Defying the mainstream: building technology that respects our rights
Laura Kalbag, laurakalbag.com@LauraKalbag Small Technology Foundation small-tech.org
A presentation at New Adventures in January 2020 in Nottingham, UK by Laura Kalbag

Laura Kalbag, laurakalbag.com@LauraKalbag Small Technology Foundation small-tech.org
So I’m browsing the Pink News site, because I think we can agree that the same-sex dance on Strictly at the end of last year was a dream…

And as I scroll down below the article, I am presented with reams of classic clickbait: “Cork, Want To Get The Latest Vista Hearing…”

“25 Celebs You Didn’t Realize Are Gay - No. 8 Will Surprise Women”

“Drink This Before Going to Bed to Help Burn Belly Fat”
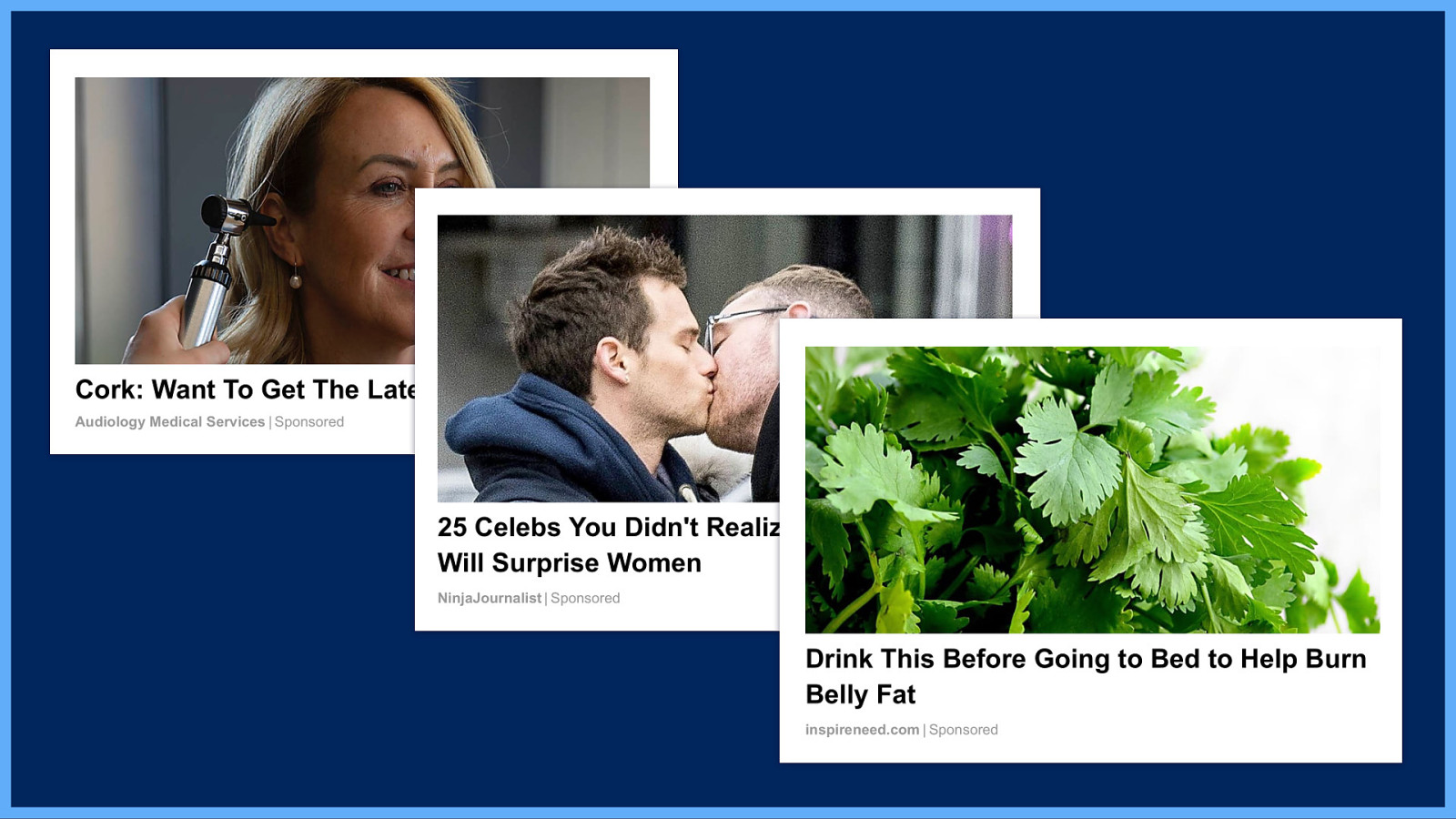
This clickbait is quite revealing through its chosen topics alone. It knows I’m in Cork. It knows the broad subject matter of the content of the article I’m reading, or the site I’m on. It appears to suspect I’m a woman. And well, who doesn’t feel targeted by clickbait ads about belly fat.

This clickbait is provided to Pink News by Taboola.
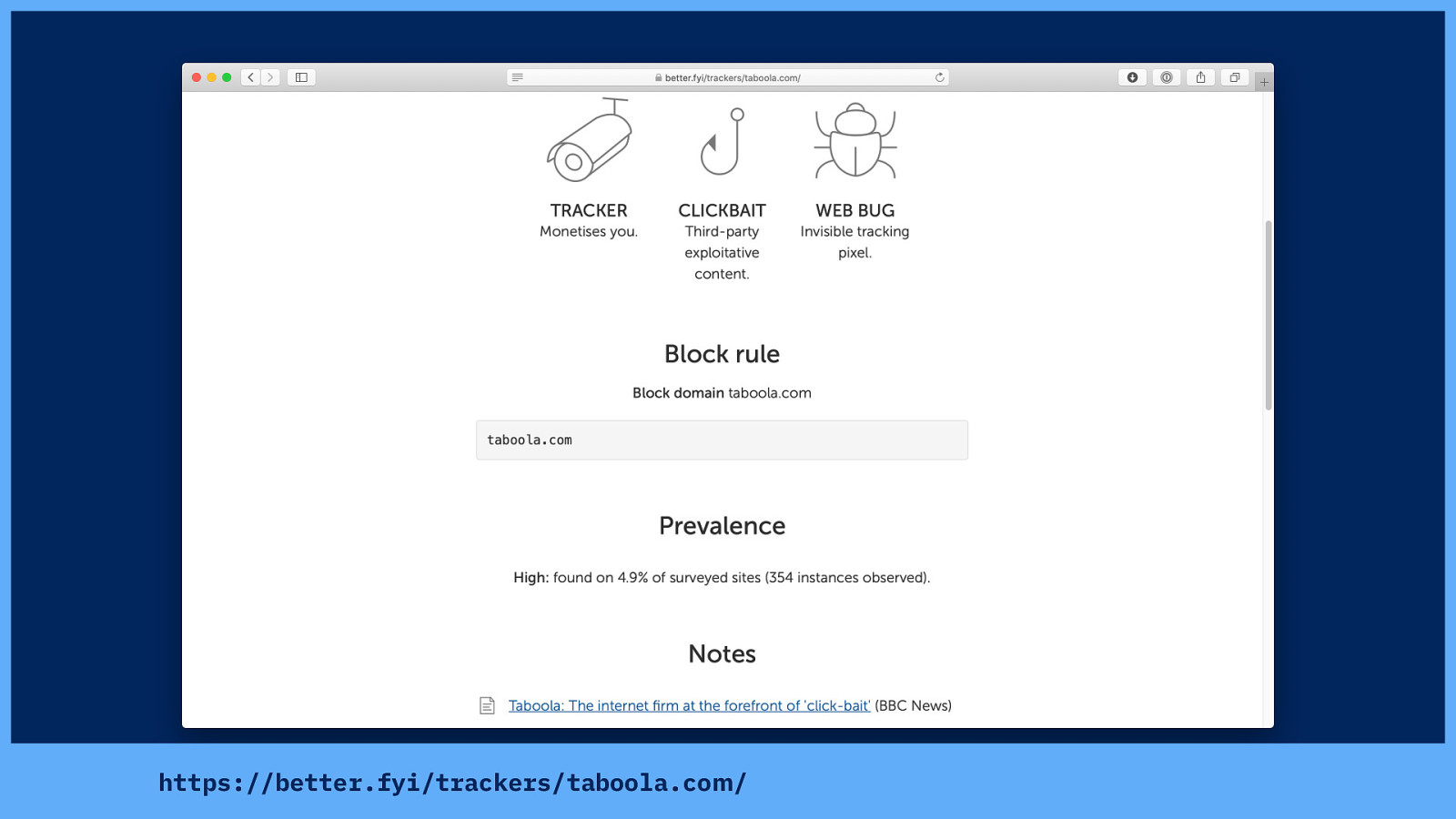
I work on blocking trackers with a privacy tool called Better Blocker, and we’ve looked into Taboola. In our crawls of the most popular sites on the web, we found Taboola on nearly 5% of sites.
Taboola’s aim is to:
“Drive marketing results by targeting your audience when they are most receptive to new messages.”
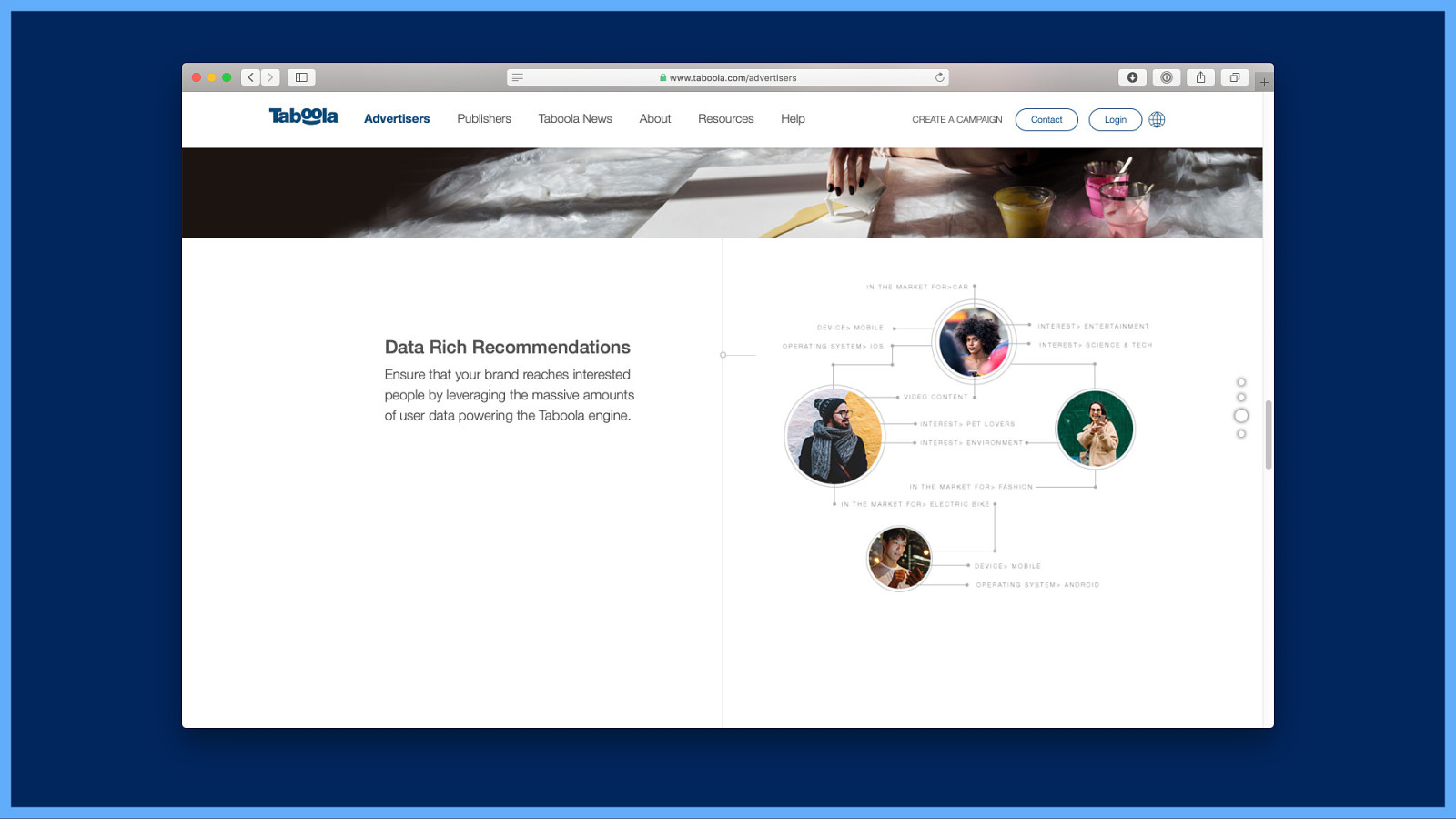
You can do that with their:
“Data Rich Recommendations: Ensure that your brand reaches interested people by leveraging the massive amounts of user data powering the Taboola engine.” (Emphasis my own!)
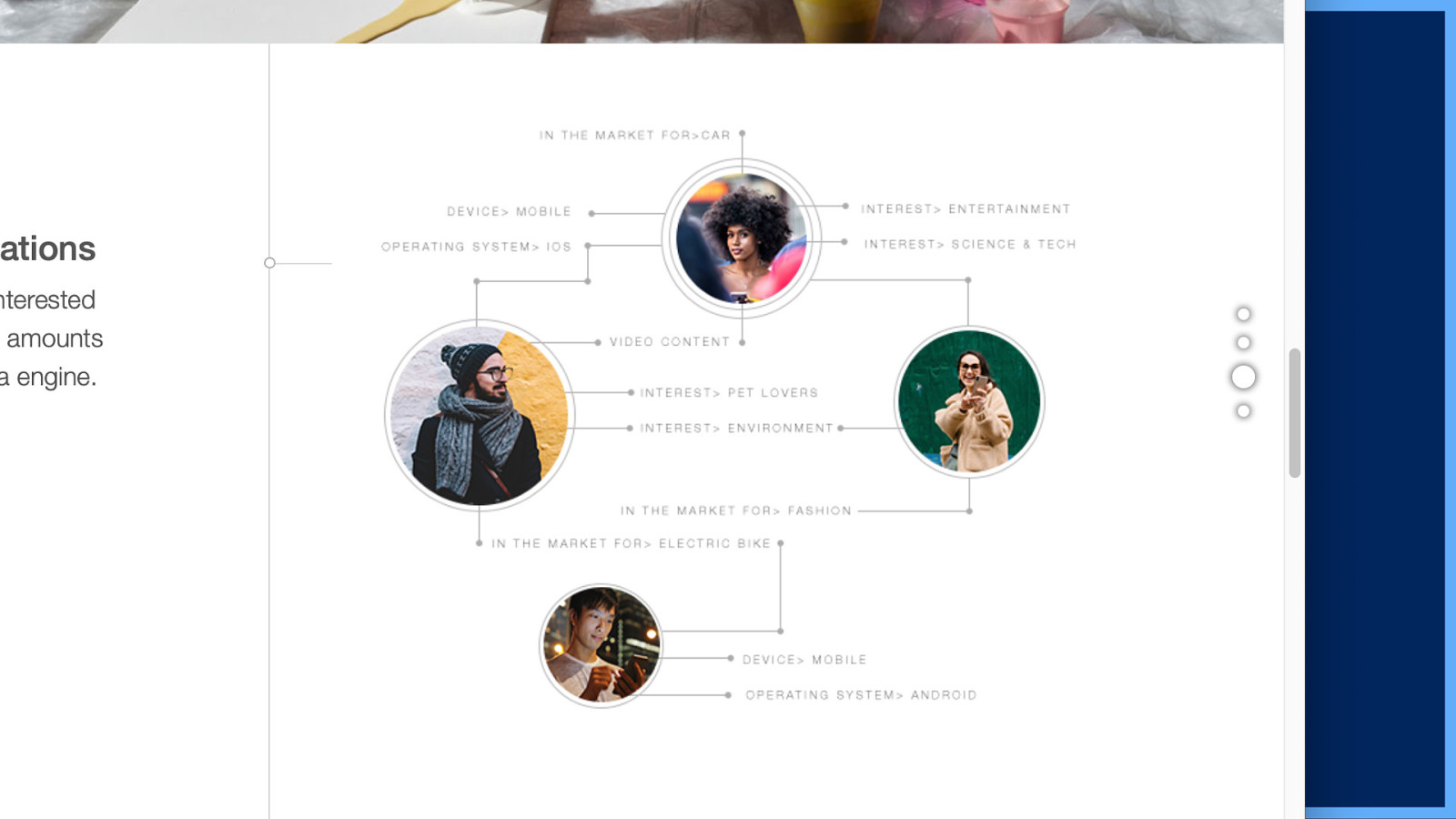
In fact, they provide a handy graphic here showing some of the information that might be useful about a site’s visitor. “Device and operating system”… but also… “In the the market for > car, fashion, electric bike”… “Interest > pet lovers, environment, entertainment, science & tech.”
So I scroll down to Taboola’s privacy policy, to see how they know this information about me, and what they intend to do with it. They seem to have a specific policy for “Third Party Online Advertising”, so I’ll check that out.

