters, words, … Design requirements Padding Documentation requirements lines, and paragraphs • How the component handles text at 200% and zoom to 400% Design requirements 200% text Documentation requirements Design requirements Zoom Documentation requirements … Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 40
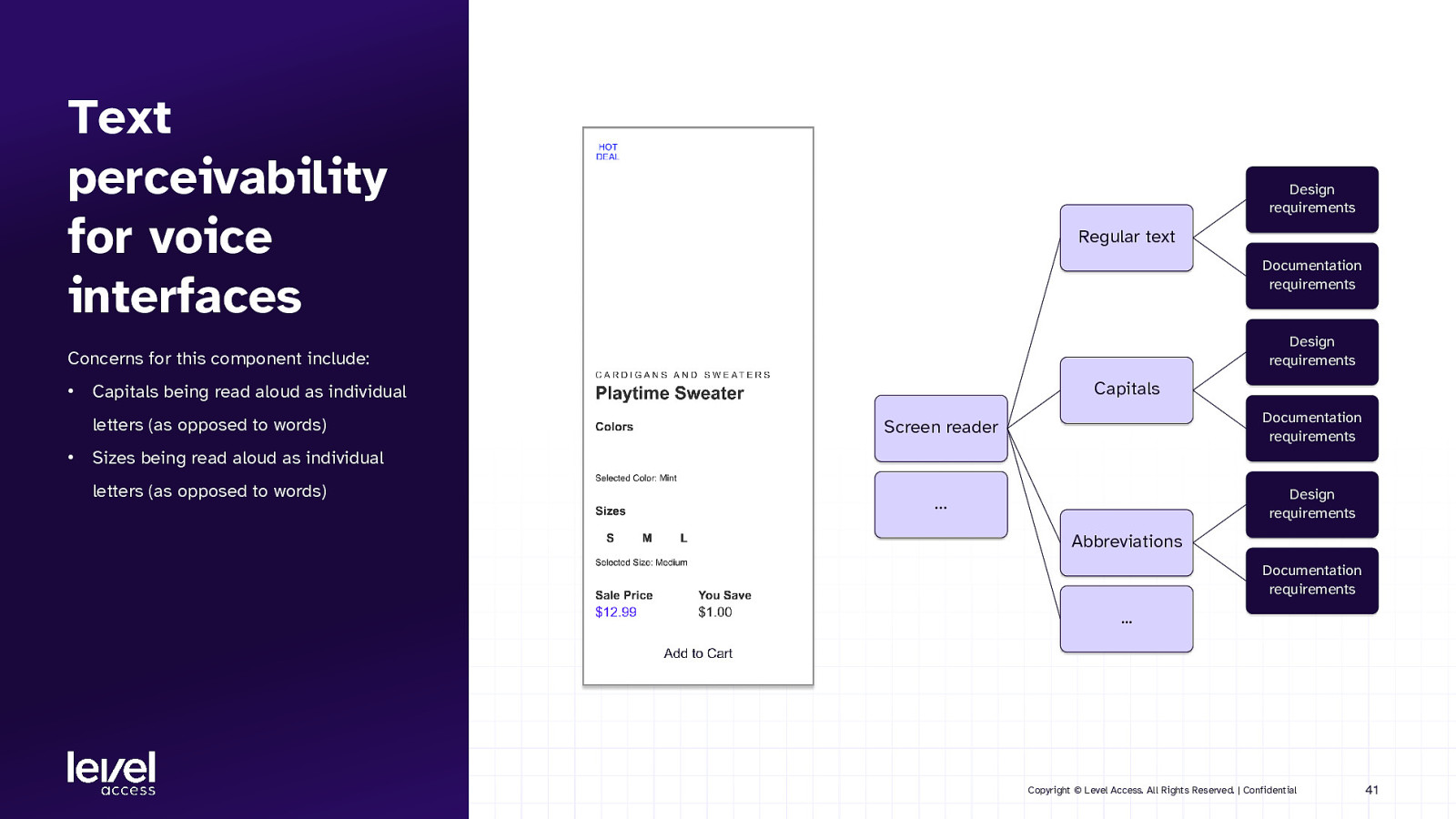
Text perceivability for voice interfaces Design requirements Regular text Documentation requirements Design requirements Concerns for this component include: • letters (as opposed to words) • Capitals Capitals being read aloud as individual Screen reader Documentation requirements … Design requirements Sizes being read aloud as individual letters (as opposed to words) Abbreviations Documentation requirements … Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 41

