To push, or not to push?! A journey of resource loading in the browser JSConf EU, June 2018 Patrick Hamann @patrickhamann
A presentation at JSConf EU 2018 in June 2018 in Berlin, Germany by Patrick Hamann

To push, or not to push?! A journey of resource loading in the browser JSConf EU, June 2018 Patrick Hamann @patrickhamann

I’m a software engineer at the Edge Cloud provider Fastly. We specialise in real-time content delivery for some the worlds largest brands.
Where I get a lot of time to think and research how to make our customers websites faster. Which is what I’m here to discuss today :)

So why am I here to talk to you today? You’re probably wondering what the title “To push, or not to push” even means?

“HTTP/2 will solve this” – Everybody
If like me, you’ve probably heard a lot of people say something along the lines of “HTTP/2 will solve this”. Myself included.

However, sadly it’s not as simple as that. Resource loading in the browser is hard.
Hopefully after this talk you’ll have a better understanding of why and what techniques we can use today and in the future to solve this.

Why is it hard?

So how can we load our resources most efficiently today? What best practice patterns and techniques should I be using to load my resources?

First we must determine what our critical resources are that we need to prioritise. Lets do a thought exercise with this page. What do we think are the critical resources required for a fast user experience?

When we talk about resource loading, we commonly discuss the critical path and critical requests.
"A critical request is one that contains an asset that is essential to the content within the users viewport." – Ben Schwarz, Calibre

What are my critical resources?
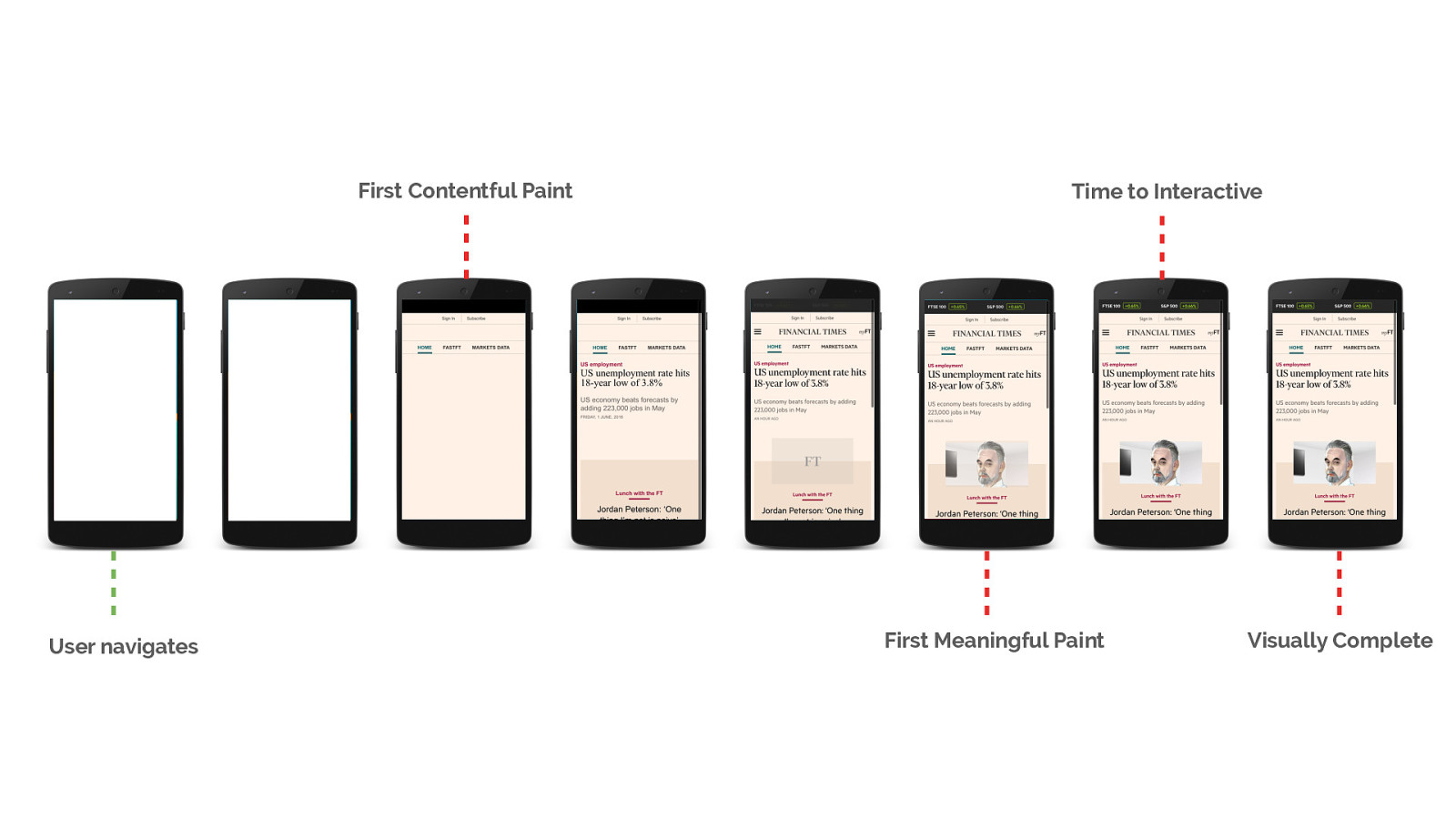
Once you’ve identified the requests, determine whether they contribute to the user experience of your initial load. Is it critical content? Is it needed for interactivity?
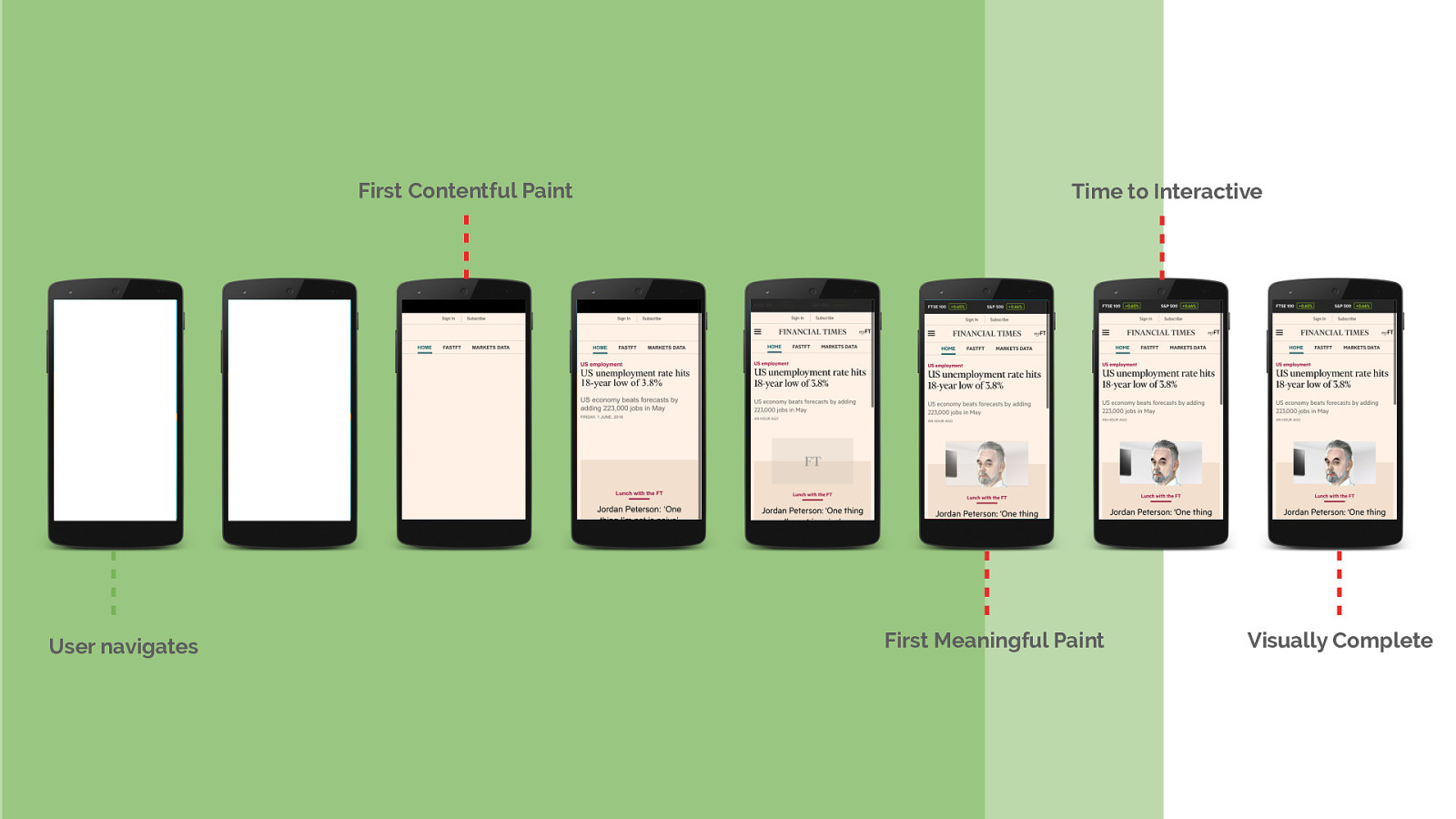
It’s this portion of the page lifetime that we’re going to focus on today. How we can help the browser discover all of our critical resources up front and ensure we send the data for them as soon as possible.

We can summaries a good loading strategy as one that optimises for a good user experience. I.e. one that:

Now we’ve identified what we should be loading, lets dive into how we can do this efficiently.
The first technique we’ll look at is the Preload API. What if we could tell the browser ahead of time what are critical resources are?
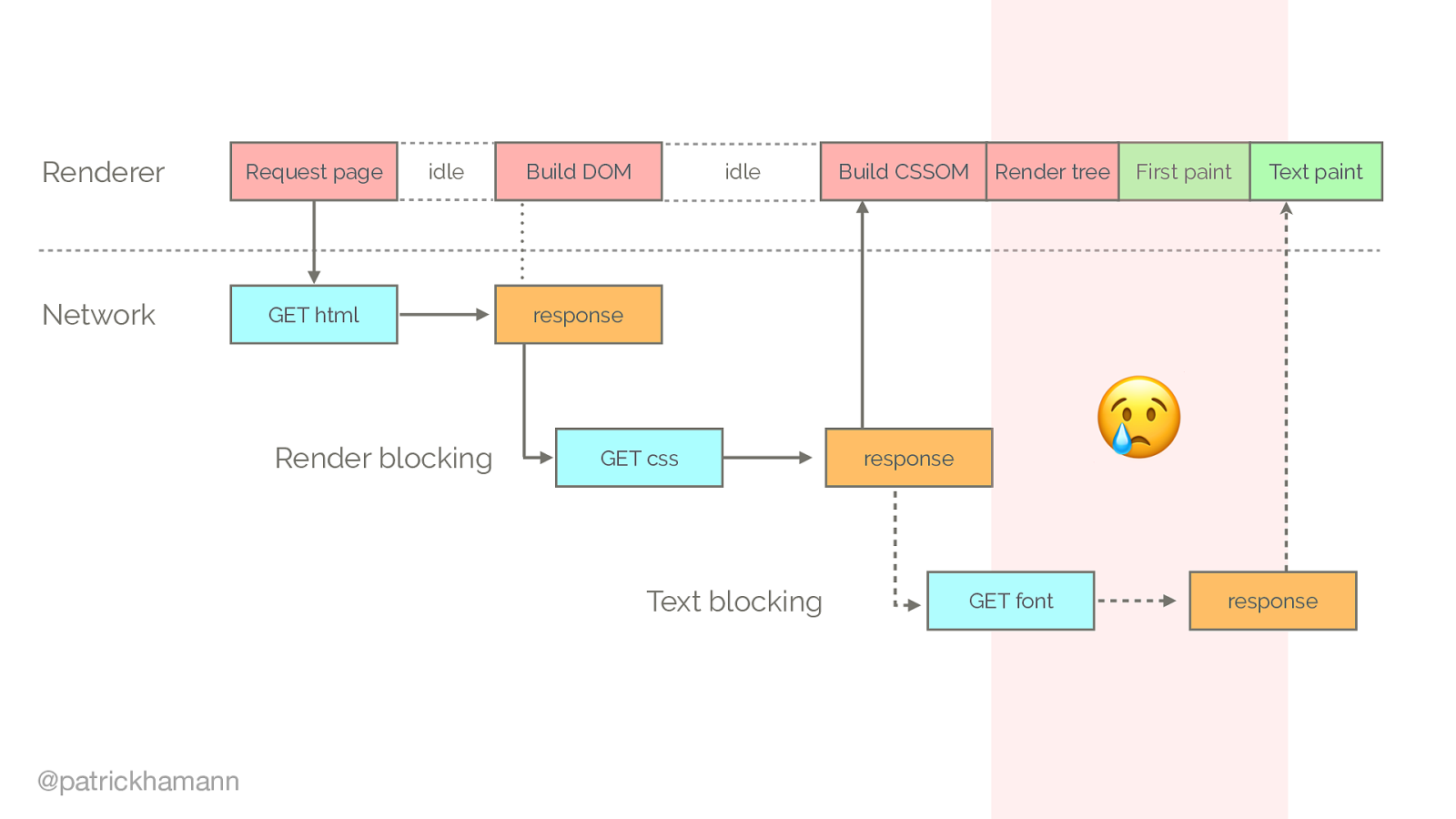
We identified that fonts are critical resources. However they’re requested late in load. Why is this?