“We automatically collect User Information when Users interact with our Services that appear on our Customers’ websites and digital properties.”

“Taboola collects only pseudonymized data, which means we do not know who you are because we do not know or process your name, email address, or other identifiable data.”

Let’s debunk this for a second. “Pseudonymised data” or “anonymised data” doesn’t mean you’re unidentifiable. Even though it’s a claim that privacy policies have been hanging off for years…

As Bruce Schneier said over a decade ago in Wired, “it takes only a small named database [(as in a database containing names)] for someone to pry the anonymity off a much larger anonymous database.” They just need to compare some data points that match in each database.

A recent study (and it’s not the only study) into methods to re-identify individuals from anonymised datasets found “Using our model, we find that 99.98% of Americans would be correctly re-identified in any dataset using 15 demographic attributes.” Attributes such as age, gender, ethnicity, post code, number of children, number of cars owned, location, status updates, and results on a personality quiz.

Returning to Taboola’s privacy policy… I want to know how the interests Taboola infers compares to these kinds of demographic attributes. They’re described by Taboola as “data segments”… “A data segment is a grouping of users who share one or more attributes (e.g., travel enthusiasts). We offer a number of data segments, both proprietary and from our data partners”. Kindly, they’ve provided a link to their data partners…
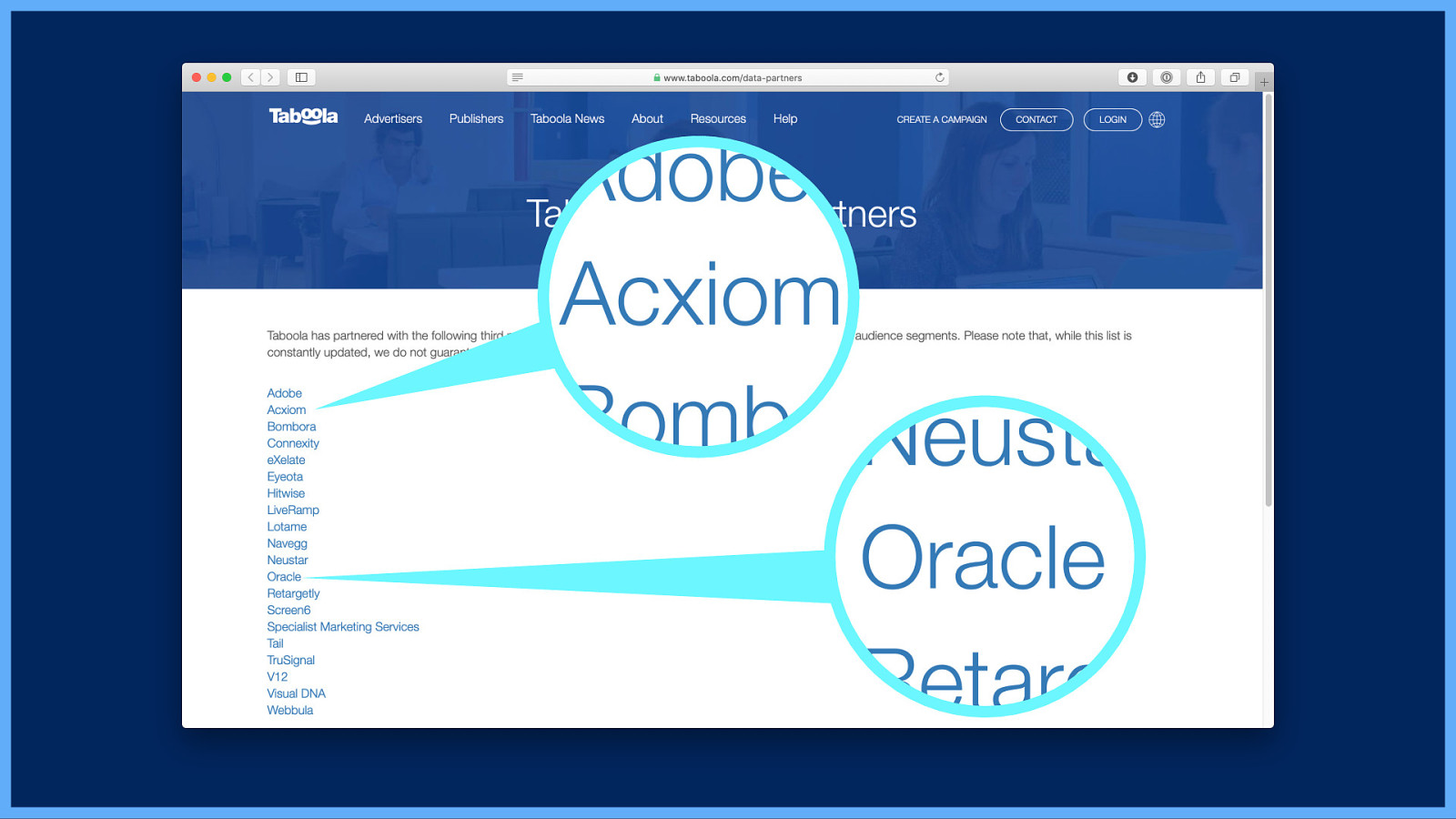
Now two of these data partners stand out to me in particular… Acxiom and Oracle
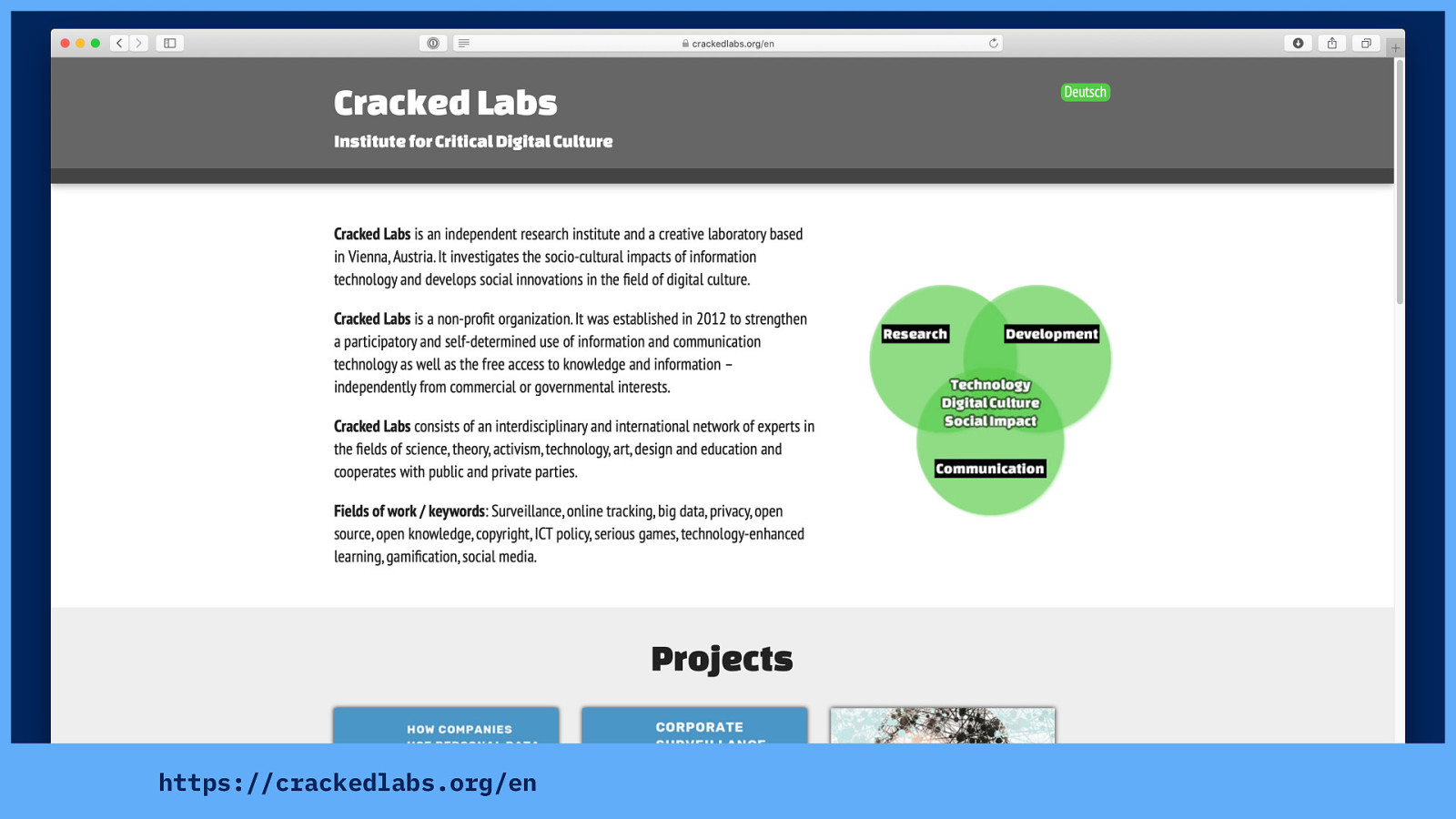
And that’s because Cracked Labs have done multiple reports into the personal data that corporations collect, combine, analyse, trade and use. And the data brokers that deal in this data.