Text perceivability for touch interfaces Design requirements Haptic Documentation requirements No touch concerns for text in this component Design requirements Braille Documentation requirements … Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 42

Text understandability Content requirements Reading order Documentation requirements Concerns for this component include: • Reading order / focus order • Plain language • Meaningful descriptions Order Content requirements Focus order Documentation requirements Content requirements Language Documentation requirements Content requirements Descriptions Documentation requirements … Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 43
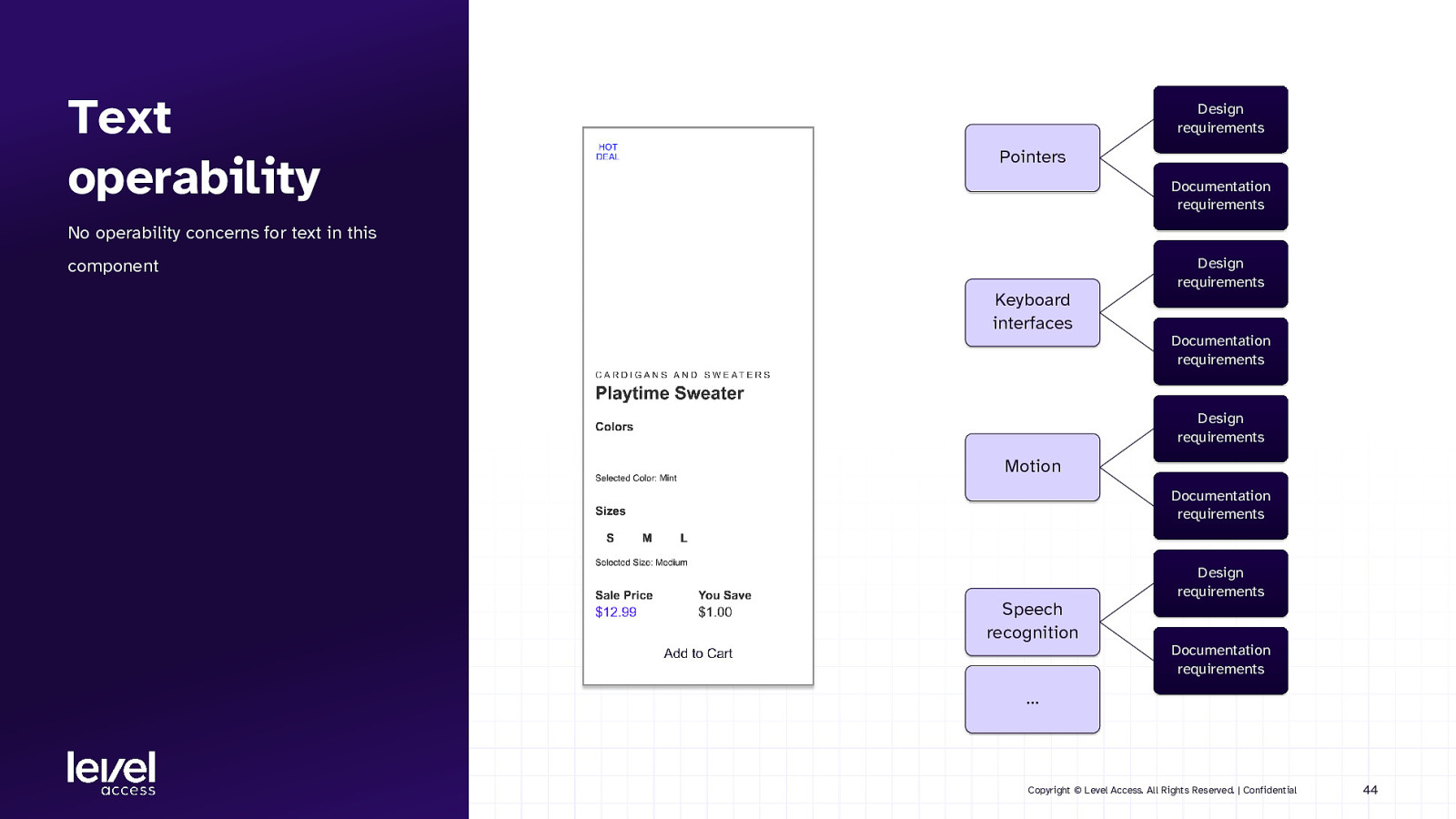
Text operability Design requirements Pointers Documentation requirements No operability concerns for text in this Design requirements component Keyboard interfaces Documentation requirements Design requirements Motion Documentation requirements Design requirements Speech recognition Documentation requirements … Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 44
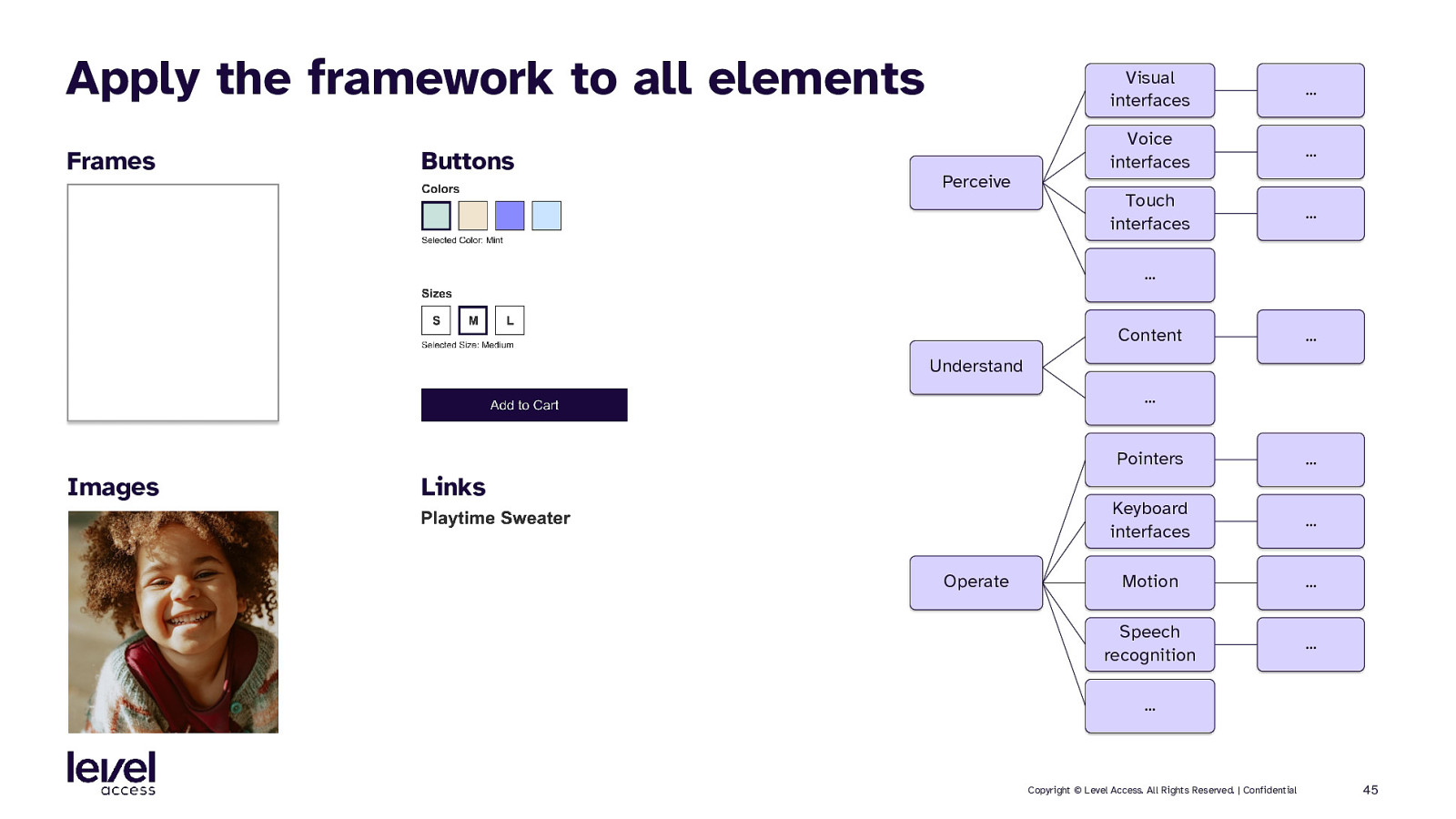