This is where the preload api comes in. It:
"Provides a declarative fetch primitive that initiates an early fetch and separates fetching from resource execution."
I.e. it allows the browser to perform the networking without yet discovering the resource during parsing.
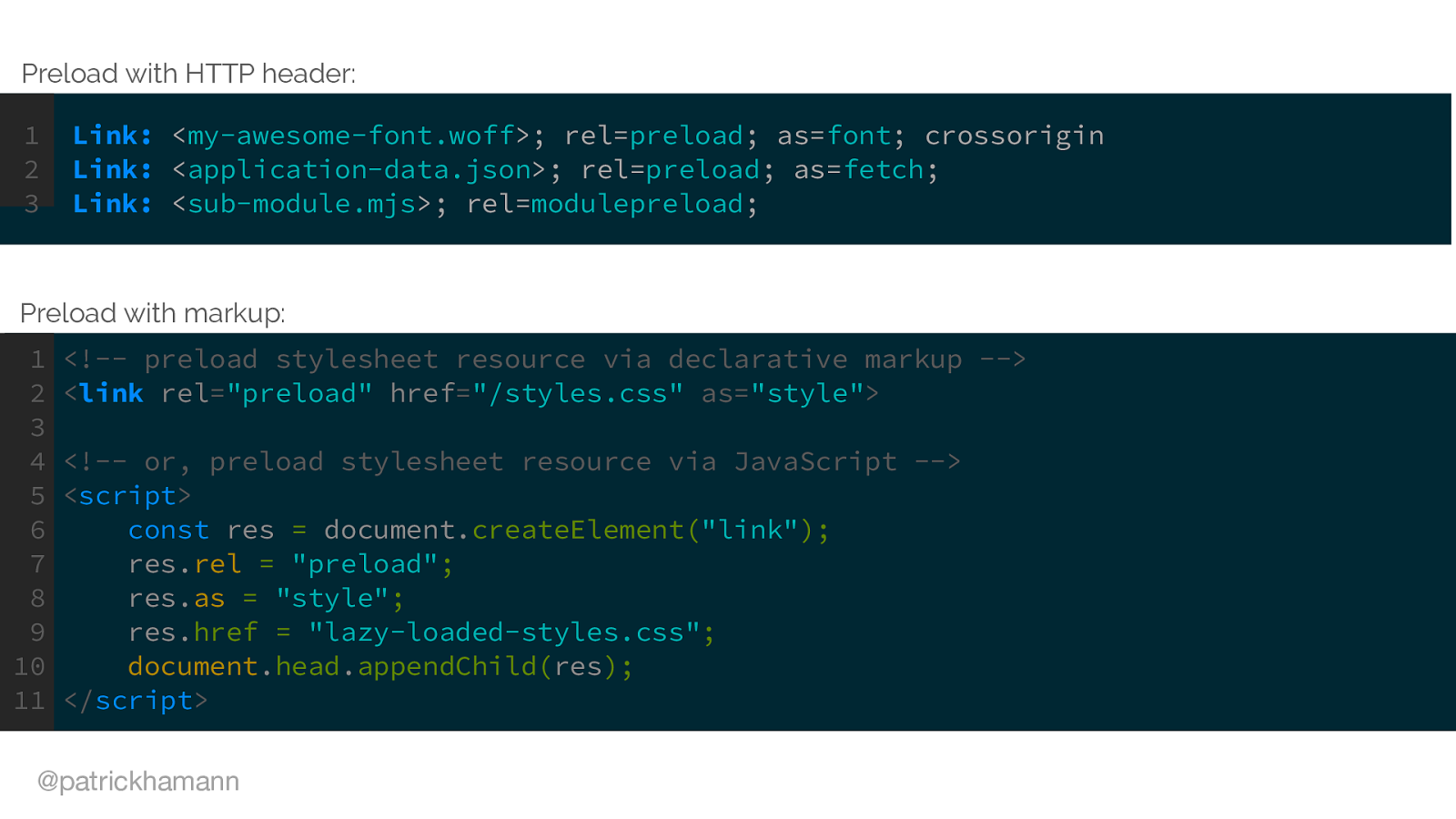
So this is what it looks like, we now have three new primitives in HTML, JS and HTTP.
My preferred method is via the HTTP Link header.
Preload JSON as fetch!
Modulepreload!
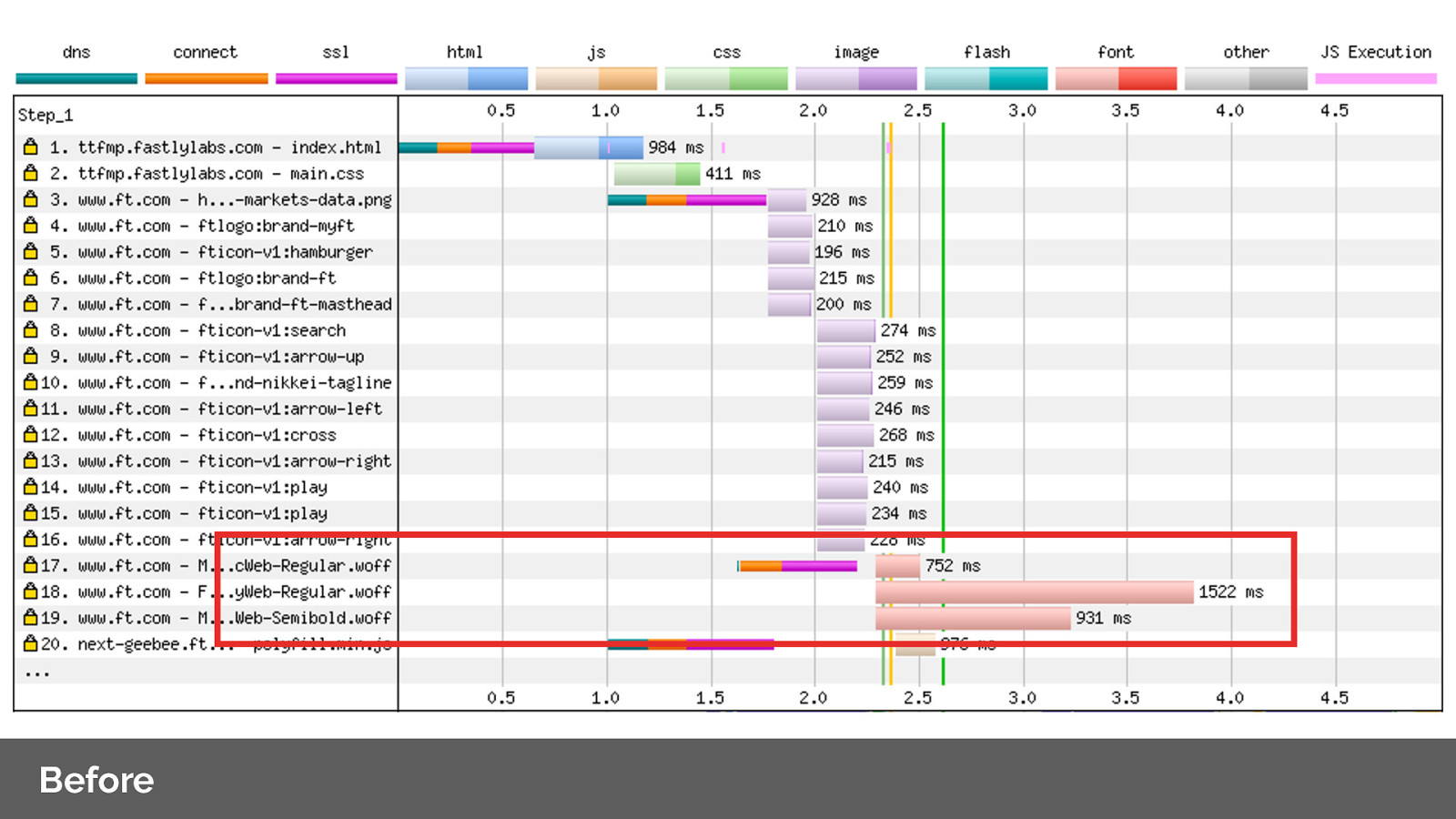
Before: Lets’s look at the network waterfall for FT.com
Note how low down the font requests are, even though they’re critical resources?
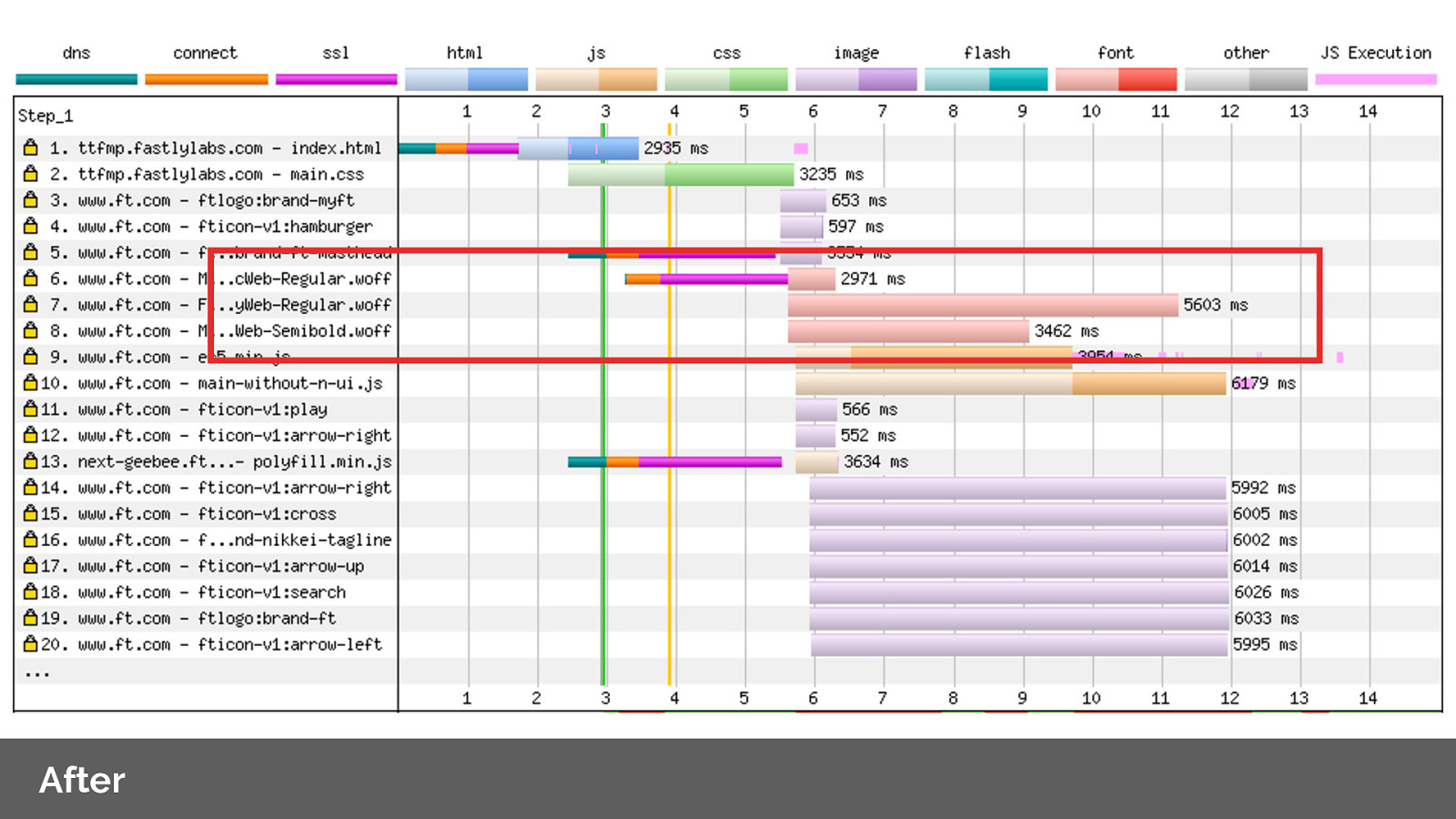
After: By applying preload headers we’re able to prioritise and initiate the fetches early for the fonts. Note the change in order of network priority for our resources.

Fastly customer Shopify switches to preloading fonts and saw a 50% improvement to time-to-text-paint. 1.2 seconds improvement of a 3G connection.
I’ve been in the perf industry a long time and have never seen a single technique give the ability to do this.

Are indicating resource hints via the HTML response too late? This is great! However, is decorating the resources priority hints via the HTML response too late?