…featuring two of the biggest data brokers: Oracle and Acxiom.

According to Cracked Labs: “Acxiom provides up to 3000 attributes and scores on 700 million people in the US, Europe, and other regions.”

And “Oracle sorts people into thousands of categories and provides more than 30,000 attributes on 2 billion consumer profiles.” But what are those attributes and categories?
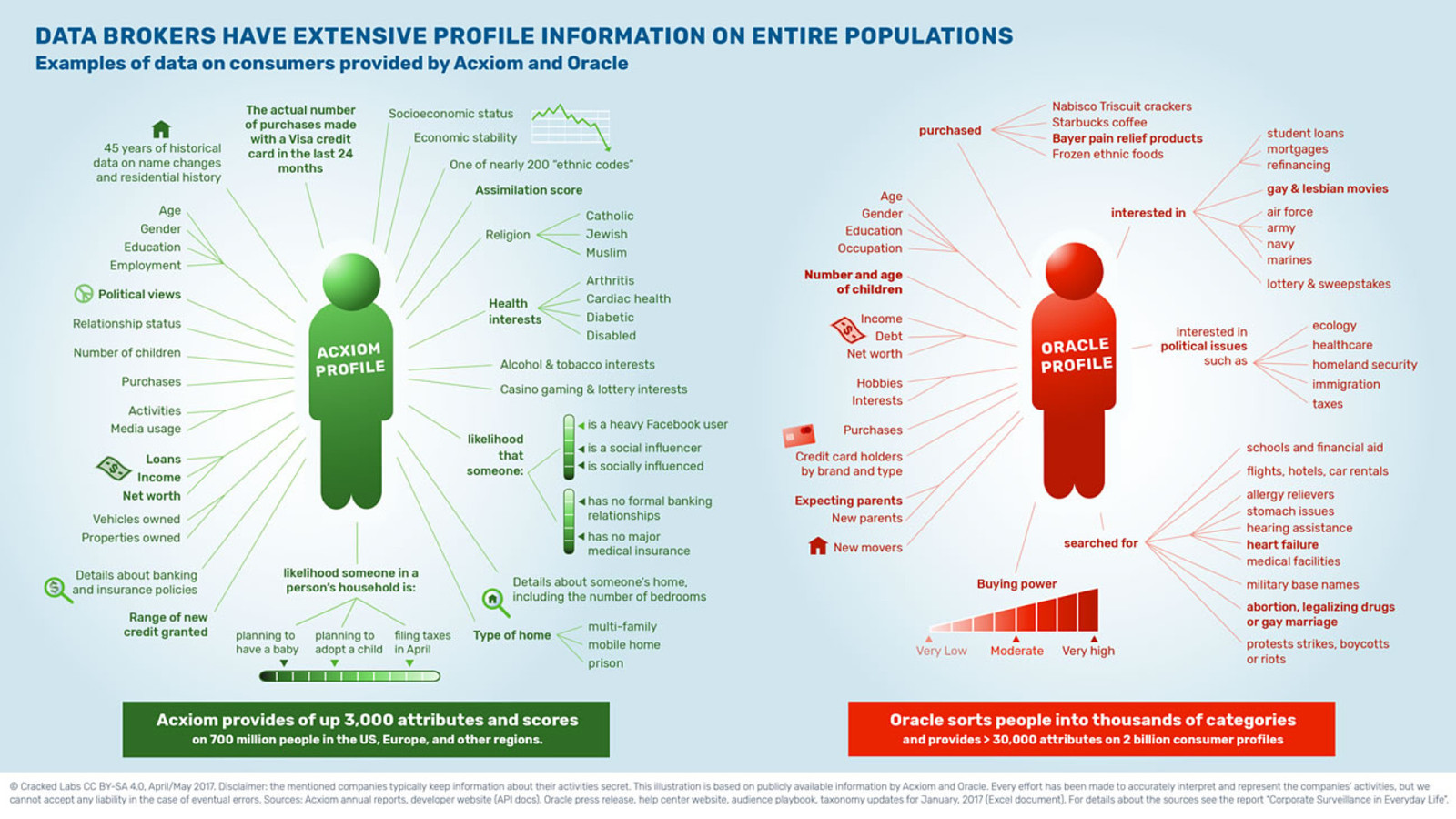
I’ve picked out some of the creepiest bits of information from the Cracked Labs reports:
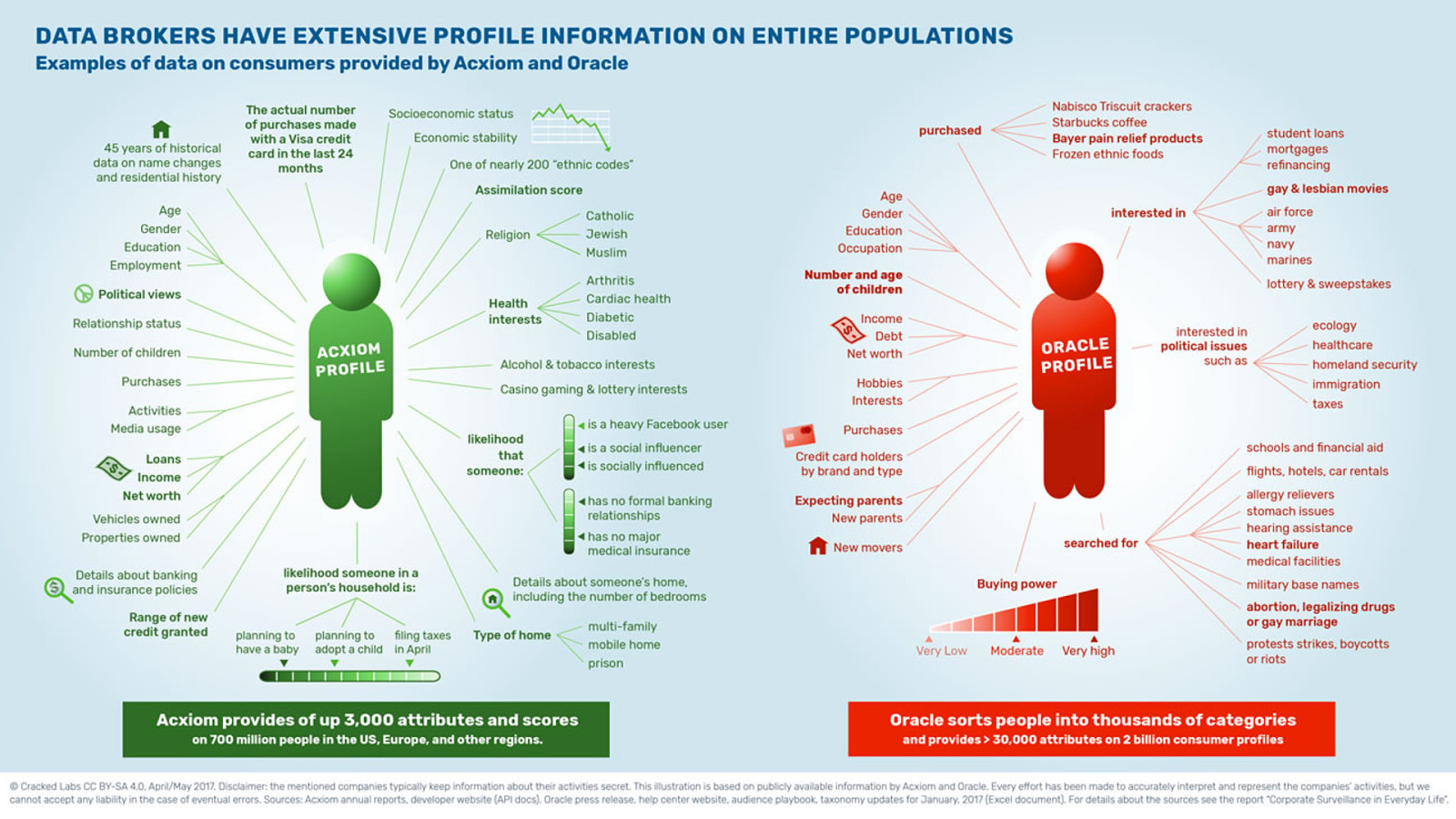
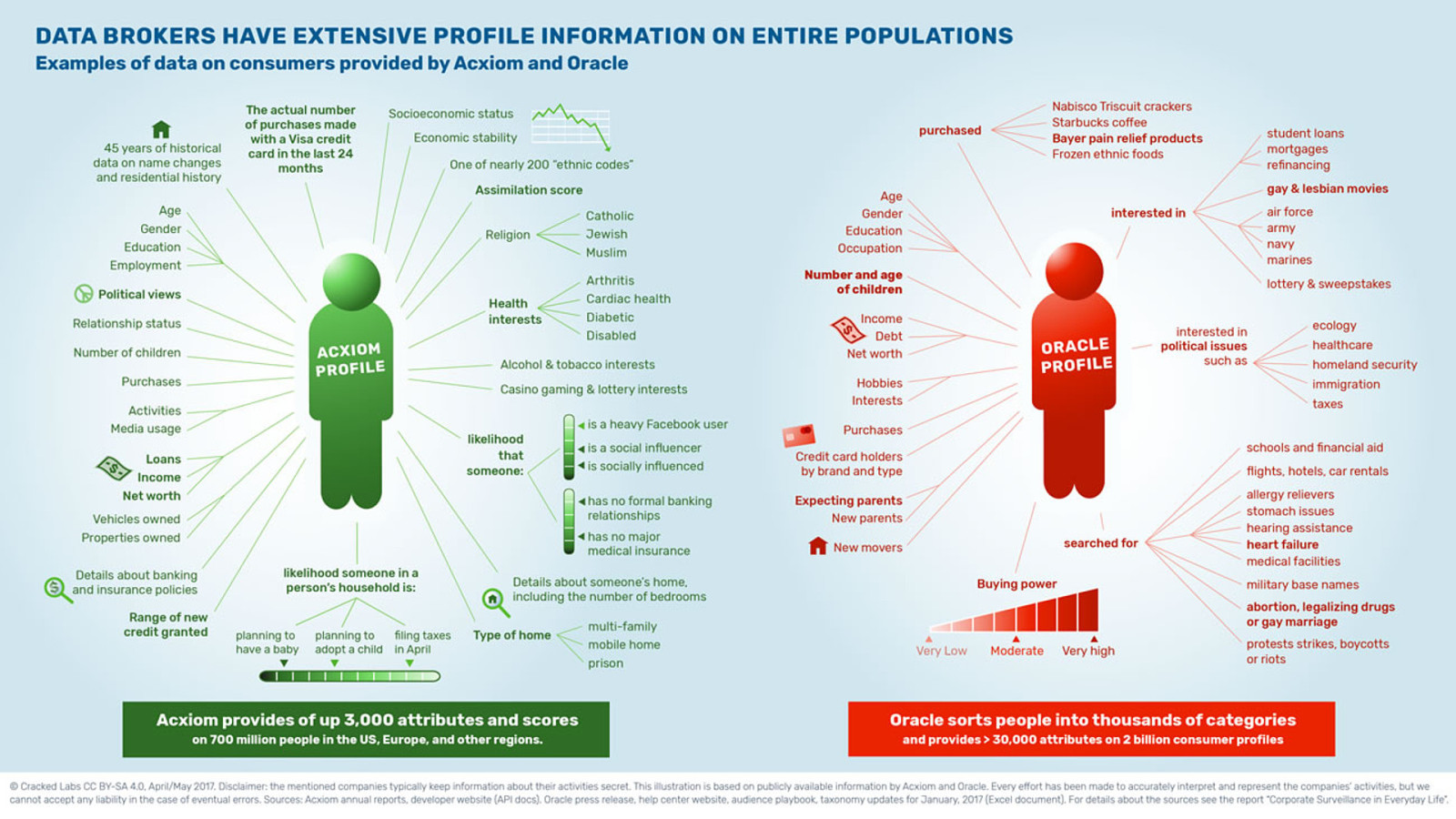
search history, including whether a person searched about: abortion, legalising drugs, or gay marriage, protests, strikes, boycotts or riots. And the likelihood that a person is a social influencer or is socially influenced.