Apply the framework to all elements Frames Buttons Perceive Visual interfaces … Voice interfaces … Touch interfaces … … Content … Understand … Images Links Operate Pointers … Keyboard interfaces … Motion … Speech recognition … … Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 45
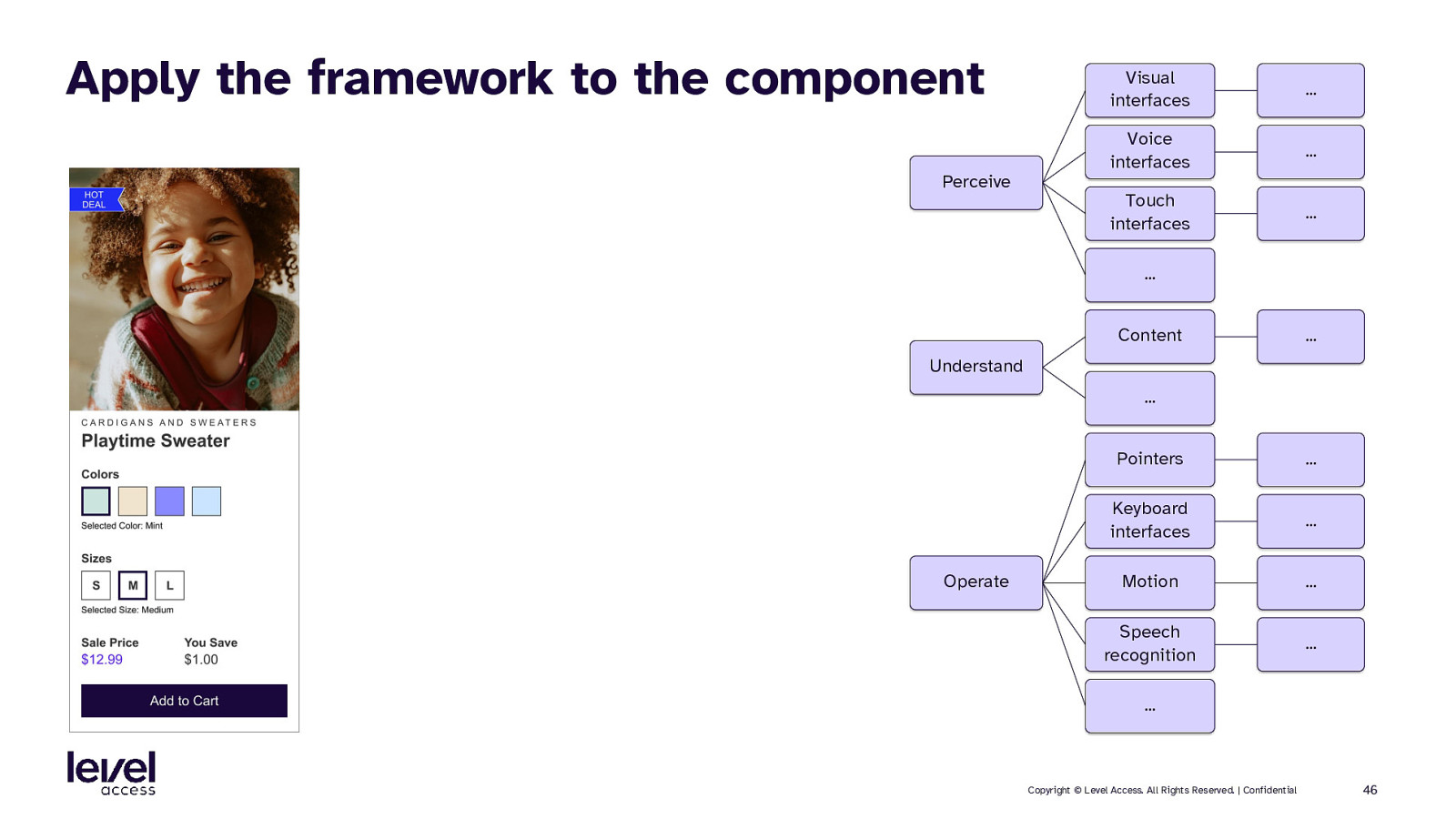
Apply the framework to the component Perceive Visual interfaces … Voice interfaces … Touch interfaces … … Content … Understand … Operate Pointers … Keyboard interfaces … Motion … Speech recognition … … Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 46