This is what HTTP/2 server push WAS designed to solve. Let’s take a look at how it can help us.
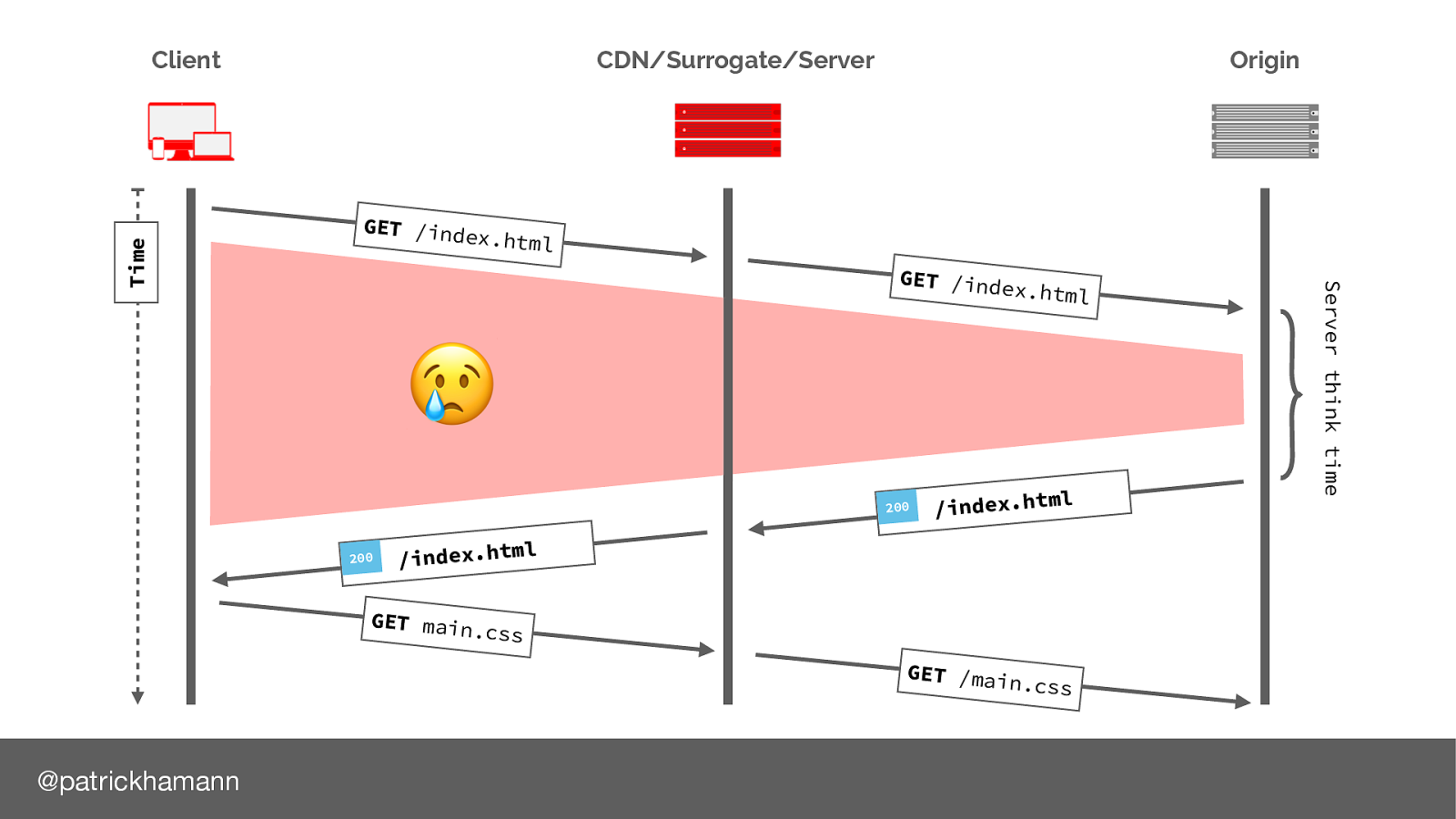
Lets look at the traditional request flow of loading a website.
Browser parses HTML finds CSS reference and makes request for it
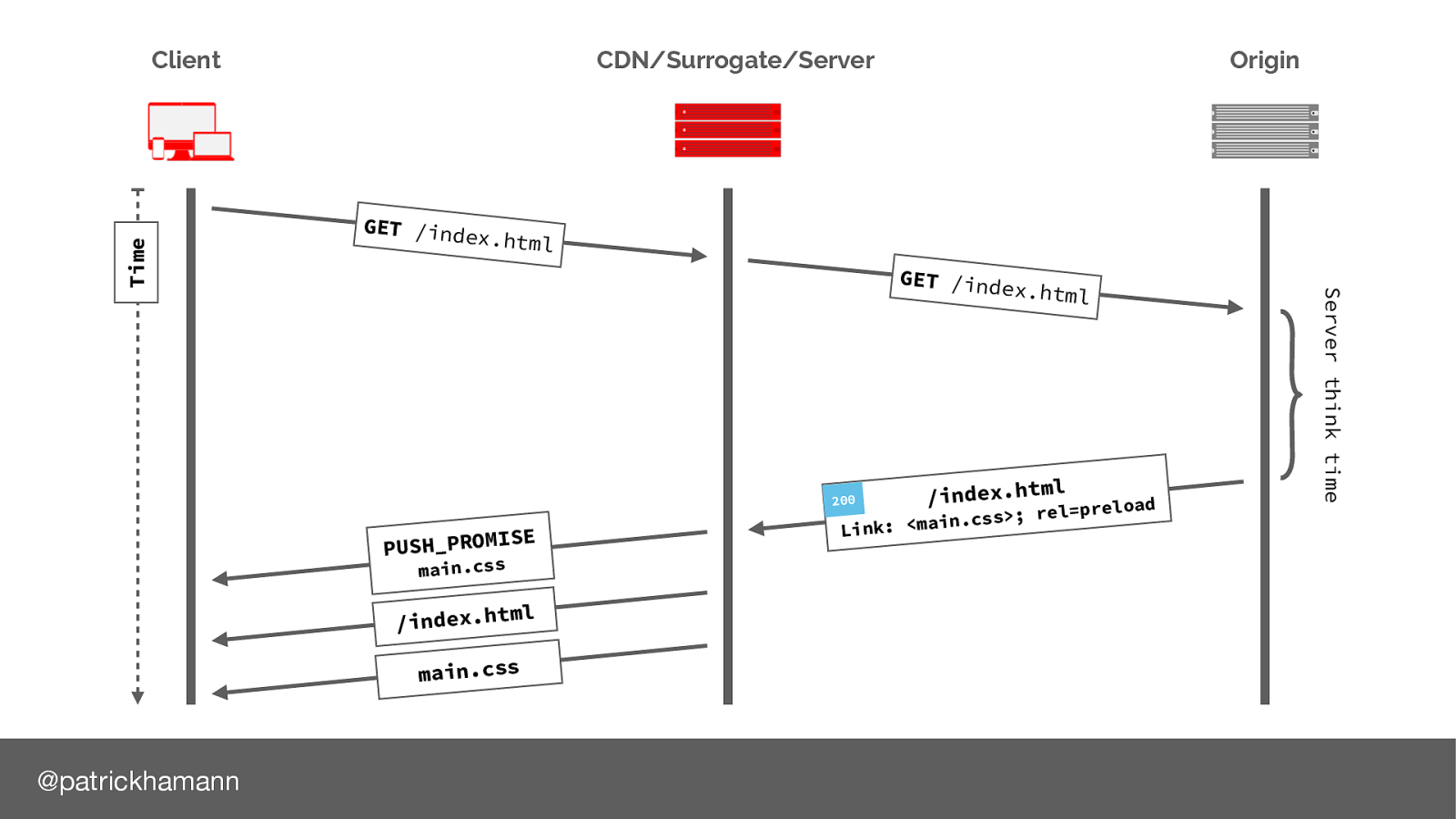
What if the server could predict that the next resource the client will request is the main.css file and push/flush the bytes down the connection whilst the server is constructing the HTML response. HTTP/2 calls this a push promise, a data frame that signals to the client we will send you the bytes for this file so no need to request it.

So the question is should we be using server push at all?

So how can you programmatically indicate a resource to be pushed
The most common mechanism the industry has converged on is via the Link header and our preload friend. You must have a HTTP/2 enabled server with push support. Not that we don’t have the no push directive.

Comparing before and after, we’ve effectively reduced our page load by 1 round trip. Average ~800ms on a 3G connection. This is great if our RTT time has high latency, I.e. on mobile connections in developing countries.
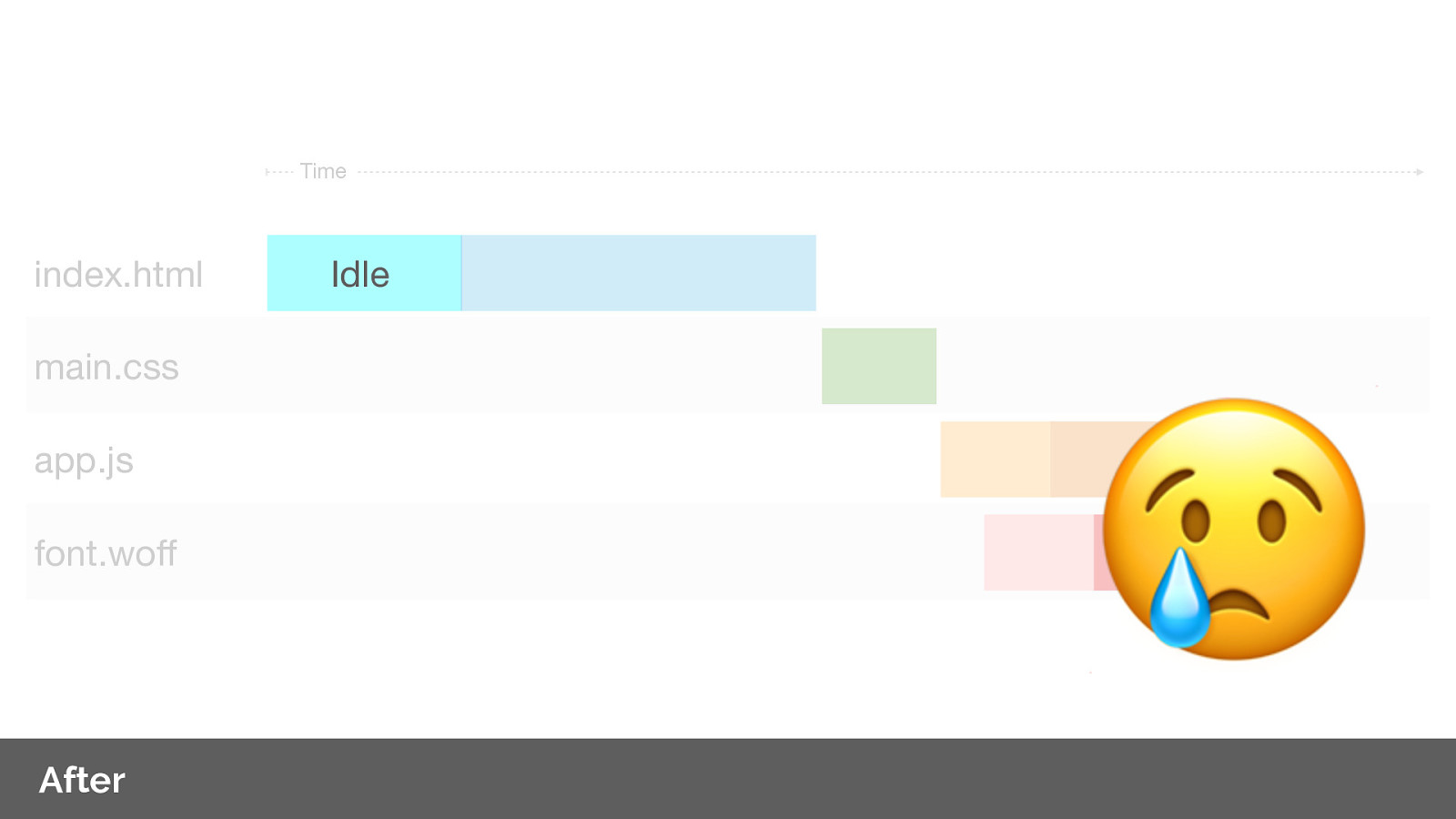
Note that we have still idle time whilst we wait for the server to respond with the HTML.
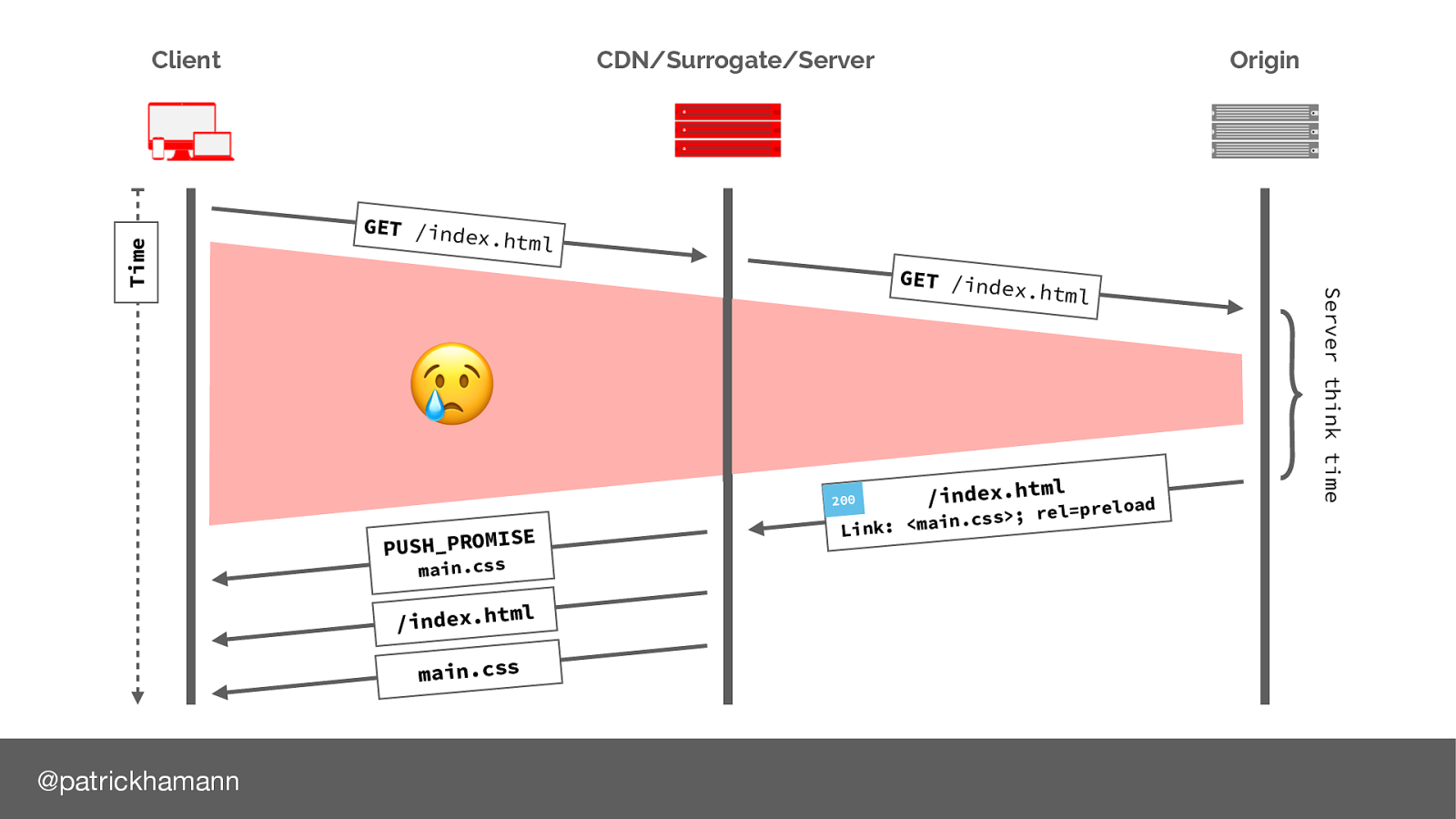
Why is this? Let’s look at the request flow again. As server push is indicated via a Link header on the response of our document we have to wait for the server to generate the response before we can push. This leaves a lot of wasted time on the connection, especially if we are using a CDN or proxy service.
THIS MAKES ME SAD!
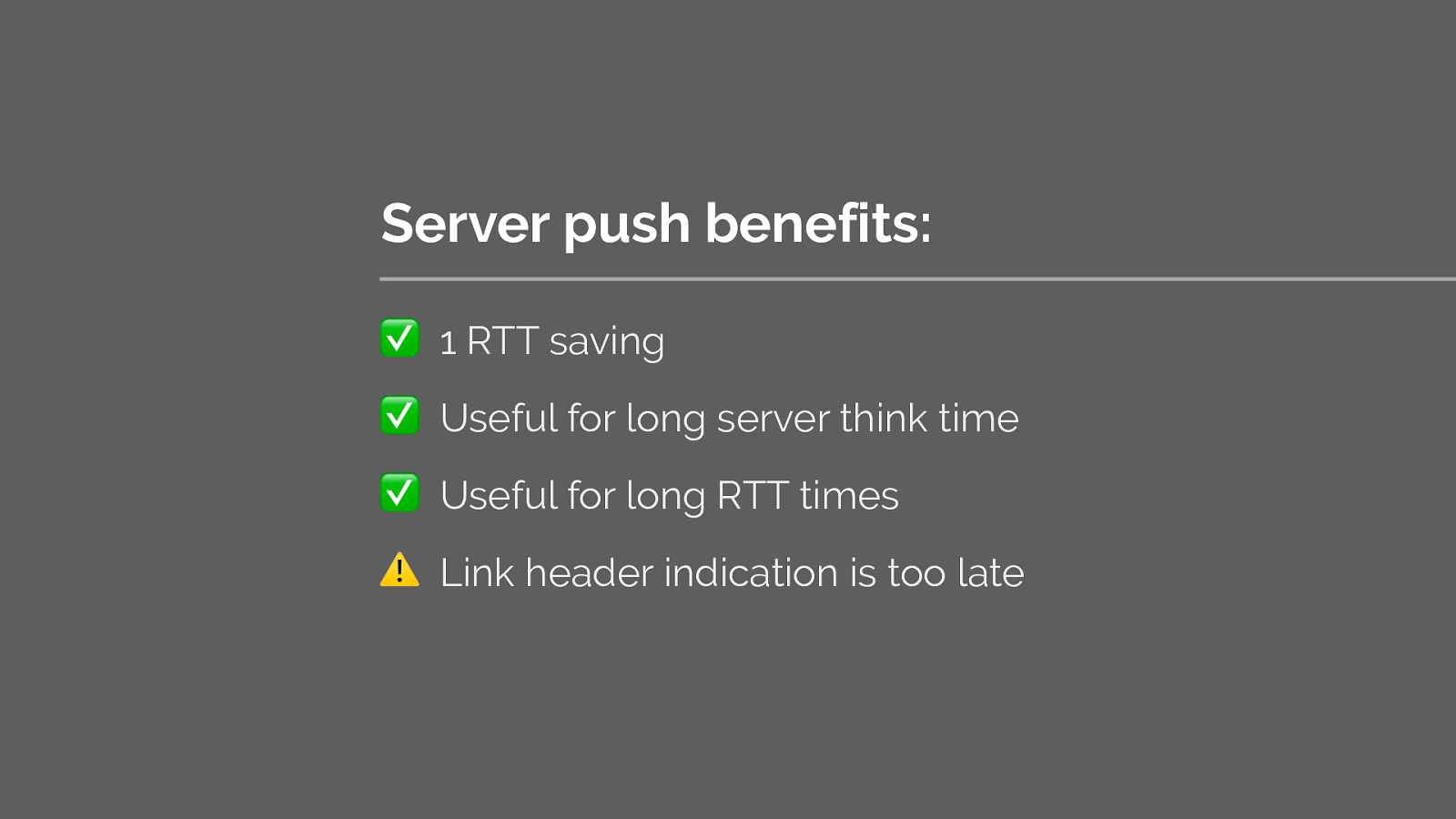
To recap server push gives us these benefits.