Taboola says it “does not knowingly create segments that are based upon what we consider to be sensitive information…” Hmm… Helpfully, Taboola also provides a detailed list of all their apparently not-sensitive “standard health-related segments”…


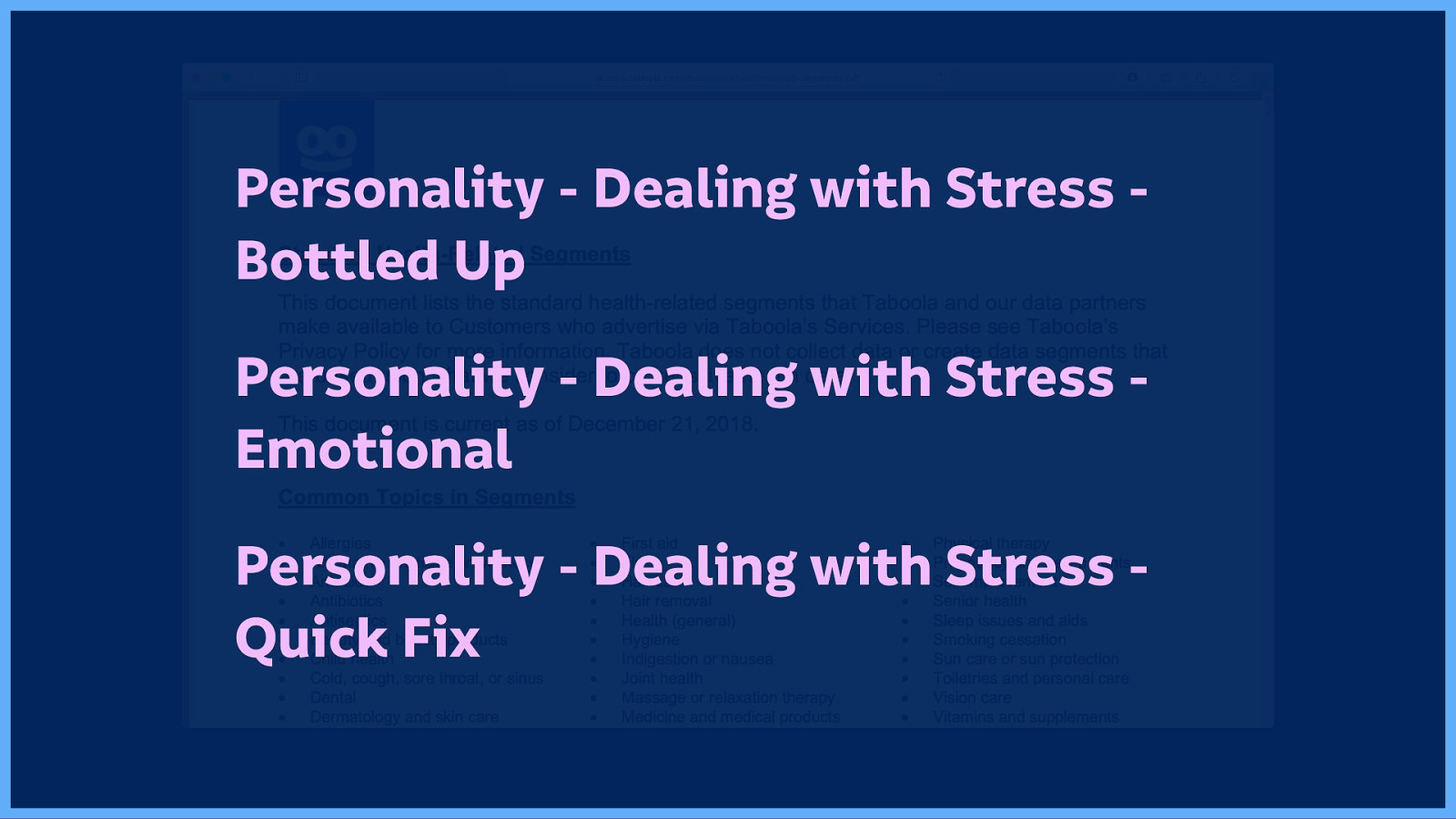
This isn’t exactly the kind of information you want marketers to use to sell to you… It is personal.

Personality attributes were also used by Cambridge Analytica. They collected them through a personality test app on Facebook that also harvested the profiles of the participant’s friends and friend’s friends.

In this personality test app, “Users were scored on ‘big five’ personality traits – Openness, Conscientiousness, Extroversion, Agreeableness and Neuroticism – and in exchange, 40% of them consented to access to their Facebook profiles.” Source: https://www.theguardian.com/news/2018/mar/17/data-war-whistleblower-christopher-wylie-faceook-nix-bannon-trump

“[Cambridge Analytica] itself claimed to be able to analyse huge amounts of consumer data and combine that with behavioural science to identify people who organisations can target with marketing material.” Source: https://www.theguardian.com/news/2018/mar/18/what-is-cambridge-analytica-firm-at-centre-of-facebook-data-breach

It’s profiling.

Cambridge Analytica was a venture of SCL Elections whose “expertise was in “psychological operations” – or psyops – changing people’s minds not through persuasion but through “informational dominance”, a set of techniques that includes rumour, disinformation and fake news.” Source: https://www.theguardian.com/news/2018/mar/17/data-war-whistleblower-christopher-wylie-faceook-nix-bannon-trump

That’s targeting.
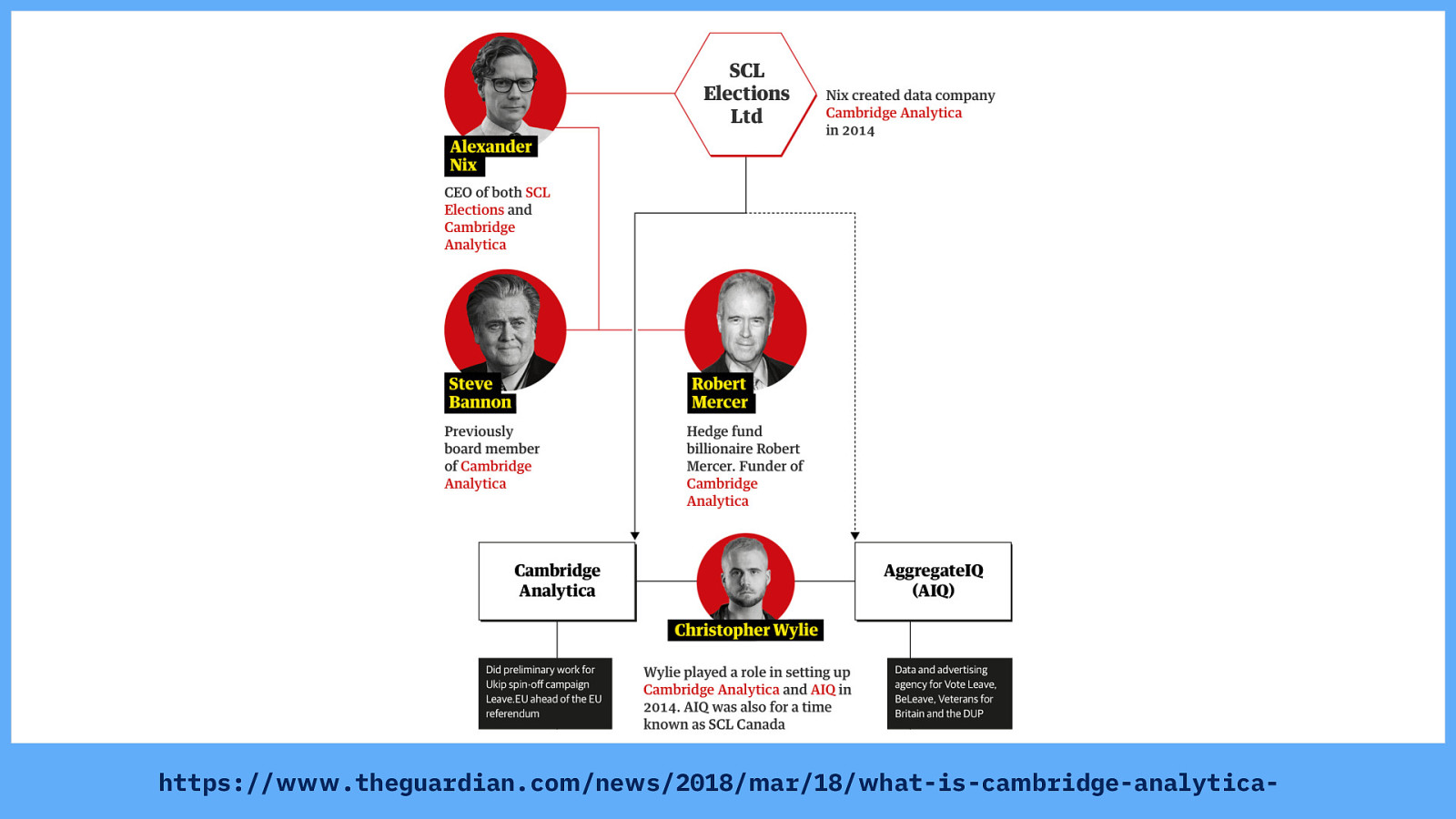
The same SCL worked with Steve Bannon on the Trump election campaign. And as this neat graphic from The Guardian shows, SCL’s ventures, Cambridge Analytica and AggregateIQ, worked on multiple Brexit Leave campaigns too. Source: https://www.theguardian.com/news/2018/mar/18/what-is-cambridge-analytica-firm-at-centre-of-facebook-data-breach

We, as citizens, could be manipulated by the profiling and targeting.
This is all the topic of a recent documentary on Netflix called The Great Hack. And I’d really recommend it if you want a lot of the information without having to do all the reading. It’s accessible for your friends who don’t speak tech-y too.

It means it’s not exaggerating to say that tracking affects democracy. And if we use tracking, we have to consider its ethical implications.

I could talk about this in more depth for much longer, but I’ve just not got the time. If you want a read, the book ’Surveillance Capitalism’ by Shoshana Zuboff contains both the history and the predicted future of these massive complex surveillance systems:

Shoshana Zuboff coined the term ‘surveillance capitalism’ and describes it in this book…
“Surveillance capitalism unilaterally claims human experience as free raw material for translation into behavioral data. Although some of these data are applied to product or service improvement, the rest are…fabricated into prediction products that anticipate what you will do now, soon, and later.”

And if you take one look at the size of that book and decide to opt-out, try listening to Shoshana Zuboff interviewed on the Adam Buxton podcast instead.

Many people use the argument that profiling and targeting is ok because it makes technology more convenient for the majority of us.

Convenient exploitative technology is like fluffy handcuffs. They may look cute and fluffy, they might lead to some fun. But they’re still handcuffs, and you always want to have access to the key.

How can we protect ourselves (as individuals)? Let’s look at a few of the things you can do:

Avoid logging in. (If you can.) For example, when you’re watching videos on YouTube.