NOTE This framework provides your scaffolding. You need additional guidance on accessibility requirements. Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 47

Summary and questions Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 48

Key takeaways summarized • Our scope of design is a system that includes an able yet flawed human, as well as the set of technologies that enable them to execute their desired tasks in digital environments. • Design for human abilities and limitations, and for technology’s abilities and limitations, all within a given environment or context. • It’s the quality of the content that’s important to help people understand it. • Content can be thought of as a technology that enables the understandability of the system. • Content needs to be thoughtfully designed so it can move through the system quickly and efficiently. • Appropriately design the features and functionality against which the realized page will be tested. • To cover the full set of accessibility requirements, you need to comb over your designs multiple times, each time with a different perspective: o Can they perceive all pertinent information? o Can they understand all the information? o Can they execute the actions they want to take? Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 49
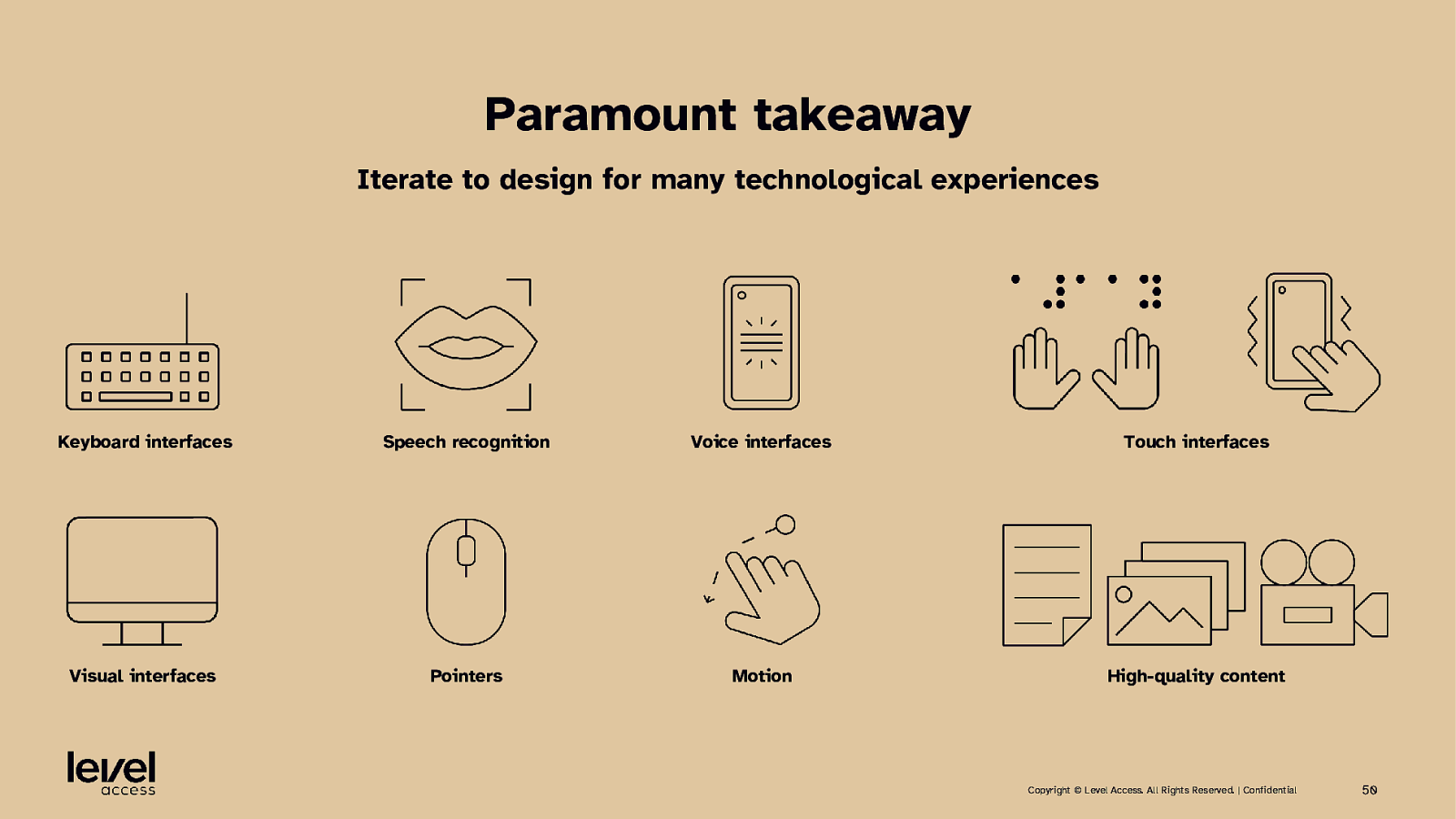
Paramount takeaway Iterate to design for many technological experiences Keyboard interfaces Speech recognition Voice interfaces Touch interfaces Visual interfaces Pointers Motion High-quality content Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 50

NOTE Article and examples coming soon! Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 51

We’re Hiring We’re building more than a team. Everyone is welcome! Come chat with us at Booth 609 for more details! Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 52

Questions? Copyright © Level Access. All Rights Reserved. | Confidential 53

Thank you