So the question is should we be using server push at all?
Is using Link rel=preload as the push indicator in-fact too late in the connection state?

How can we achieve the holy grail and push our critical resources during this period.
Do do this we need to decouple the push behaviour from the HTML response. This is what at Fastly we’re calling async push.
A more common architecture will be for the HTTP server to be decoupled from the application server. Think a reverse proxy etc? nginx/apache/varnish
This allows us to decouple the push logic from the application and initiate a push of the resource as soon as receive a request for the HTML even before we despatch the request to the application server. Achieving our holy grail of pushing during idle think time on the connection.
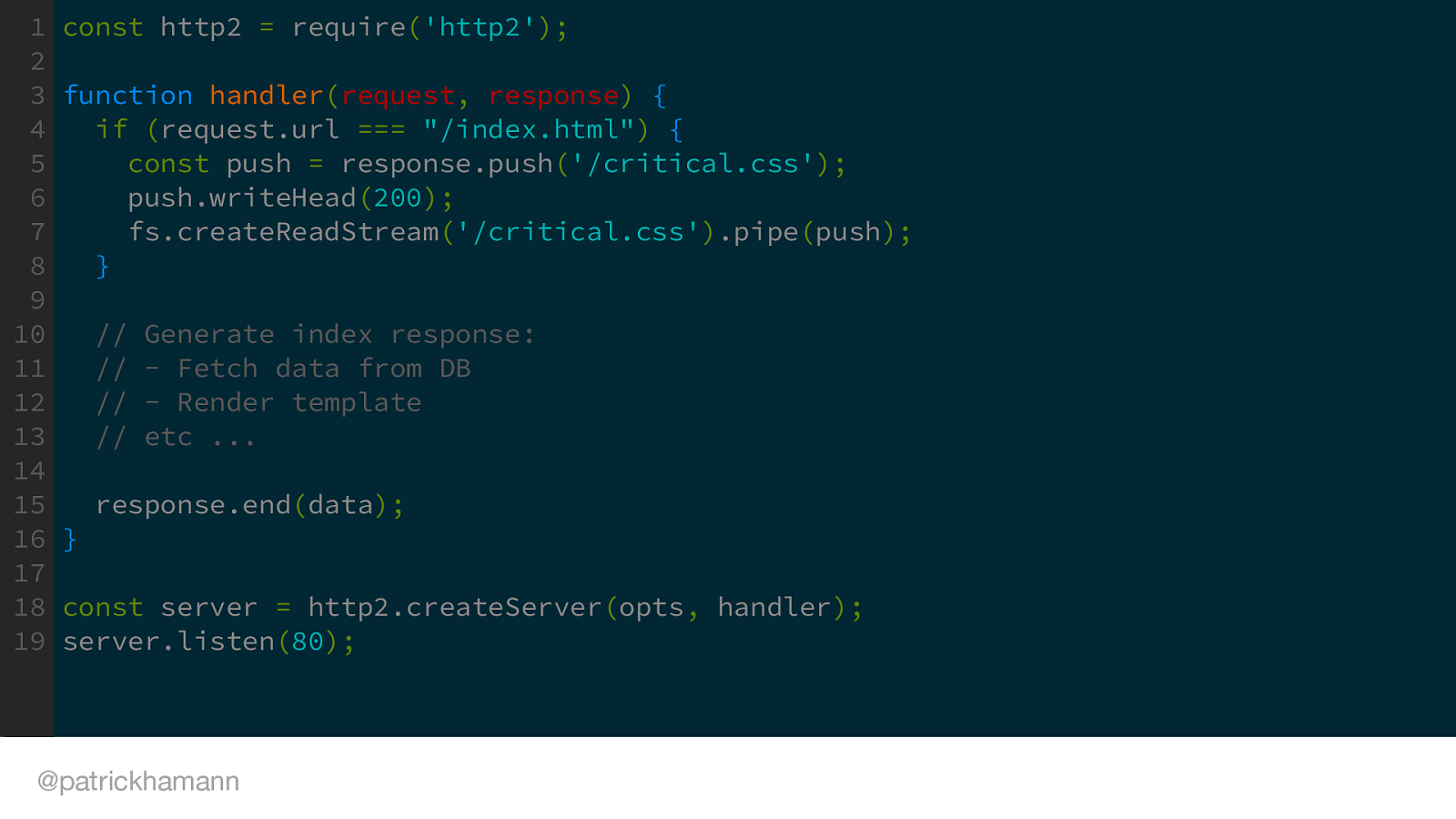
If we have programatic access to the open network connection within our application server we can flush the CSS push before we generate the HTML. Here is an example using Node’s http/2 server to flush the push at the beginning of a request middleware.
Note the first thing we do in the response handler is to push the CSS.
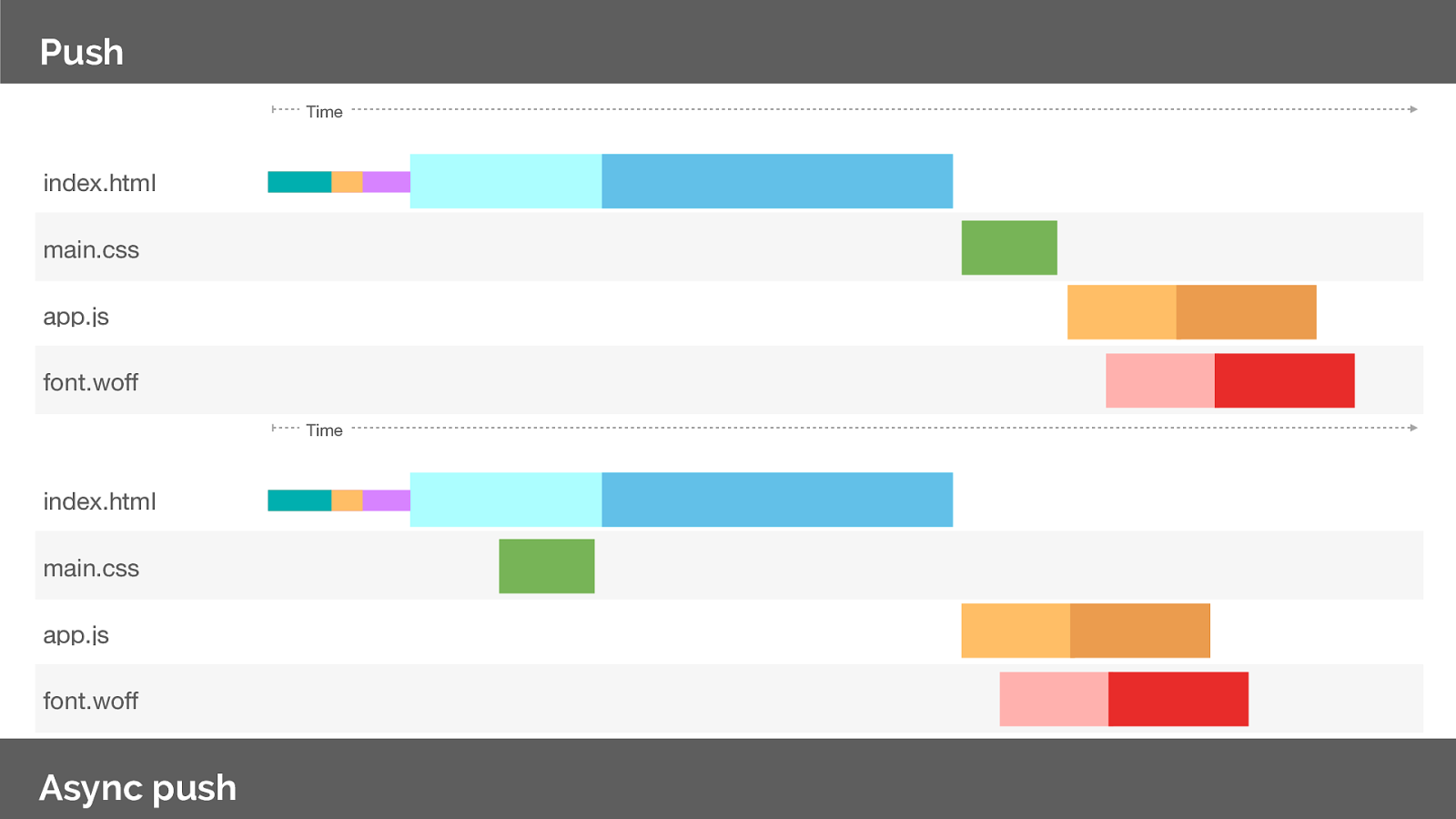
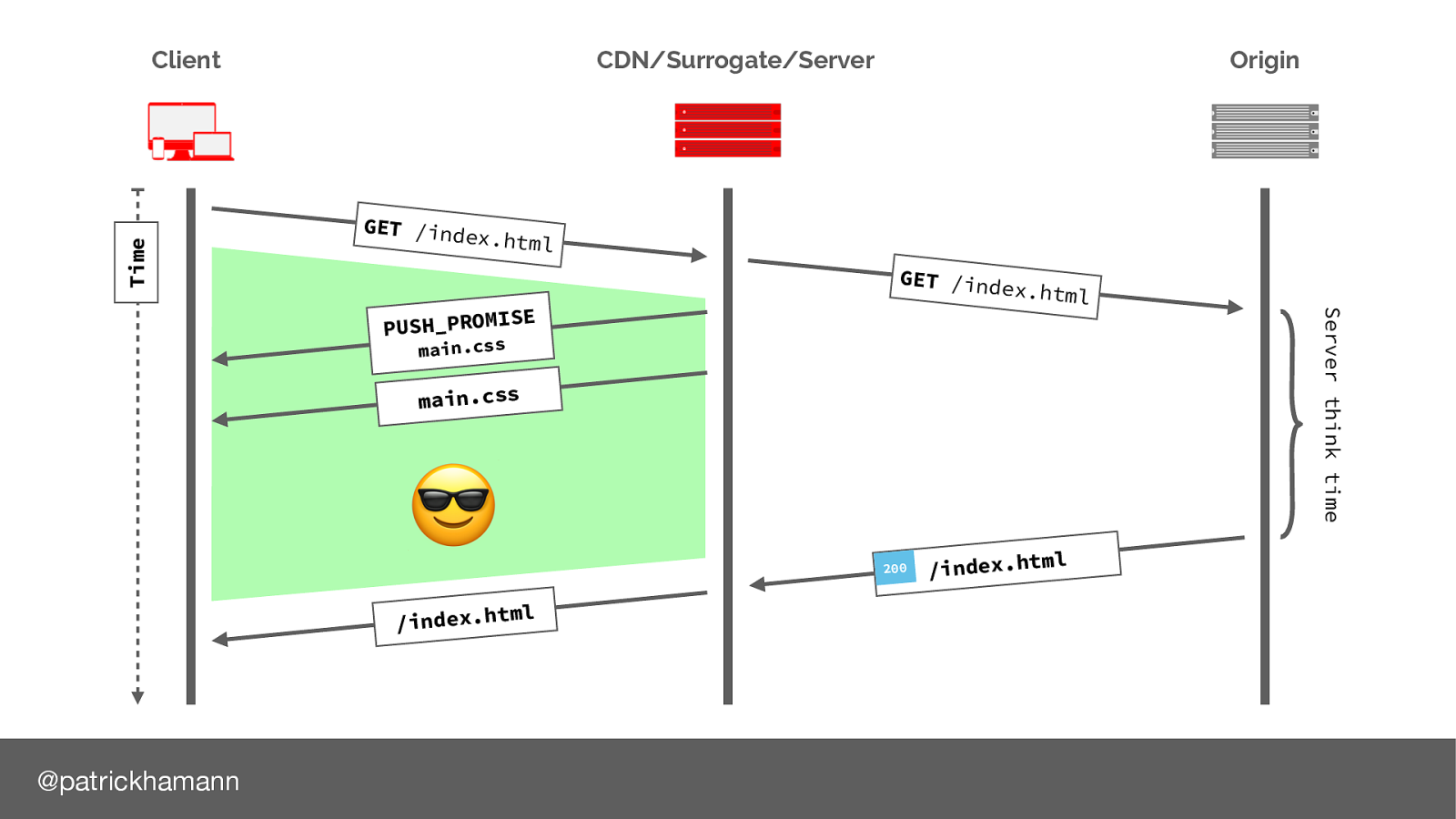
So lets look at he network utilisation from our previous push example. Note that we have still idle time whilst we wait for the server to respond with the HTML.
So instead of using a Link header on the html response, lets use async push to decouple the initialisation. Note that are now utilising the idle connection time whilst we wait for the server to respond with the HTML
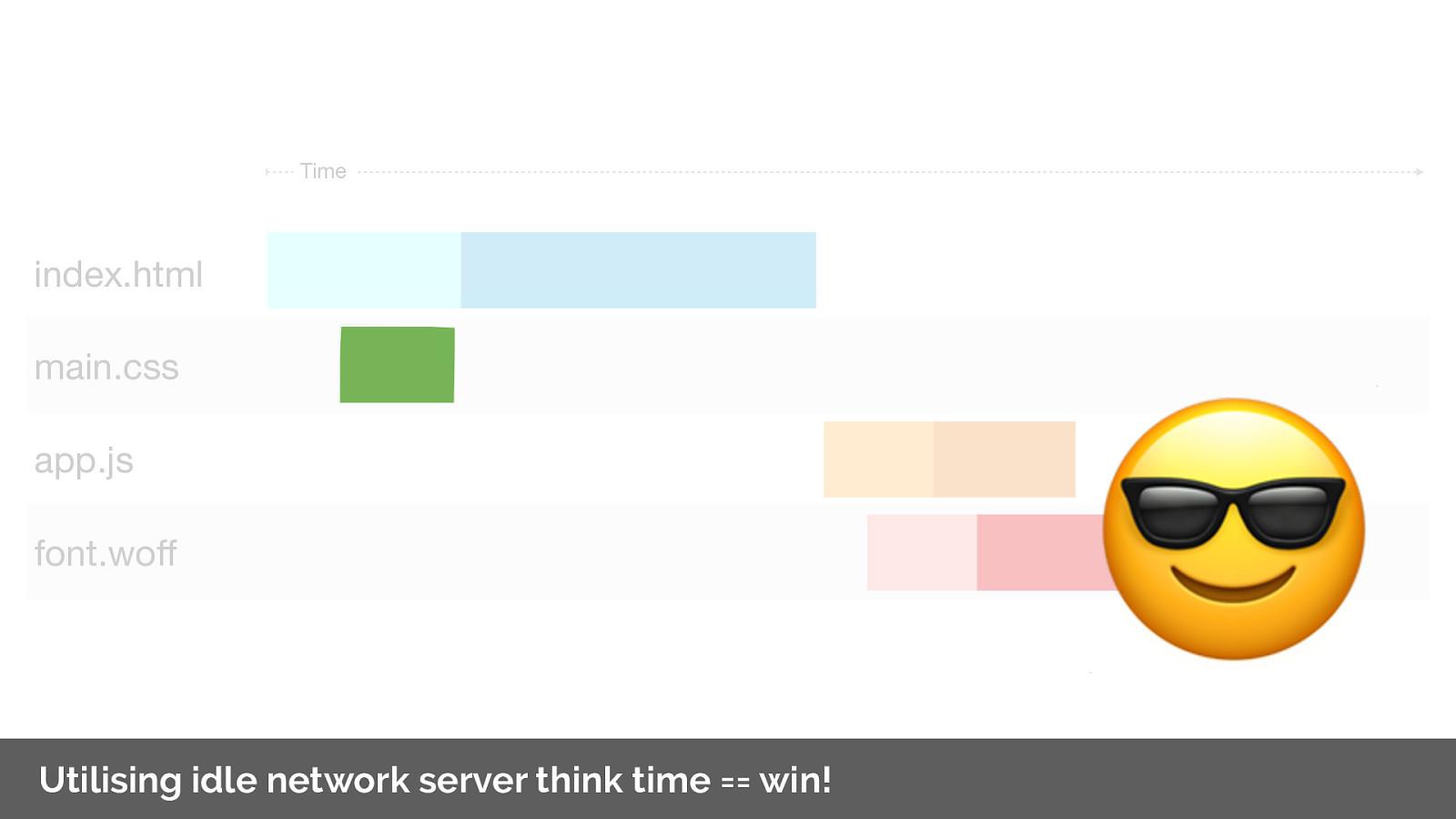
This is a big win and makes me very happy.