However, many platforms will still track you via fingerprinting. These are a combination of identifiers unique to your browser that act as a fingerprint. Identifiers like your browser height and width, the device you’re using, (and ironically) whether you have ‘Do Not Track’ set in your browser preferences.
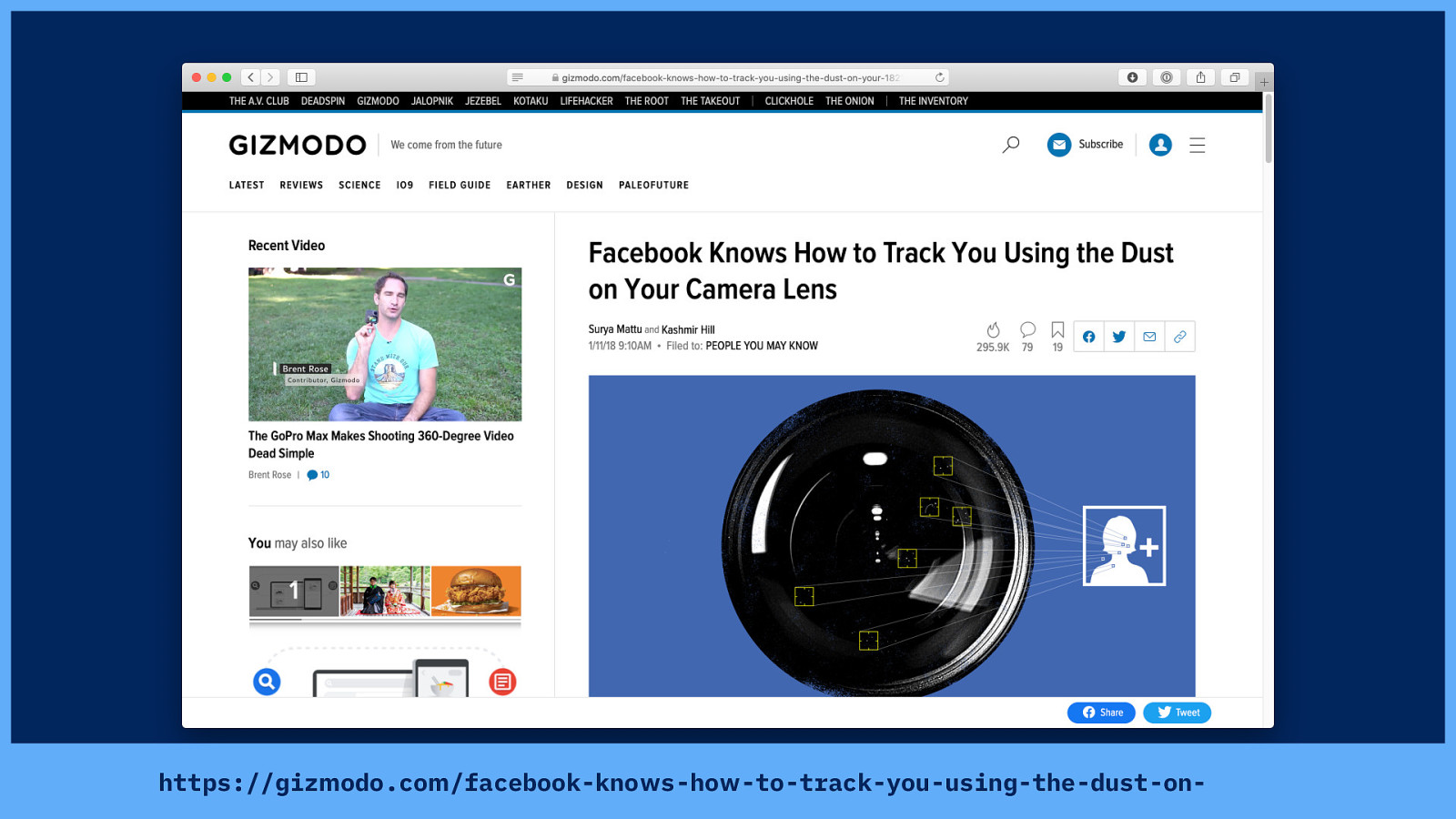
In 2015, Facebook even filed a patent saying it could identify people who might know each other because they appear in photos taken by the same camera… the camera being identified by identical lens scratches and dust. Source: https://gizmodo.com/facebook-knows-how-to-track-you-using-the-dust-on-your-1821030620

Avoid providing your phone number. Folks recommend using two-factor authentication to prevent nefarious strangers from getting into your accounts. But be aware that phone numbers are a little risky for authentication…

A study into whether Facebook used personally-identifiable information for targeted advertising found that when “We added and verified a phone number for [two-factor authentication] to one of the authors’ accounts… the phone number became targetable [by advertising] after 22 days”

And not long ago, Twitter admitted they did the same thing: “When an advertiser uploaded their marketing list, we may have matched people on Twitter to their list… based on the email or phone number the Twitter account holder provided for safety and security purposes.” Source: https://www.wired.com/story/twitter-two-factor-advertising/

Disallow cookies in your browser preferences.

Thing is, if we block cookies, many sites fall to pieces, and usually silently. Even if we only block cookies from third-parties. If a site relies on a third-party anything persistent, be it logins, preferences, even shopping baskets… that’ll probably break.

Don’t use Gmail. Your email not only contains all your communication, but the receipts for everything you’ve bought, the confirmations of every event you’ve signed up for, and every platform, newsletter, and service you’ve joined. (logged in thing)

From our own crawls of the web for Better Blocker, we discovered Google has its tentacles in around 80% of the popular web. Think of all the information Google can extract from those sites.

Though if your friends and family use Gmail, you’re a bit stuck. Likewise, your choices affect your friends and family.

Of course, these are all choices we can make once we’re on the web, but we need to be aware of other places where we are tracked.…

Google Nest knows everything about your home. Source: https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2015/jun/18/googles-nest-cam-always-watching-live-streaming-video

Amazon Ring and Alexa can hear everything you say and spy on your neighbours. Source: https://reallifemag.com/false-alarm/

Hello Barbie knows all your kids’ secrets. Source: https://europe.newsweek.com/privacy-advocates-want-take-wifi-connected-hello-barbie-offline-313432
A smart pacifier means you can put a chip in your baby. Source: https://www.pacif-i.io

Of course it was only a matter of time before someone made a smart menstrual cup… Source: https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/700989404/looncup-the-worlds-first-smart-menstrual-cup

And let’s not forget the smart dildo…
We Connect (the smart dildo makers) were even sued for tracking users’ “habits”. Source: https://www.vocativ.com/358530/smart-dildo-company-sued-for-tracking-users-habits/

Have you ever wondered how many calories you’re burning during intercourse? How many thrusts? Speed of your thrusts? The duration of your sessions? Frequency? How many different positions you use in the period of a week, month or year? You want the iCondom And have you ever wanted to share all that information with advertisers, insurers, your government, and who knows else?

Avoiding it all seems like a lot of work, right? I KNOW! I advocate for privacy…and I don’t have the time or the resources to do all of this all the time.

That’s why it’s unfair to blame the victim for having their privacy eroded.

Not to mention that our concept of privacy is getting twisted by the same people who have an agenda to erode it. One of the biggest culprits in attempting to redefine privacy: Facebook.
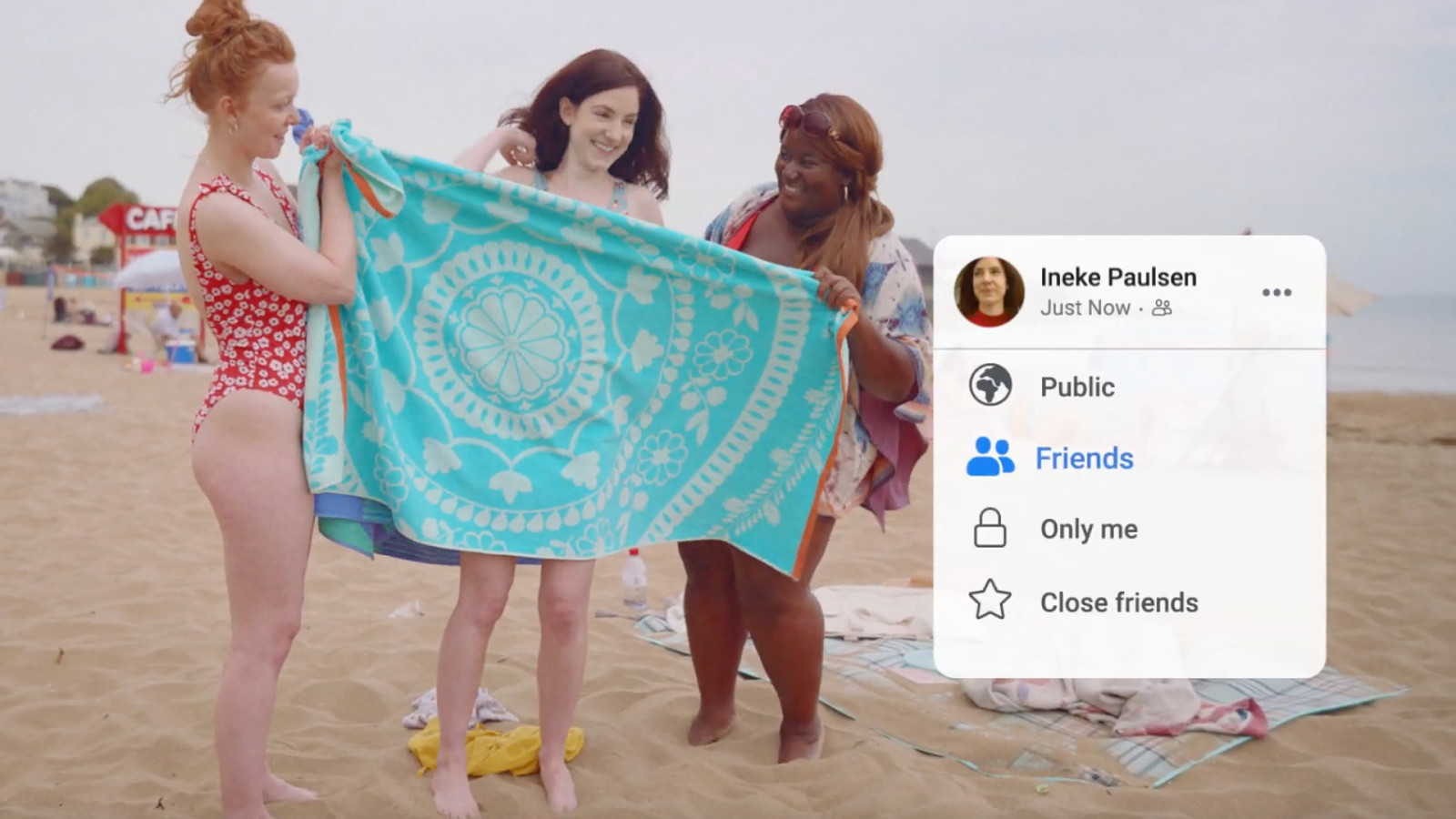
Here is a Facebook ad that’s recently been showing on TVs. It shows a person undressing behind towels held up by her friends on the beach, alongside the Facebook post visibility options, “Public, Friends, Only Me, Close Friends,” explaining how we each have different privacy preferences in life. It ends saying “there’s lots of ways to control your privacy settings on Facebook.”…
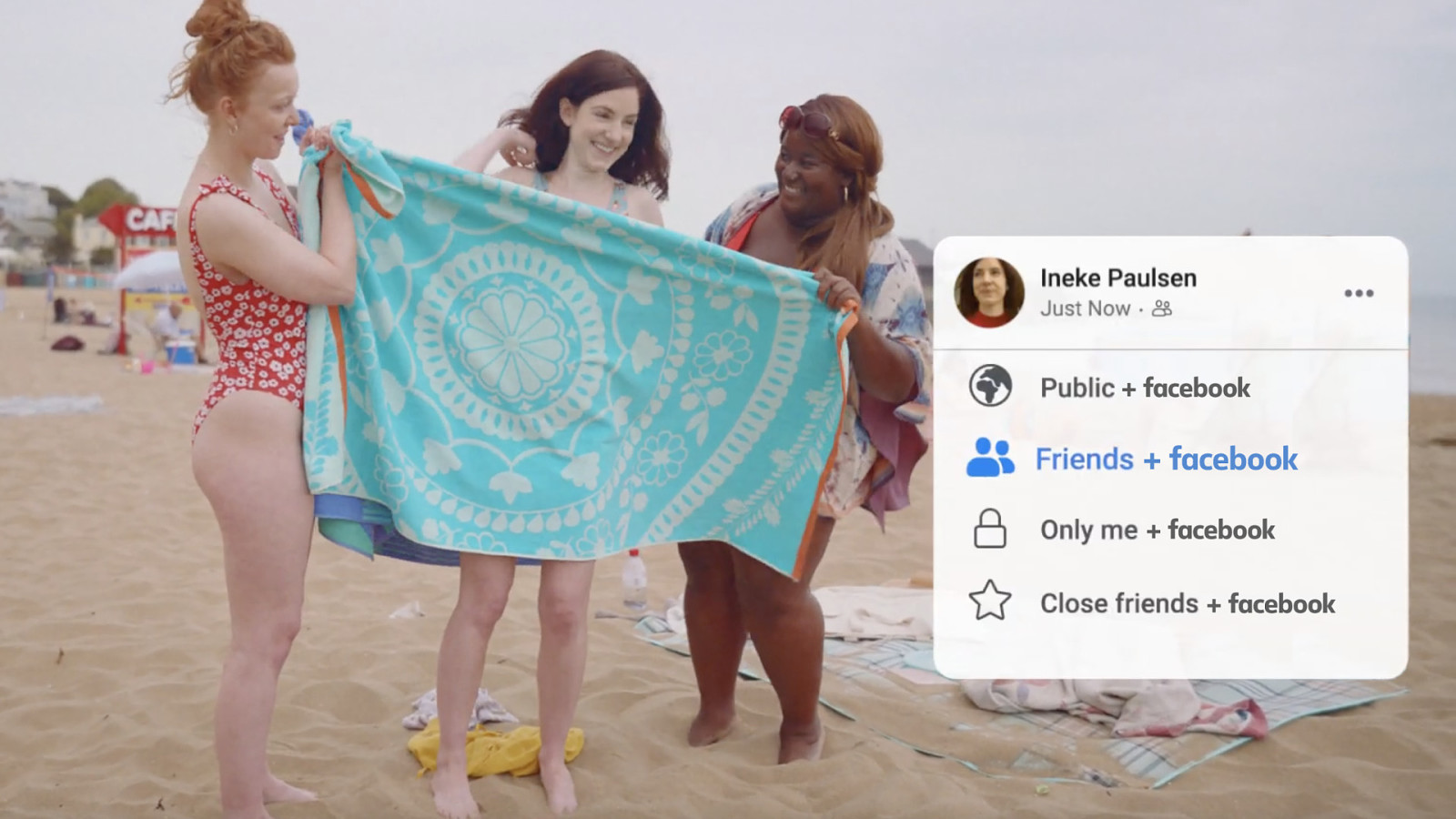
But it doesn’t mention that “Friends”, “Only Me”, and “Close Friends” should really read: “Friends (and Facebook)”, “Only Me (and Facebook)” and “Close Friends (and Facebook)”. Because you’re never really sharing something with “Only Me” on Facebook. Facebook Inc. has access to everything you share.

Privacy is the ability to choose what you want to share with others, and what you want to keep to yourself. Facebook shouldn’t be trying to tell us otherwise.

Google has an interesting interpretation of privacy too. Ten years ago, Eric Schmidt, then CEO of Google (now Executive Chairman of Alphabet, Google’s parent corporation), famously said:
“If you have something that you don’t want anyone to know, maybe you shouldn’t be doing it in the first place.”
A lot of people will say lines like this. But would they feel comfortable sharing their own (uncleared) browser history?
Do we need to be smart about what we share publicly? Sure! Don’t go posting photos of your credit card or your home address. Maybe it’s unwise to share that photo of yourself blackout drunk when you’ve got a job interview next week. Perhaps we should take responsibility if we say something awful to another person online.… But this isn’t about what we knowingly share publicly.

Right now, the corporations are more than happy to blame us for our loss of privacy. They say we agreed to the terms and conditions, we should read the privacy policies, it’s our fault.

This in itself is the subject of a whole documentary that was made way back in 2013, called “Terms And Conditions May Apply” covering the ridiculous length and legalese in terms and conditions, and how we couldn’t possibly read them for every service we use.

More recently, an editorial board op-ed in the New York Times pointed out the flaws in privacy policies for consent:
“The clicks that pass for consent are uninformed, non-negotiated and offered in exchange for services that are often necessary for civic life.”

There are studies that speak to how difficult it is to understand these policies too: “Two law professors analyzed the sign-in terms and conditions of 500 popular US websites, including Google and Facebook, and found that more than 99 percent of them were “unreadable,” far exceeding the level most American adults read at, but are still enforced.” Source: https://www.vice.com/en_us/article/xwbg7j/online-contract-terms-of-service-are-incomprehensible-to-adults-study-finds

It’s not informed consent when you can’t understand the terms. And how can we even truly consent if we don’t know how our information can be used against us?

And it’s not true consent if it’s not a real choice. We’re not asked who should be allowed access to our information, and how much, and how often, and for how long, and when…
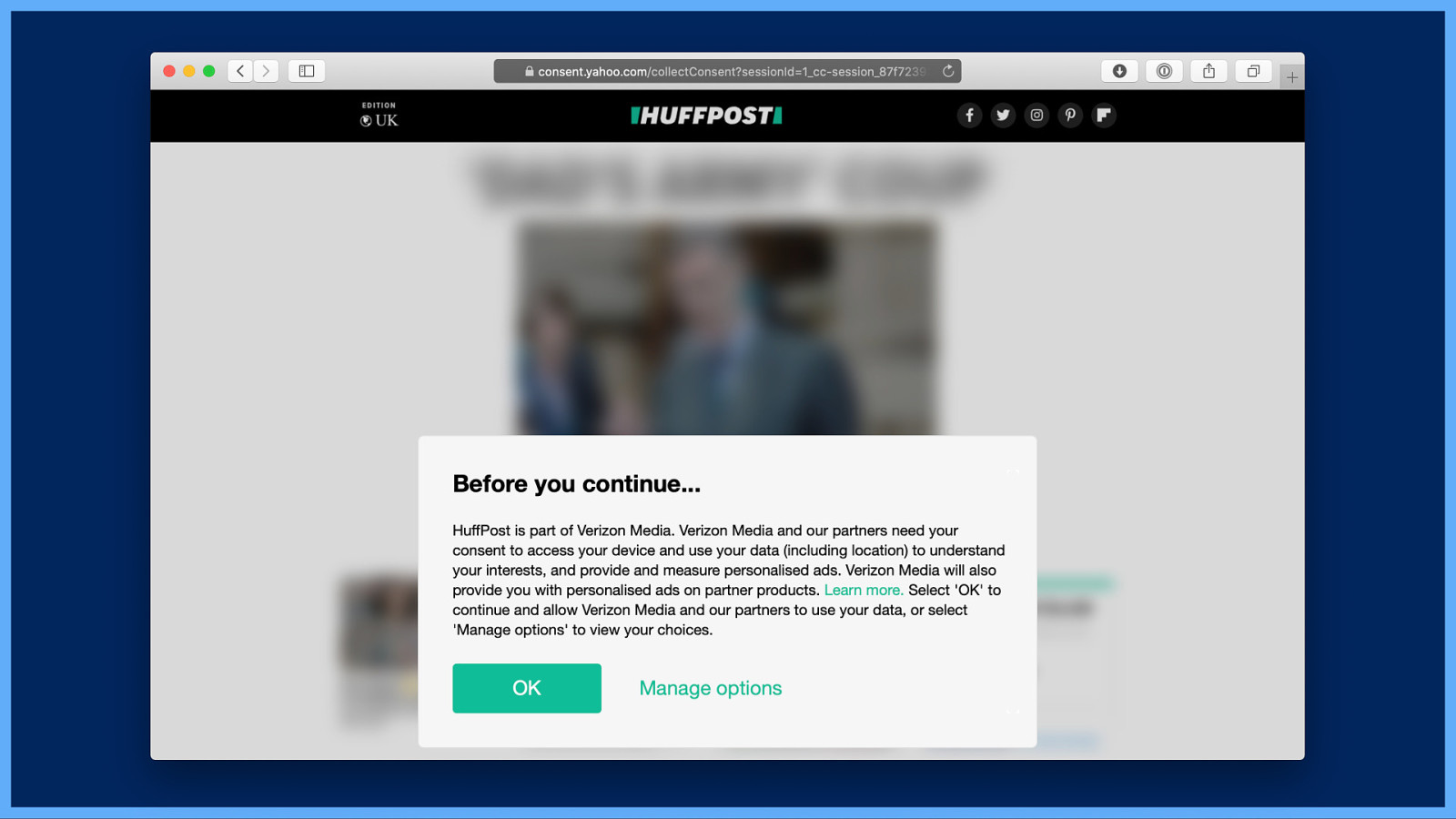
Like this fresh hell from Huffington Post. They’ve got this because the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) requires they ask for consent before tracking you… I go to read a post on their site and I get an option that essentially reads “Before you continue… and OK” because who is going to read that boring paragraph of text in between? I select Manage options, because I want to opt out!
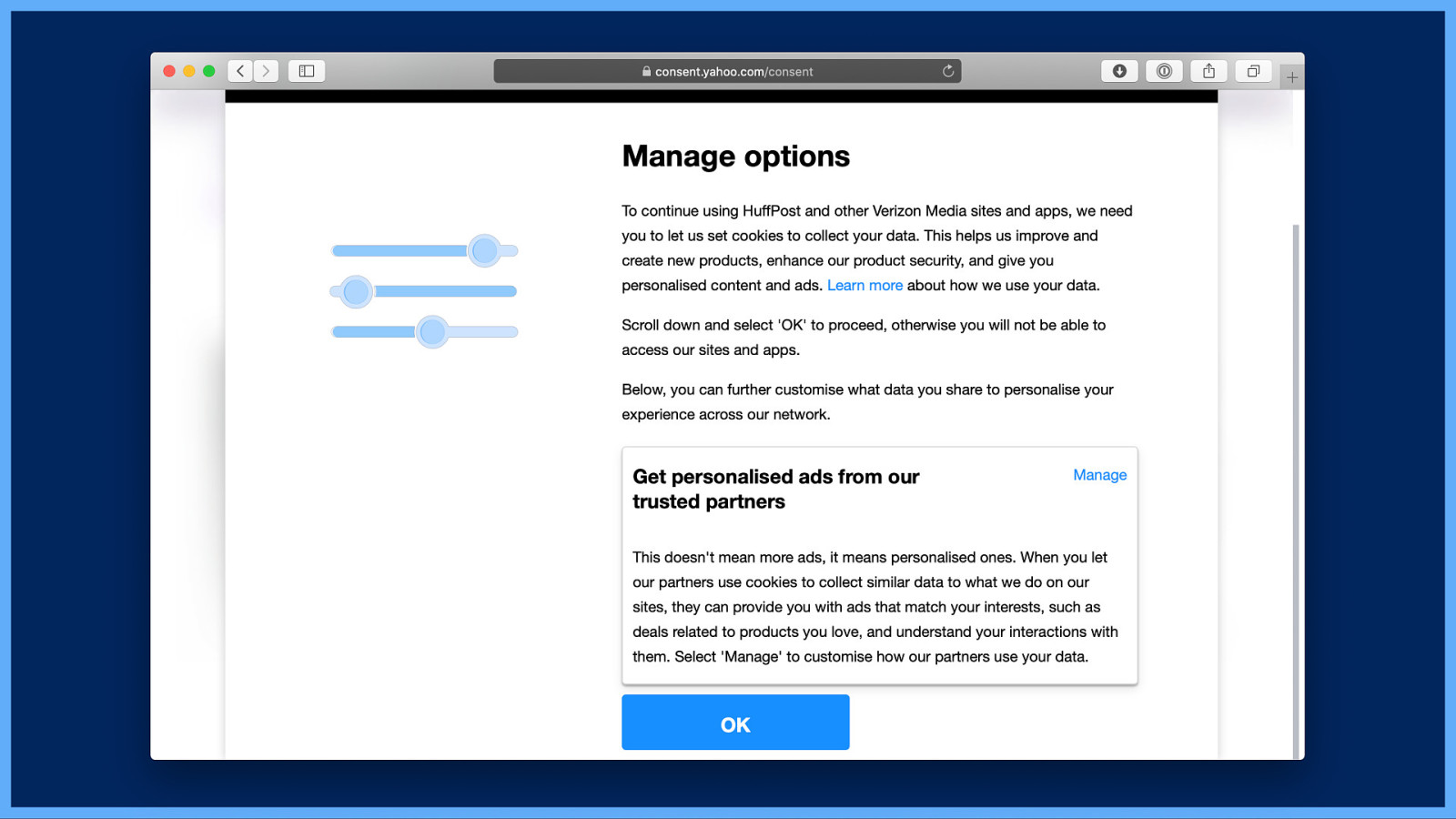
And I’m presented with yet more text saying the same nothing and another OK button. I want to opt out, so I choose “Manage.”
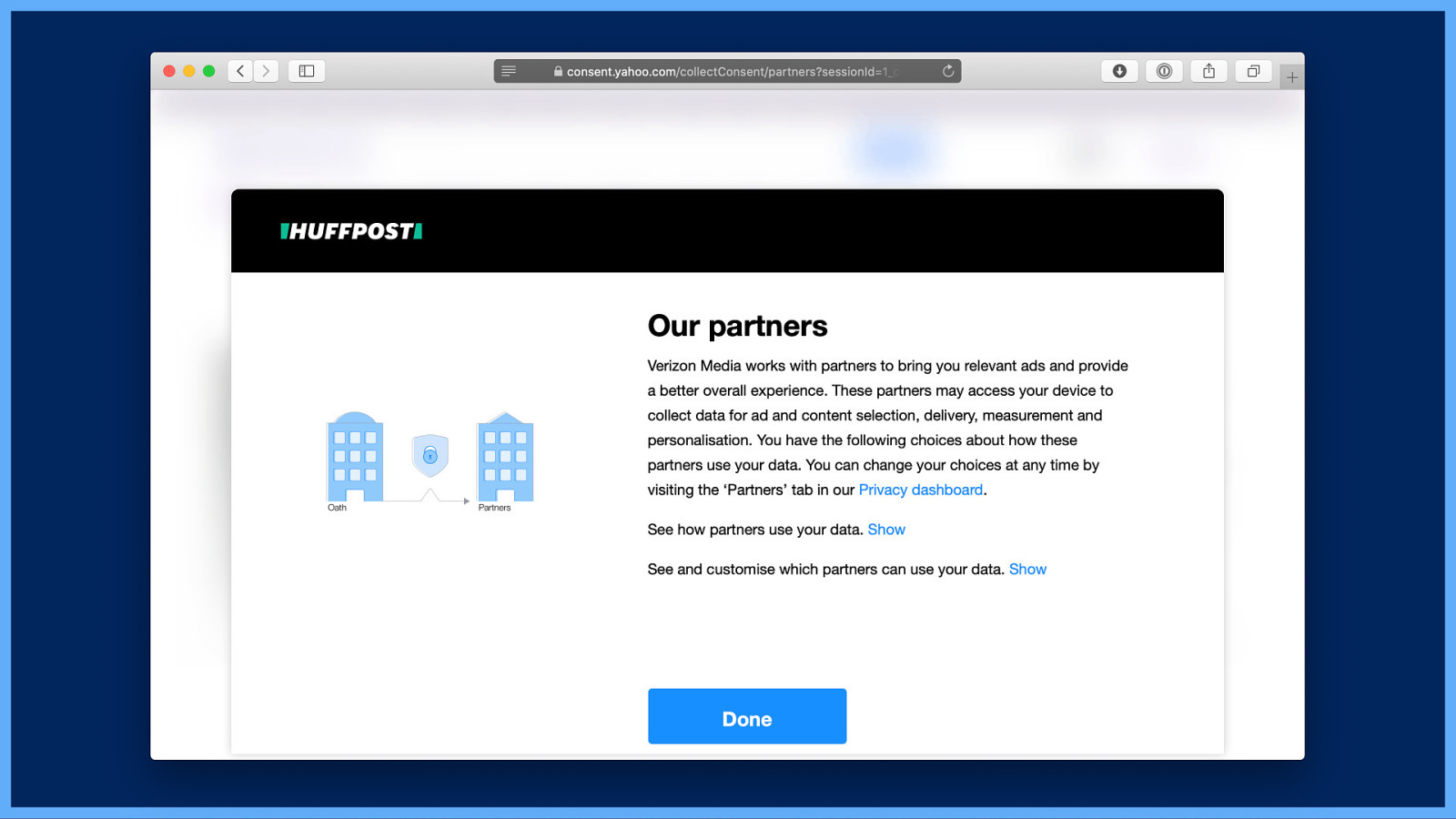
Yet more text saying the same nothing and “Done.” Well, as much as I’m done with it all, I came here to opt out. So I guess I look at the small text that says “See how our partners use your data”. I select “Show…”
Ooh, a box of text saying the same nothing again, but in small white text on blue this time. I have to hover over a tiny blue “i” icon to read it. Still no option to opt out. I select “Hide” to hide that…
What about in “See and customise which partners can use your data”?
Ah nice, a list of every third party service they use and a link to their privacy policy. Many of which have no reference to the third-party use of their services. Delightful.