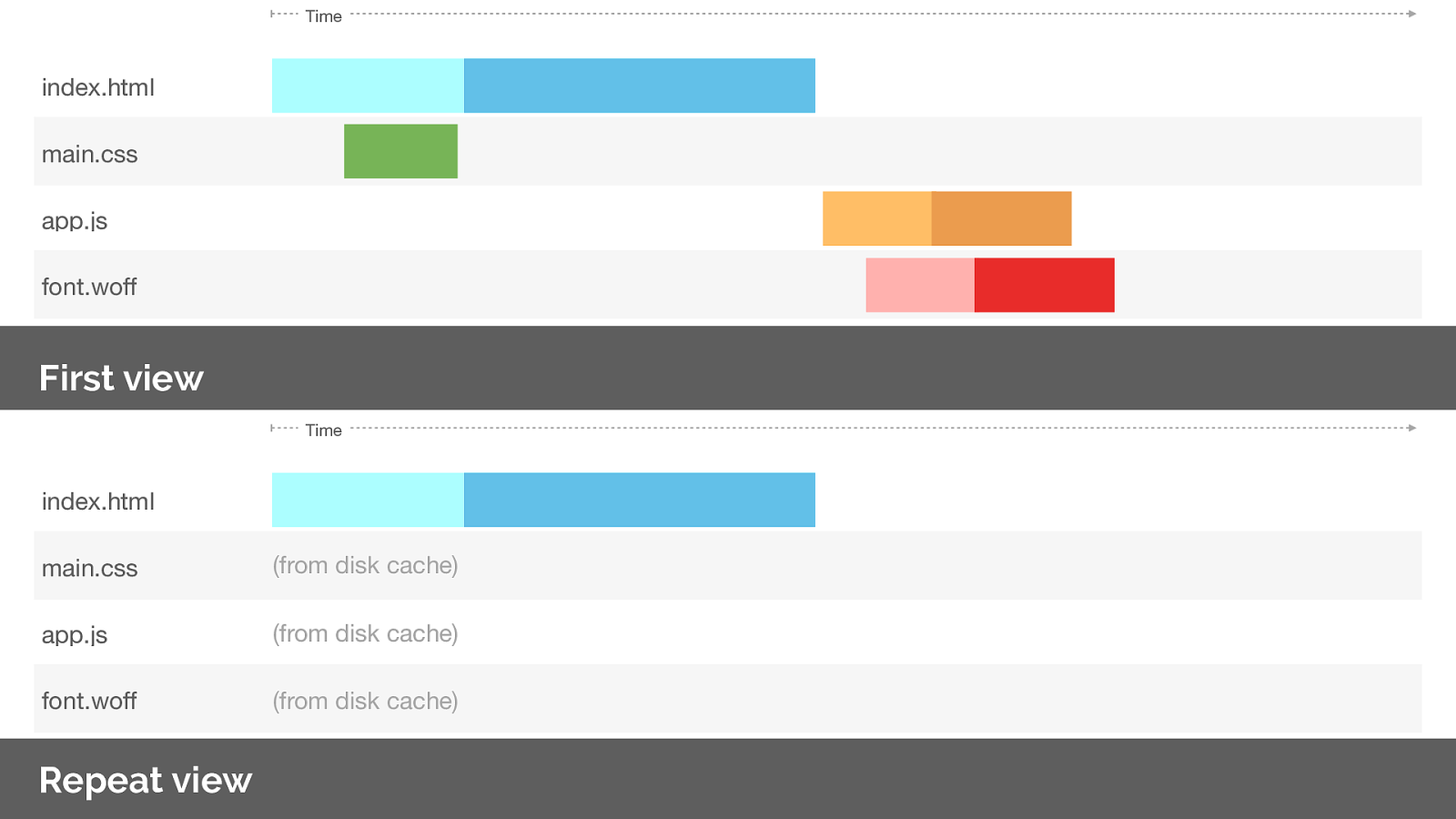
Whilst push is useful on the first view, what do you think would happen on a repeat view?
The client already has the asset cached. We have no way of indicating to the server what is in our cache!
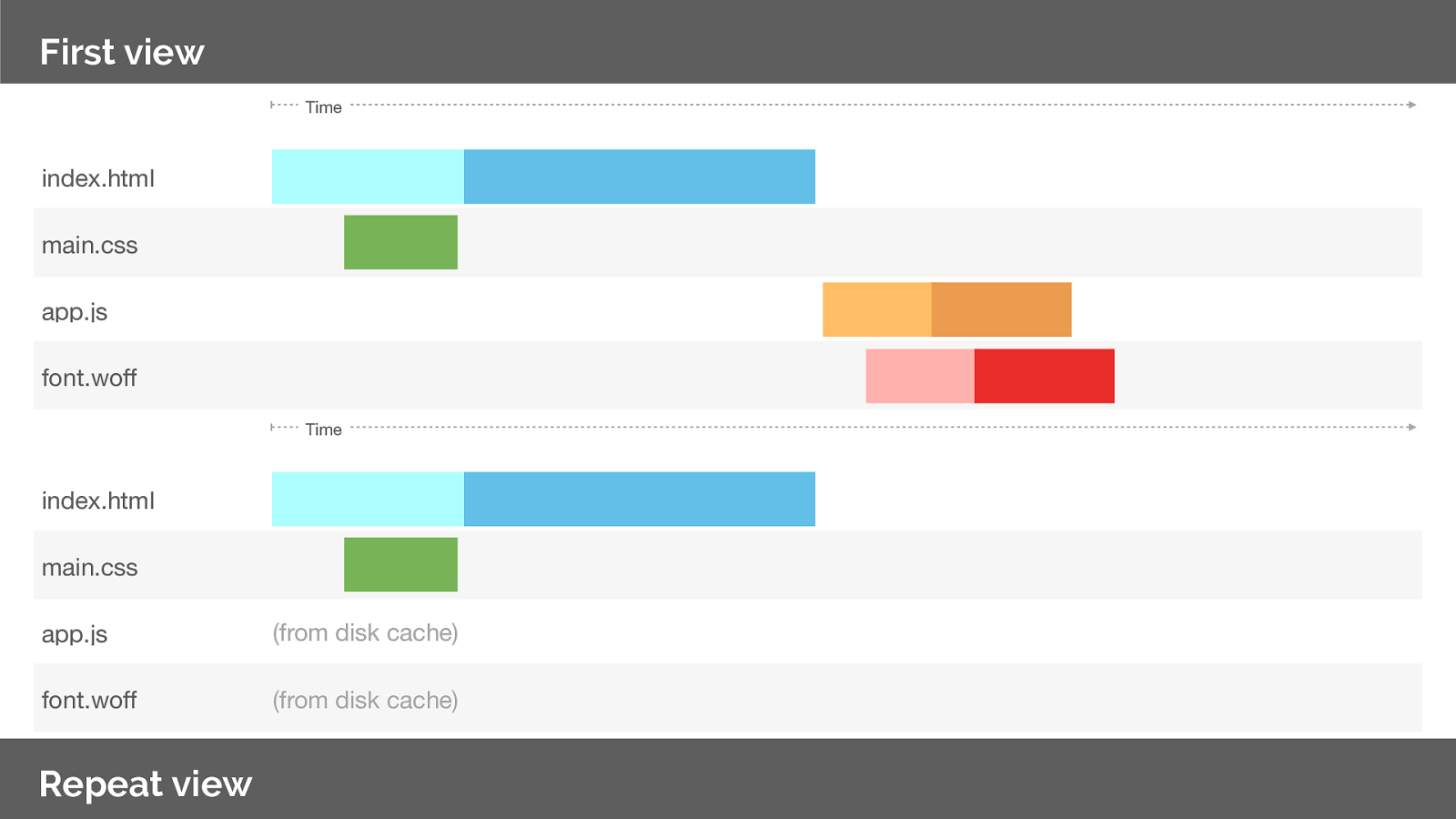
So lets look at he network utilisation from our push experiment.
If we were to request the same page again what happens? Note we’ve over-pushed the resource, and could potentially create contention on the network or delay our HTML response. Worse than not pushing at all.
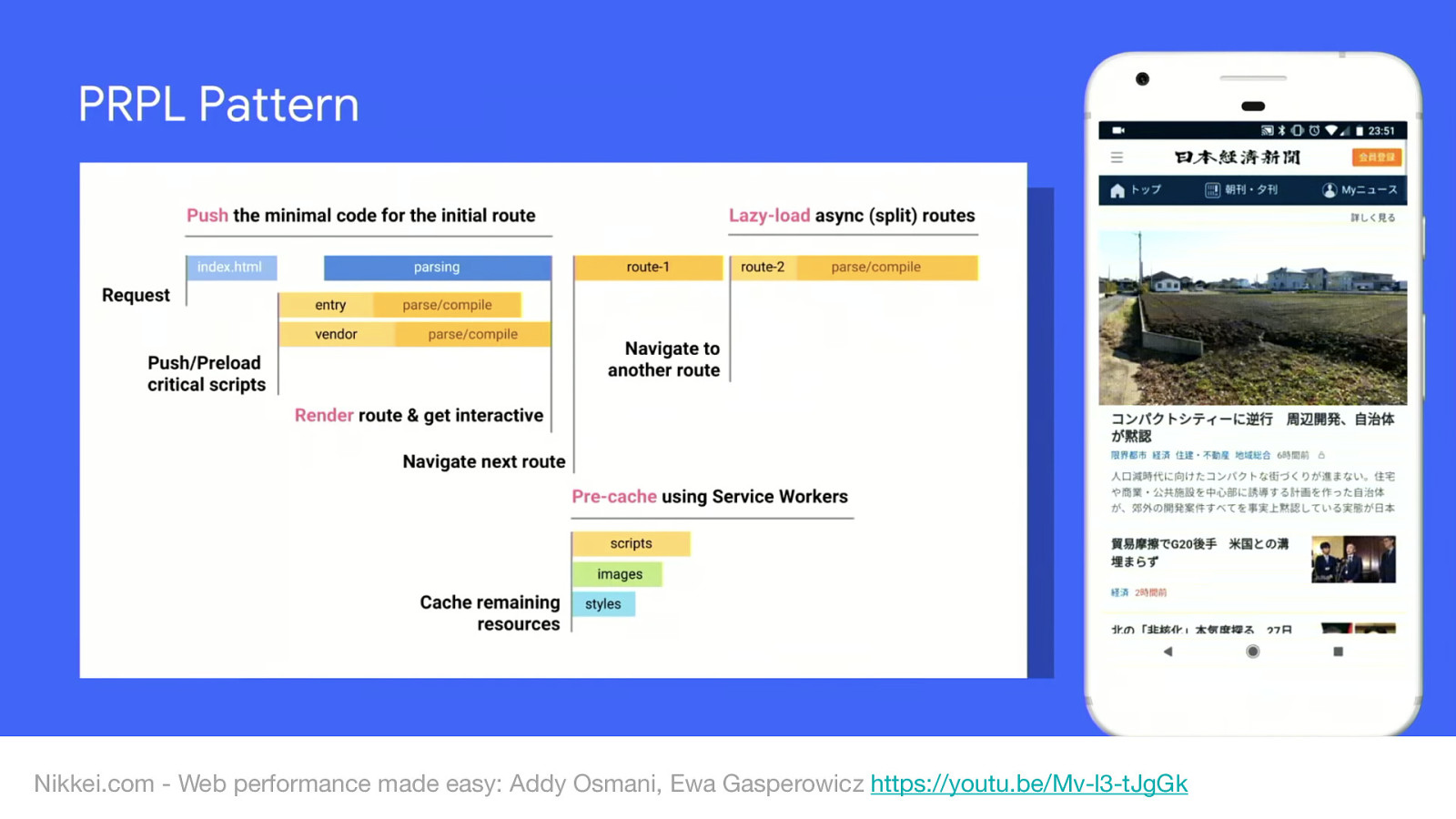
Nikkei.com - Web performance made easy: Addy Osmani, Ewa Gasperowicz https://youtu.be/Mv-l3-tJgGk
One solution to this is to use the PRPL pattern:

Whilst push is useful on the first view, what do you think would happen on a repeat view?
The client already has the asset cached. We have no way of indicating to the server what is in our cache!

So if the theory is right, this should be an extremely useful technique for resource loading? But the adoption is extremely low. So whats the problem?
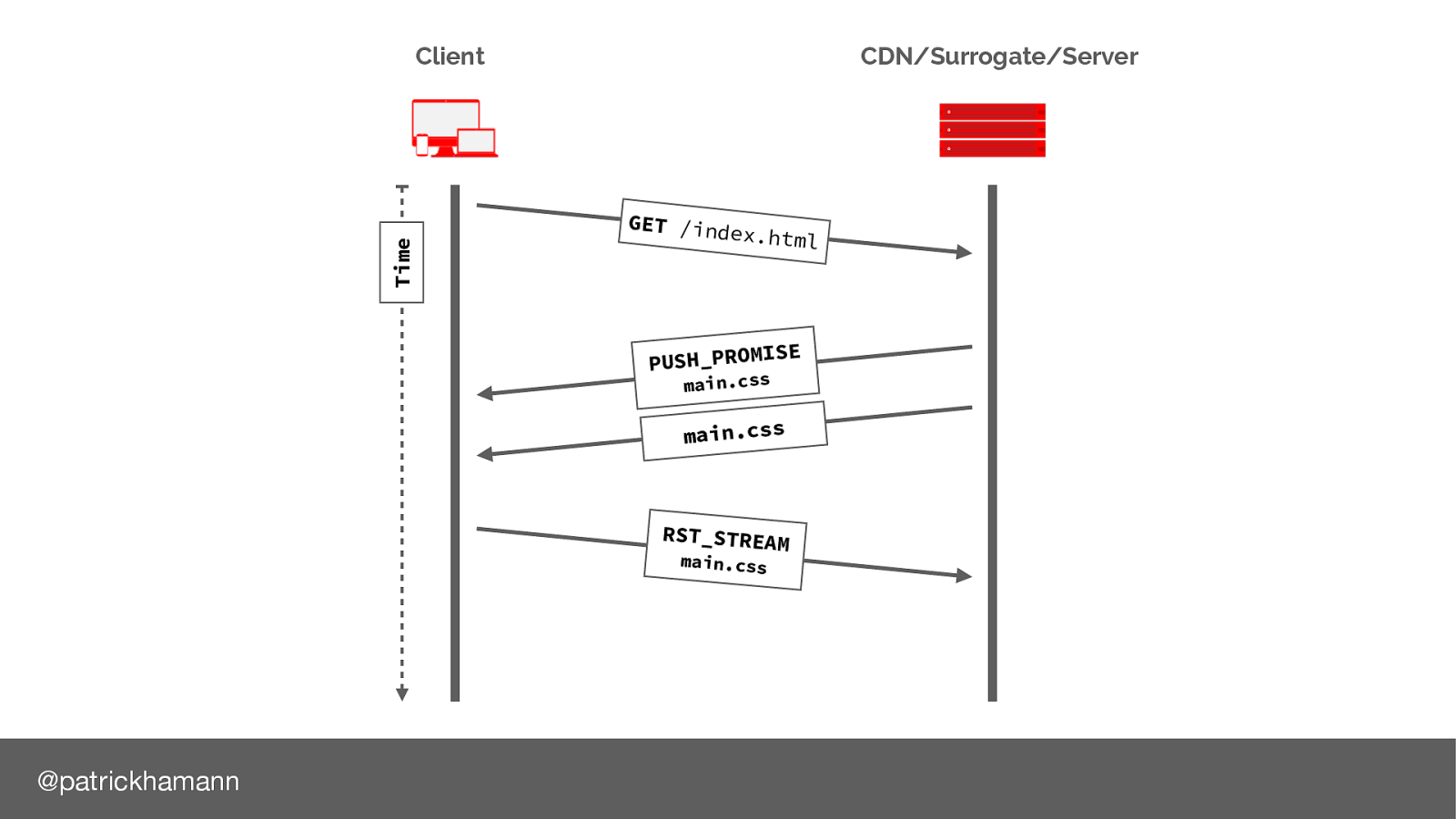
After we have sent the push promise frame to the browser it’s common that we’d start flushing the data frames.
If the browser already has the resource in it’s cache, it can send a RST_STREAM message to cancel the data. However this is normally too late, by the time the reset reaches the server most of the bytes for the resource have already been flushed to the physical network link, or are in the kernel TCP buffer.
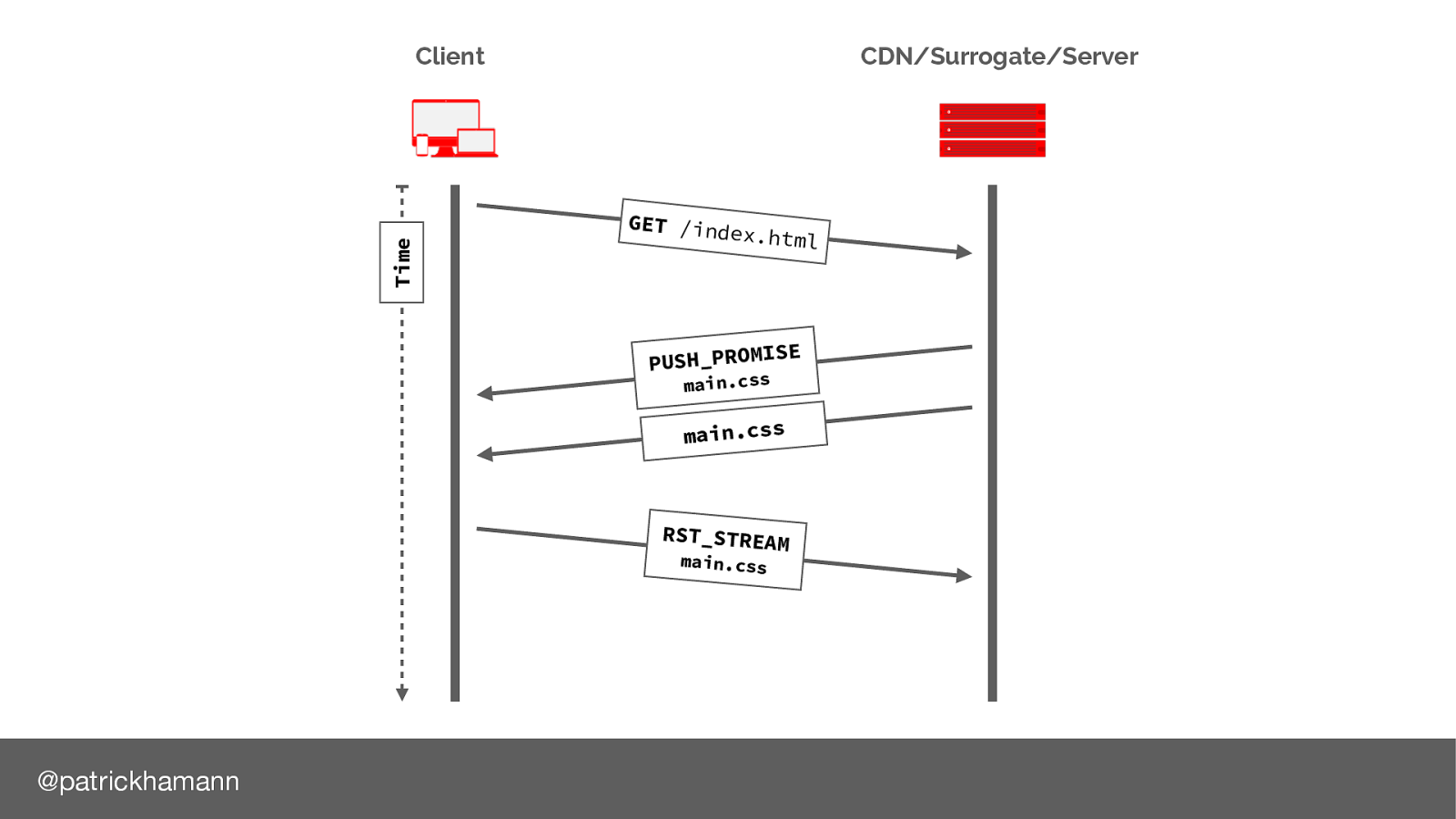
The new QUIC protocol can solve this moving more work to user space instead of the kernel.
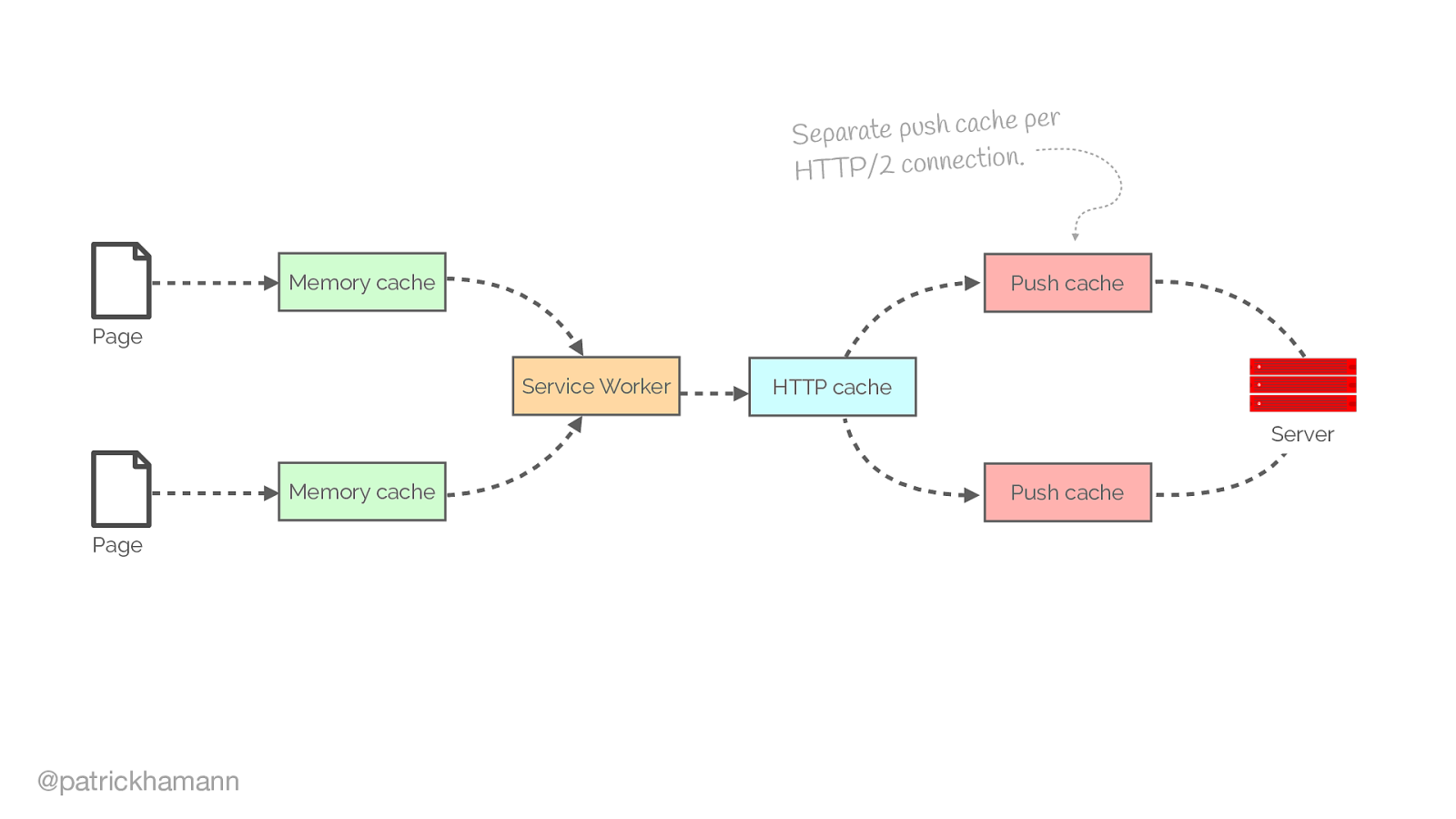
Another common area of issue is how the browser caches the push resource
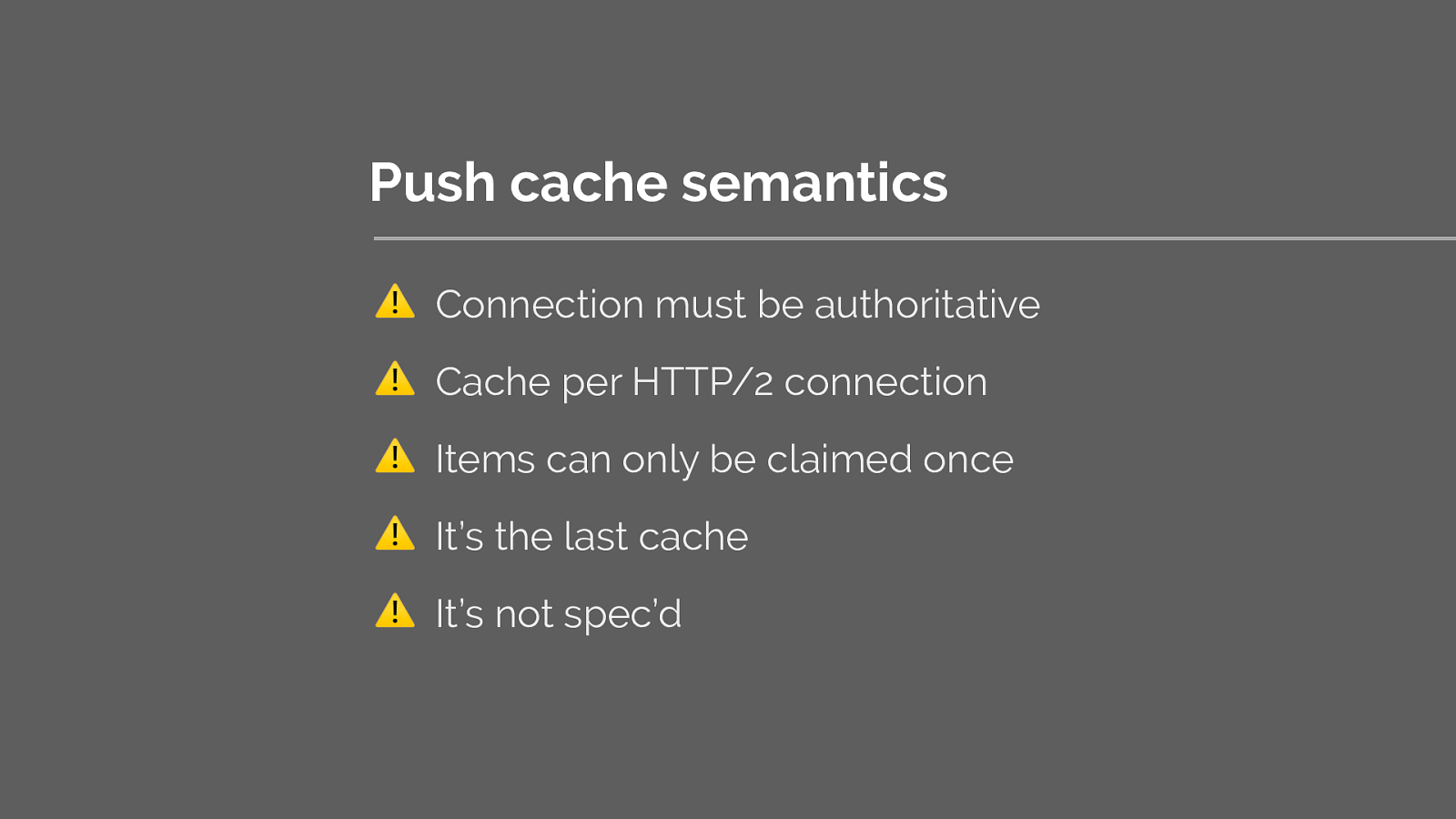
I’ve detailed some of the issues surrounding this here:

HTTP/2 push is tougher than I thought – Jake Archibald https://jakearchibald.com/2017/h2-push-tougher-than-i-thought/
Jake Archibald has done extensive research into the browser inconsistencies of push. I urge you to read this blog post if you’re considering using push.

The TL;DR the browser inconsistencies of the push cache results in only chrome and Firefox having reliable implementations.
Thus leaving us to resort to UA sniffing if we want to use without any gotchas.

Lastly the rate of adoption of push is leading to many implementers to abandon the pattern.
On Fastly we observe 800 out of 1000000 responses on our network are push initiated. 6 million requests a second.

So should you really be pushing at all? My short answer is I doubt it. However it can still be useful if you:

So is the 1RTT saving worth the complexity?

So if push might not be worth it? What are our other options?

Each of the techniques I’ve presented so far, have had trade-offs. However, I’m really excited by the what the near future holds for us with regards to resource loading in the browser.

So can we just fix the problems with push?

This is where cache digests may be able to help.
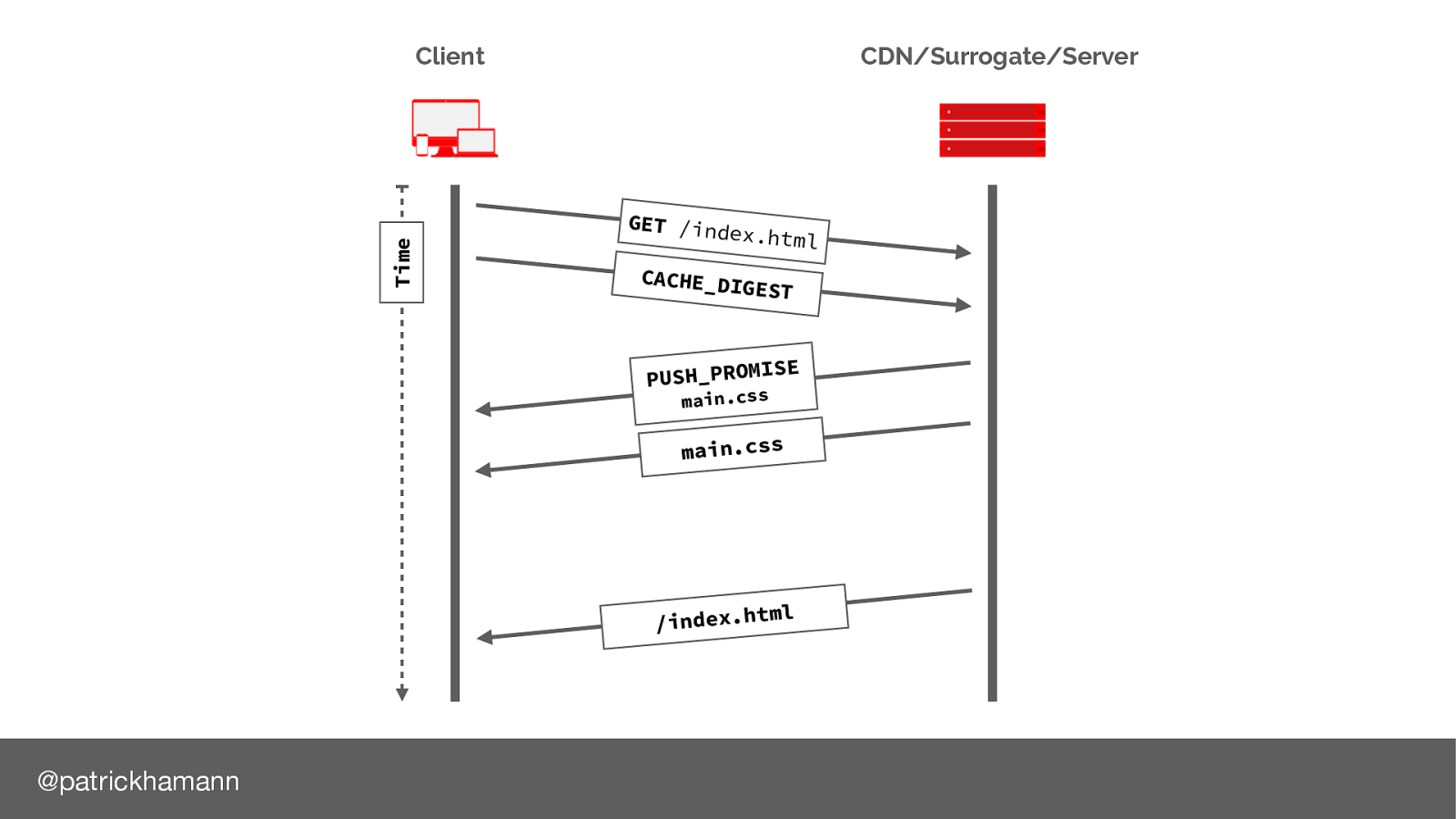
What if the browser could send an indication of its cache state when it initialises the connection with the server:
Now the server has enough information to decide whether it should push the resource. I’m also excited by the other possibilities this gives us to create intelligent applications on the server.
With cache digests this fixes the repeat view issue.
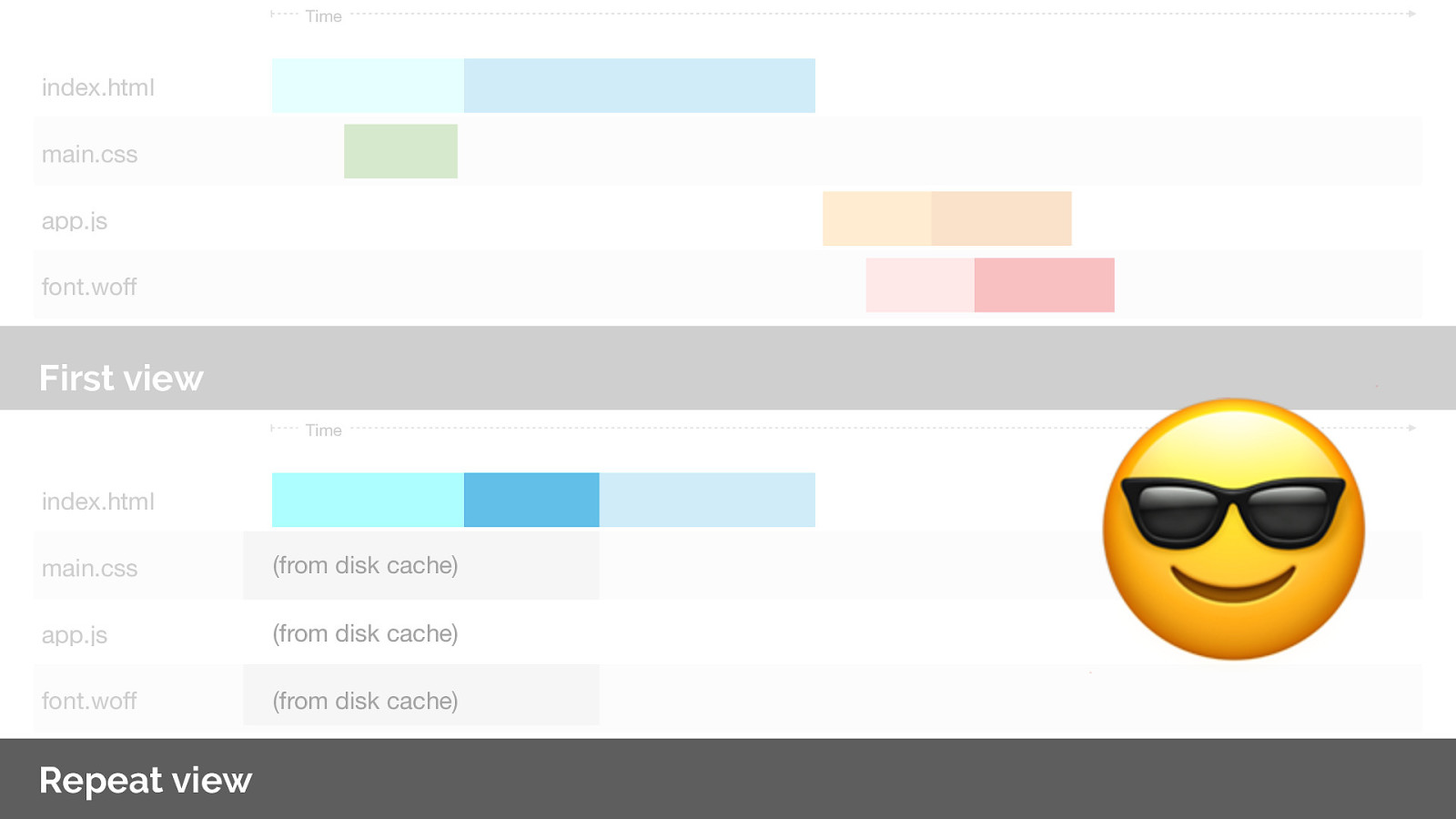
Win.
IETF Draft Cache Digests for HTTP/2 - K. Oku, Y. Weiss https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-httpbis-cache-digest-04
The specification is still being actively worked on in draft. However implementations are starting to appear.
Fastly’s open-source H20 HTTP/2 server was the first to have a working implementation.