At no point there was there a choice for me. Nothing that resembles consent. Just lots of text saying the same thing over and over again until I give up and just select OK. (Incidentally, these interfaces have already been ruled not compliant with the GDPR.)

We’re asked to give up everything or get nothing. That’s not a real choice.

The cost of not consenting is to lose access to social, civil and labour infrastructure. It’s certainly not a real choice when the cost of not consenting is to lose access to social, civil, and labour infrastructure.

There’s a recent paper by Jan Fernback and Gwen Shaffer, ‘Cell Phones, Security and Social Capital.’ The paper examines the privacy tradeoffs that disproportionately affect mobile-mostly internet users. What they found shows the cost of not giving consent.

Speaking about this paper, Gwen Schaffer explained
“All individuals are vulnerable to security breaches, identity fraud, system errors, and hacking. But economically disadvantaged individuals who rely exclusively on their mobile phones to access the internet are disproportionately exploited…”

“Some focus group participants reported that, in an effort to maintain data privacy, they modify online activities in ways that harm personal relationships and force them to forego job opportunities.”
Source: https://www.miccenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/CellPhones_1a.pdf

The technology we use are our new everyday things. It forms that vital social, civil, and labour infrastructure. And as (largely) helpless consumers, there’s often not much we can do to protect ourselves without a lot of free time and money.

When the technology you use is a lifeline to access, you are impacted more severely by its unethical factors.
Two years ago, Dr Frances Ryan covered this in her article, ‘The missing link: why disabled people can’t afford to #DeleteFacebook’. After the Cambridge Analytica scandal was uncovered, many people started encouraging each other to #DeleteFacebook. In fact, it’s been happening again the last few weeks.

“I can’t help but wonder if only privileged people can afford to take a position of social media puritanism. For many, particularly people from marginalised groups, social media is a lifeline – a bridge to a new community, a route to employment, a way to tackle isolation.”

Like so many issues we have with technology, what we’re dealing with are the underlying social and systemic issues. As technologists, we often can’t help ourselves trying to fix or smooth over problems with technology. But technology can’t fix issues of domination, oppression or discrimination.

Technology can make those issues worse. We can (and do) amplify and speed up systemic issues with technology.
Mike Ananny recently made the point in an article about tech platforms, that we still seem to operate with the notion that online life is somehow a different life, detached from our everyday existence.

Tech platforms often take advantage of that notion by suggesting that if we don’t like “technology” we can just log out, log off, and be mindful or some other shit instead. People with this mindset often show how shallow they are by saying “if you don’t like the technology, you don’t have to use it…”

But we can’t escape technology:
“Platforms are societies of intertwined people and machines. There is no such thing as “online life” versus “real life.” We give massive ground if we pretend that these companies are simply having an “effect” or “impact” on some separate society.”

Which brings me to another issue rife in technology today. Technology colonialism.

He started with some history:
“Colonial powers always saw themselves as superiors over the native people whose culture was rarely recognized or respected. The colonizers saw economic value in… foreign relations, but it was always viewed as a transaction based on inequality.”

And then comparing it to what we so often do in technology:
“Technology companies continue this same philosophy in how they present their own products. These products are almost always designed by white men for a global audience with little understanding of the diverse interests of end users.”

We have to reckon with our colonial history. This speaks to us politically too, but today I’m talking about our tech industry, our tech community. We have to reckon with the colonial way in which we’ve created technology…

We don’t speak to users. Instead, we use analytics and data to design interfaces for people we’ll never try to speak to, or ask whether they even wanted our tech in the first place. We’ll assume we know best because we are the experts, and they are “just users.” We don’t have diverse teams, we barely even try to involve people with backgrounds different from our own. We fetishise our tools, valuing the designer experience over that of the people using what we build.

We can say we had the right intentions, but that truly means nothing. This has been explored in depth recently by Tatiana Mac, who invokes “intent does not erase impact” to describe our often-haphazard approach to designing technology.
We not only have a responsibility to design more ethical technology, but to consider the impact our design has outside of its immediate interface.

As the people advocating for change, we can’t exactly go around telling people to stop using this technology unless there are real, ethical alternatives.

That’s where you and me come in. As people who work in technology, and who create technology, we have far more power for change. We can encourage more ethical practice. We can build alternatives.

How do we build more rights-respecting technology?

As an antidote to big tech, we need to build small technology.

Everyday tools for everyday people designed to increase human welfare, not corporate profits.
Yeah, sure it’s a lofty goal, but there are practical ways to approach it.

First off, make it easy to use.

Plenty of privacy-respecting tools exist for nerds to protect themselves (I use some of them.) But we mustn’t make protecting ourselves a privilege only available to those who have the knowledge, time and money.

It’s why we must make easy-to-use technology that is


We must ensure people have equal rights and access to the tools we build and the communities who build them, with a particular focus on including people from traditionally marginalised groups. Current privacy-respecting tools (and most of our tools) are particularly terrible at this, not building inclusive technology, and often surrounding themselves with toxic communities.


Our teams must reflect the intended audience of our technology.

If we can’t build teams like this (some of us work in small teams or as individuals), we must ensure people with different needs can take what we make and specialise it for their needs. We can build upon the best practices and shared experiences of others, but we should not be making assumptions about what is suitable for an audience we are not a part of.


We’ve got to stop our infatuation with growth and greed. Focus on building personal technology for everyday people, not spending all our focus, experience, and money on tools for startups and enterprises.


I’m saying it again, to undo Facebook’s attempts at privacy-washing: Privacy is the ability to choose what you want to share with others, and what you want to keep to yourself.

You don’t need to know a person’s gender to provide them with services. You don’t need analytics that segment people into stereotypes based on guesswork.

Allow people to share their information for relevant functionality only with their explicit consent.

When obtaining consent, tell the person how you’ll use their information, when you’ll use it, who will have access to it, and how long you will keep that information stored. (This has recently become established as a requirement under the GDPR—the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation)

Don’t just copy and paste them from other sites (they probably copy-pasted them in the first place!) Ensure the privacy policy is up-to-date with every update to your technology.
Don’t use third-party consent frameworks. Most of these aren’t GDPR-compliant, they’re awful experiences for your visitors, and they may well get you into legal trouble.

Don’t use third-party services at all if you can avoid them. (As they present a risk to you and your users.)

Make it your responsibility to know what they’re doing with your users’ information. If you do use third-party services, make it your responsibility to know their terms and policies, what information they are collecting, and what they are doing with that information.

If you use third-party scripts, content delivery networks, videos, images and fonts, self-host them wherever possible. Ask the providers if it’s unclear whether they provide a self-hosted option.

And it’s probably worth mentioning a little bit of social media etiquette: If you know how, strip the tracking identifiers and Google amp junk from URLs before you share them. Friends don’t let corporations invade their friends’ privacy.

Post to your own site first, then mirror those posts to third-party platforms. If you feel you need a presence social media or blogging platforms, don’t make it the only option. Post to your own site first, then mirror those posts on third-party platforms for the exposure you desire.
Your basic blog is way better than Medium.


Zero-knowledge tech has no knowledge of your information. It may store a person’s information, but the people who make or host the tech cannot access that information if they wanted to.

Keep a person’s information on their device where possible.

If a person’s information needs to be synced to another device, ensure that information is end-to-end encrypted, with only that person having access to decrypt it.