But this still seems too complicated...
We are maintaining a lot of logic and state on the server.

This is where the 103 Early hints status code comes in.
Proposed by my colleague Kazuho.

Who here has heard of the 100 informational range of responses?
103 is a new HTTP response code that allows the server to indicate to the client resources that it is likely to send in the final response.
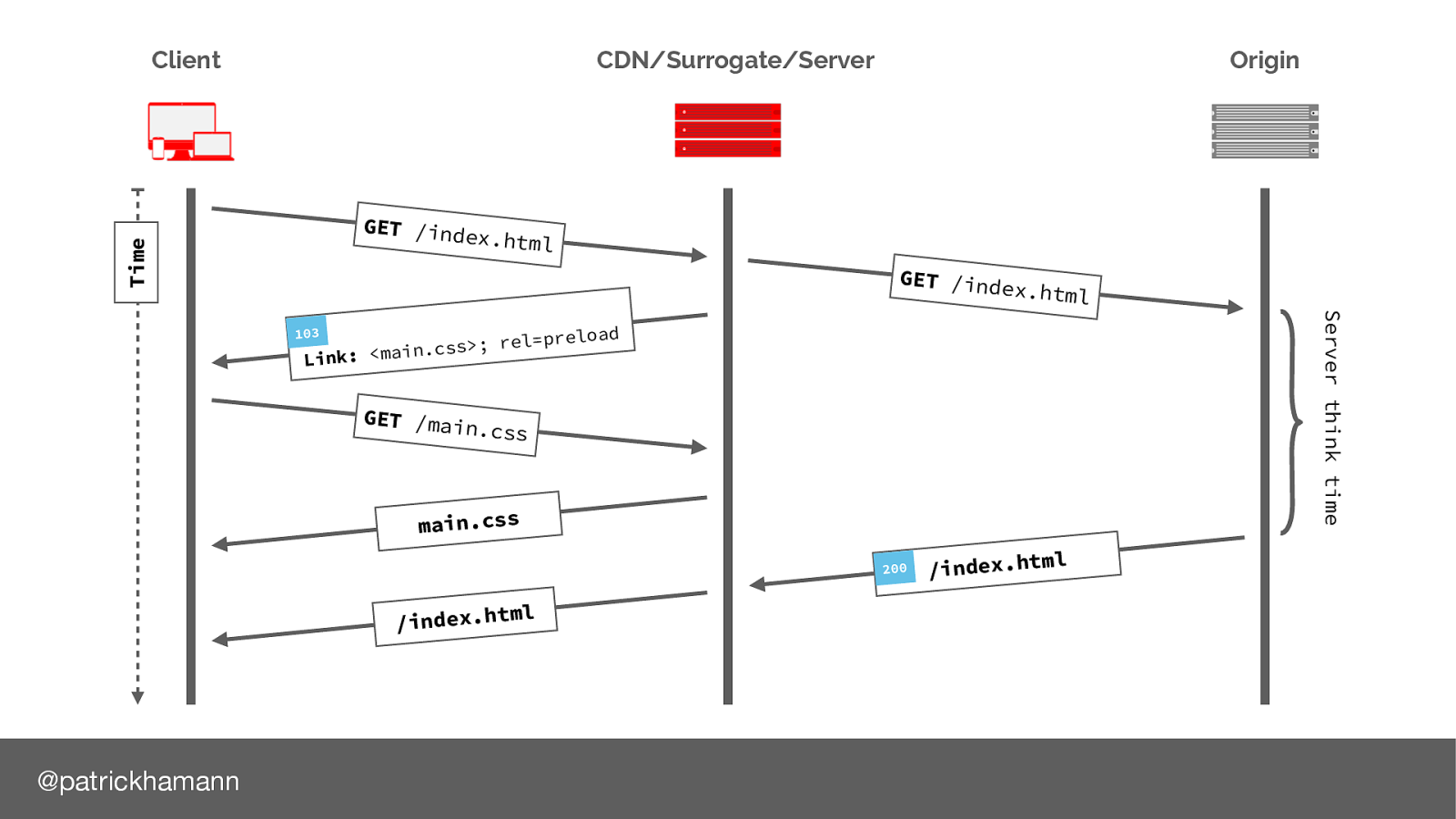
This allows the client to initiate early fetches for the critical resources before it has even received the HTML.
Much like the benefits of async push but with the simplicity of allowing the client to decide what it needs to fetch.
Just like the age old technique of header flushing.
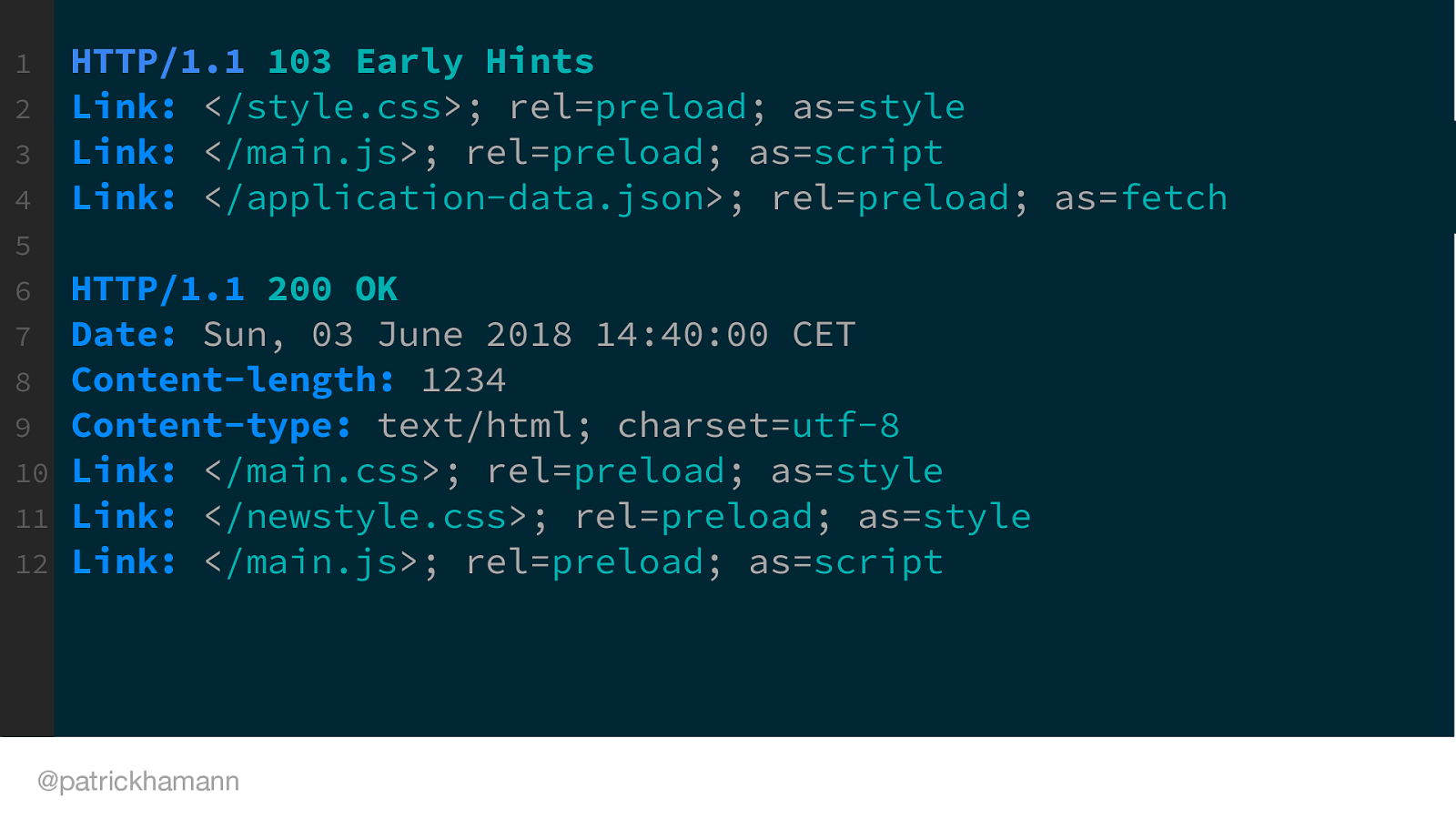
This is what a 103 HTTP response would look like on the wire, with its proceeding 200 response of the HTML.
IETF RFC8297 Early Hints - K. Oku https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc8297
The spec has been accepted by the IETF as RFC 8297 and is currently in experimental.
Browser vendors are very interested, but some are concerned about the complexity of implementation.

With early hints we get the same benefits of async push, but much simpler.
Giving the power back to the browser to make the decisions on what it wants to fetch and appropriately leveraging the browser cache.
103 Early hints:

Now we know how to decorate the HTTP responses with resource hints, using preload and early hints.
What if we could also decorate our HTML and sub-resources to change resource priorities.
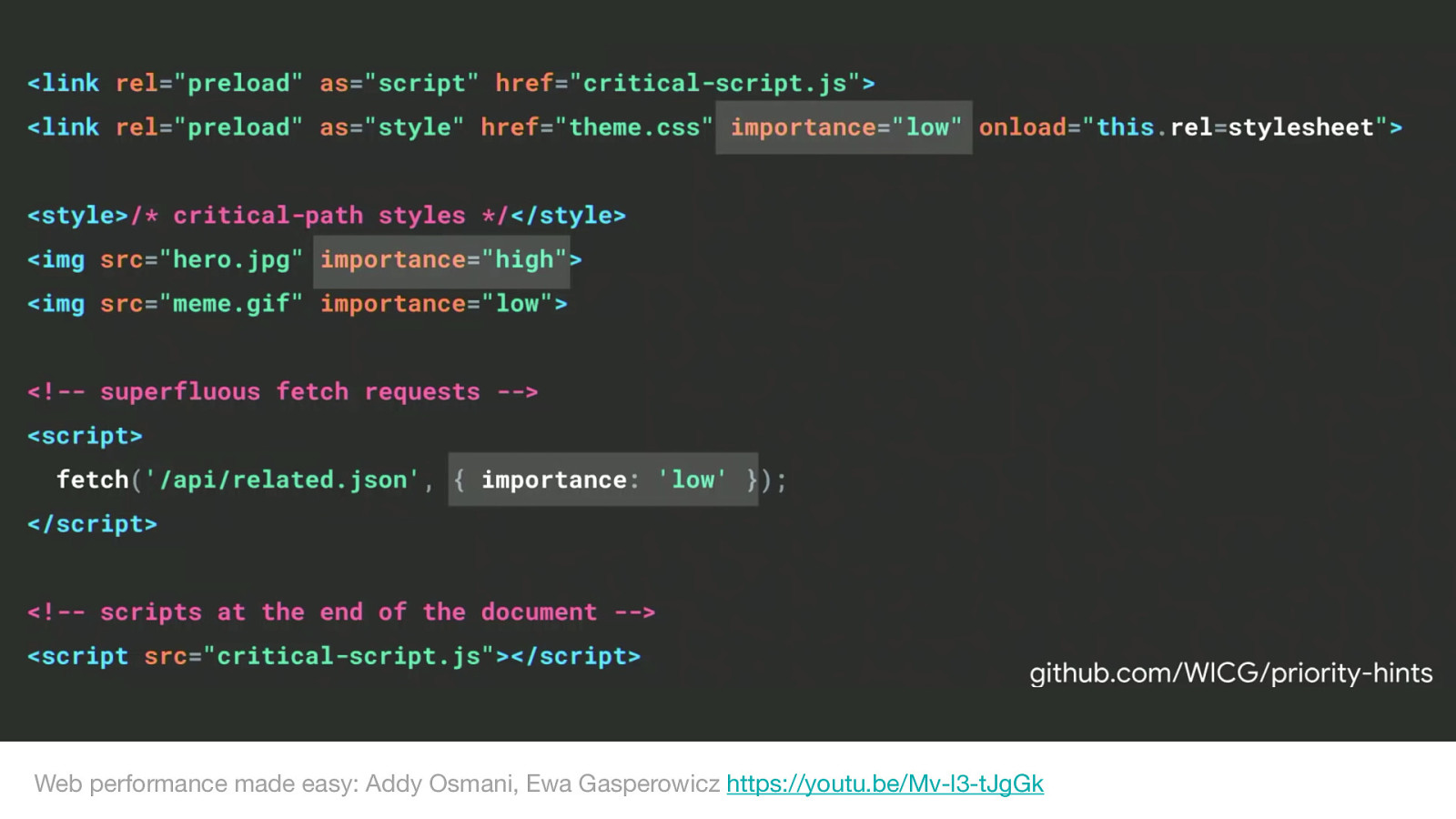
An extension to preload, priority hints aim to give the author granular control over the priority of each resource loaded by your page.
You as the application author know best the priority of your resources.
Check out Addy and Eva’s talk from Google I/O this year: Web performance made easy: Addy Osmani, Ewa Gasperowicz https://youtu.be/Mv-l3-tJgGk
If you’re interested, going the discussion on GitHub:
Priority Hints draft - https://github.com/WICG/priority-hints

So this has been a whirlwind tour of asset loading in the browser.
And have only scratched the surface on each methodology but I hope i’ve given you some new techniques to take home and try.
I’d like to leave you with some takeaways.

HTTP/2 doesn’t solve everything

Resource loading is hard.

Performance is for humans. Optimise for user experiences.
Always try to optimise for delightful user experiences and not the network.

To summarise, your resource priority strategy today should be to:

Patrick Hamann: speakerdeck.com/patrickhamann