The adage is true, the cloud is just somebody else’s computer.

And we also have to take care with how we share our technology, and how we sustain its existence. Make it share alike.

Cultivate a healthy commons by using licences that allow others to build upon, and contribute back to your work. Don’t let Big Tech use your work if they’re not going to contribute their changes back.

And we also have to take care with how we share our technology, and how we sustain its existence. Make it non-commercial.

My partner at Small Technology Foundation, Aral Balkan, coined the term stayups for the antistartup. We don’t need more tech companies aiming to fail fast or be sold as quickly as possible. We need long-term sustainable technology.

If we are building sustainable technology for everyday people, we need a compatible funding model, not venture capital or equity-based investment.

It may feel difficult or even impossible to build small technology with your current employer or organisation. It probably is! But there are steps we can take to give ourselves the opportunity to build more ethical technology.

Use small technology as a criteria when you’re looking for your next job. You don’t have to be at your current job forever.

Seek alternatives to the software you use every day.
switching.software has a great list of resources, provided by people who really care about ethical technology as well as ease-of-use.

If you can’t do it at work, do it at home. If you have the time, make a personal website, practice small technology on your own projects.
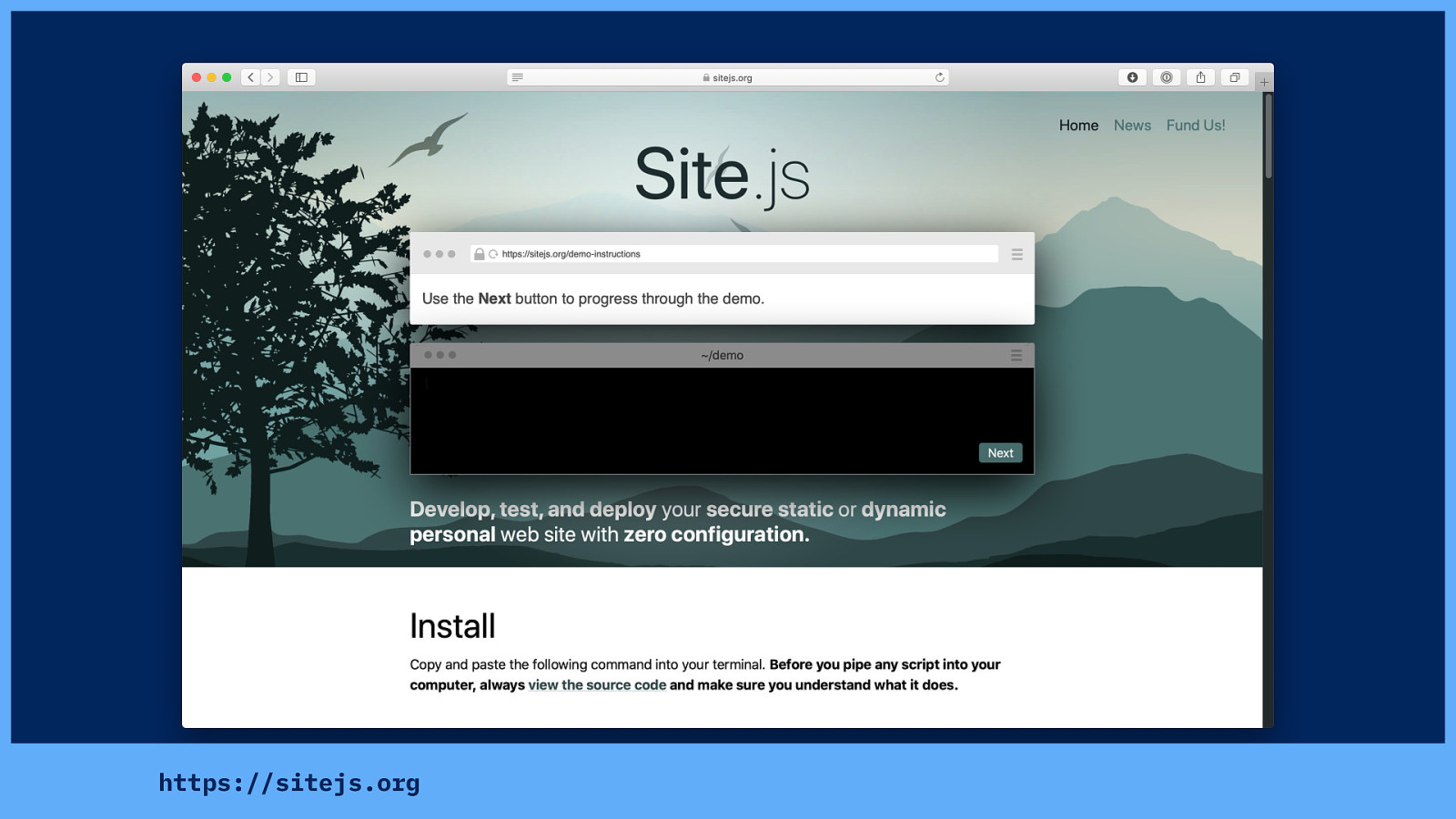
We’re trying to build tools to help people do this (without compromising their site’s visitors.) This is Site.js, and we’re building it so you can build a secure personal website without all that configuration, without relying on a third party service who might start tracking all your visitors without your consent, or pivot to a dodgy business model. (It’s free and open small technology!)

It even runs on Raspberry Pi. If you like the idea of holding a portable server in your hand, running off 4G.
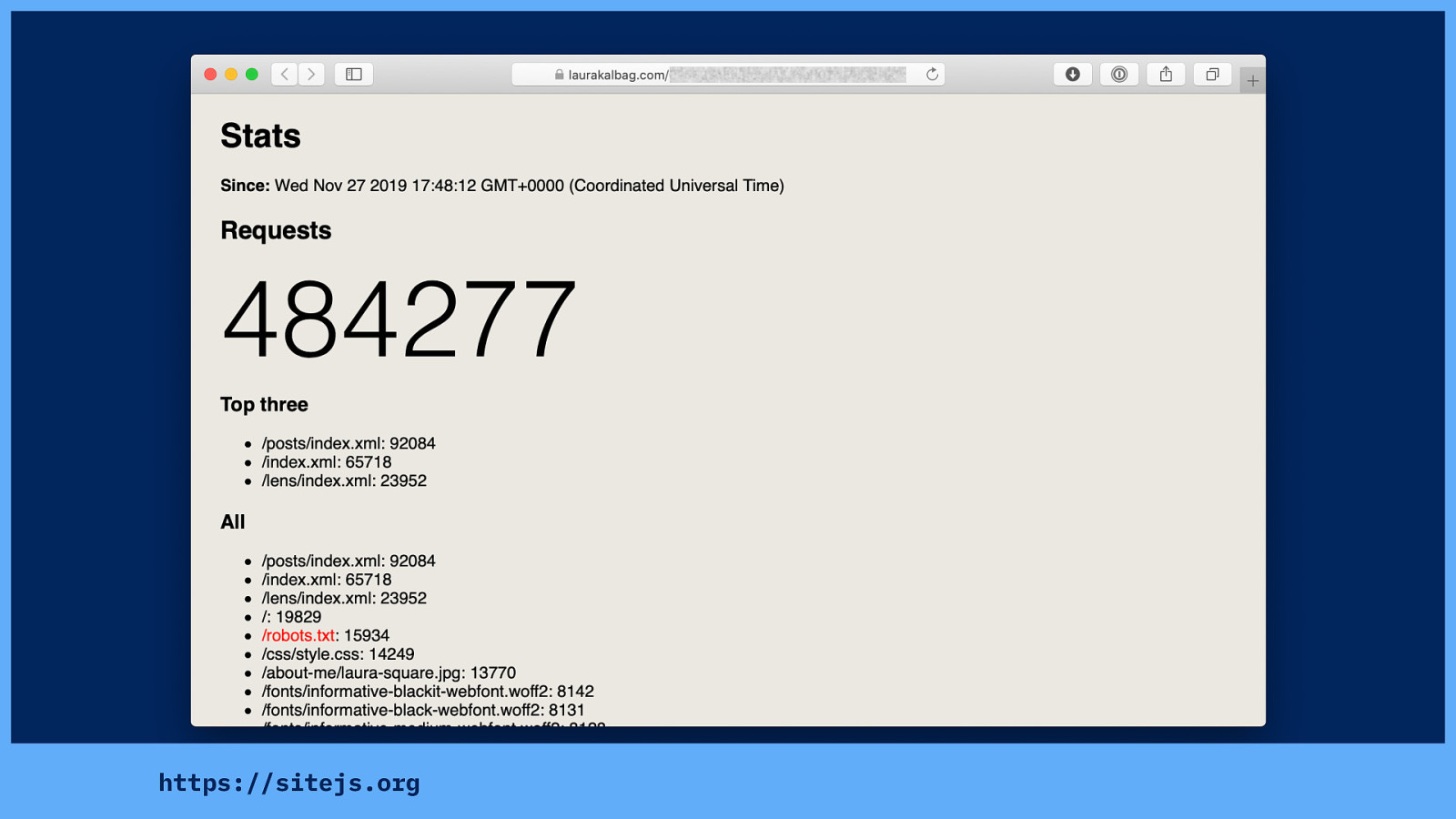
Of course there’s no tracking. It has ephemeral server statistics to see which pages are popular (and what’s being hit but isn’t there - 404s) but does not track the site’s visitors.
It’s a tiny tool in a world of choice, but it is an alternative.

I’ve been speaking about tracking and privacy for around seven years. (Luckily it’s becoming more mainstream these days!) I’ve been heckled by a loyal Google employee, I’ve been called a tinfoil-hat-wearing ranter by a Facebook employee. I’ve had people tell me there just isn’t any other way, that I’m just trying to impede the “natural progress” of technology…

As Rose Eveleth wrote in a recent article on Vox: “The assertion that technology companies can’t possibly be shaped or restrained with the public’s interest in mind is to argue that they are fundamentally different from any other industry. They’re not.”

We can’t keep making poor excuses for bad practices.

We must divest ourselves of unethical organisations. Consider who we are financially supporting or implicitly endorsing when we recommend their work and their products.

And, I’m sorry, I don’t give a fuck about all the cool shit coming out of exploitative companies. You are not examples to be held above others. Your work is hurting our world, not contributing to it.

Our whole approach matters. Our whole approach matters. It’s not just about our philosophy, or how we build technology, but our approach to being a part of communities that create technology.

You might be thinking “but I’m just one person.”

But we are an industry, we are communities, we are organisations, we are groups made up of many persons. And if we work together on this, we could have a huge impact.

We have to remember that we are more than just the organisation we work for. If you work for a big corporation that does exploitative things, you probably didn’t make the decision to do that bad thing. But I think the time has come that we can no longer unquestioningly defend our employers or clients.

We need to use our social capital (also known as privilege!), we need to be the change we want to exist.

There are different roles we can take in making change happen. Roles that fit us differently depending on our privilege and our position within an organisation…

We’ve got to be comfortable being different, we can’t just follow other people’s leads when those other people aren’t being good leaders. Don’t look to heroes who can let you down, don’t be loyal to big corporations who don’t care anything for you.

Do the research on inclusive, ethical technology, make recommendations to others. Make it harder for them to make excuses.

Marginalised folks shouldn’t have to risk themselves to make change. Advocate for others. The overrepresented should advocate for the underrepresented.

Question those defaults. Ask why was it been chosen to be built that way in the first place? Try asking a start-up how it makes its money!

When the advocacy isn’t getting you far enough, use your expertise to prevent exploitative things from happening on your watch.

Be the person who is known for always bringing up the issue. Embrace the awkwardness that comes with your power. Call out questionable behaviour.

Don’t let anybody tell you that standing up for the needs of yourself, and others, is unprofessional. Don’t let people tell you to be quiet. Or that you’ll get things done if you’re a bit nicer.

If you are not comfortable speaking up for yourself, at least be there for those that do. Remember silence is complicity.

It can be really fucking lonely. We’re often fighting entities far bigger than ourselves. Our lives, our ability to make a living is at risk.

But letting technology continue this way is riskier. Like society and democracy riskier.

People say the talks I give are scary, but I’m not here to scare you. I’m just here because I want to tell you that we deserve better.

Slides are at https://noti.st/laurakalbag
Laura Kalbag, laurakalbag.com@LauraKalbag Small Technology Foundation small-tech.org