1 Boosting Your Bias Immunity LAUREN ISAACSON Market & UX Research Consultant Curio Research @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
A presentation at Push UX in October 2019 in Munich, Germany by Lauren Isaacson

1 Boosting Your Bias Immunity LAUREN ISAACSON Market & UX Research Consultant Curio Research @curio_research www.curioresearch.net

2 PERFECTLY IMPERFECT BRAINS TYPES OF BIAS HEURISTIC CARD EXERCISE AVOIDING BIASED DECISIONS @curio_research www.curioresearch.net

3 Our Perfectly Imperfect Brains Seeing is not necessarily believing @curio_research www.curioresearch.net

4 “A cognitive bias refers to the systematic pattern of deviation from the norm or rationality in judgement, whereby inferences about other people and situations may be drawn in an illogical fashion. Individuals create their own ‘subjective social reality’ from their perception of input.” —Wikipedia @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
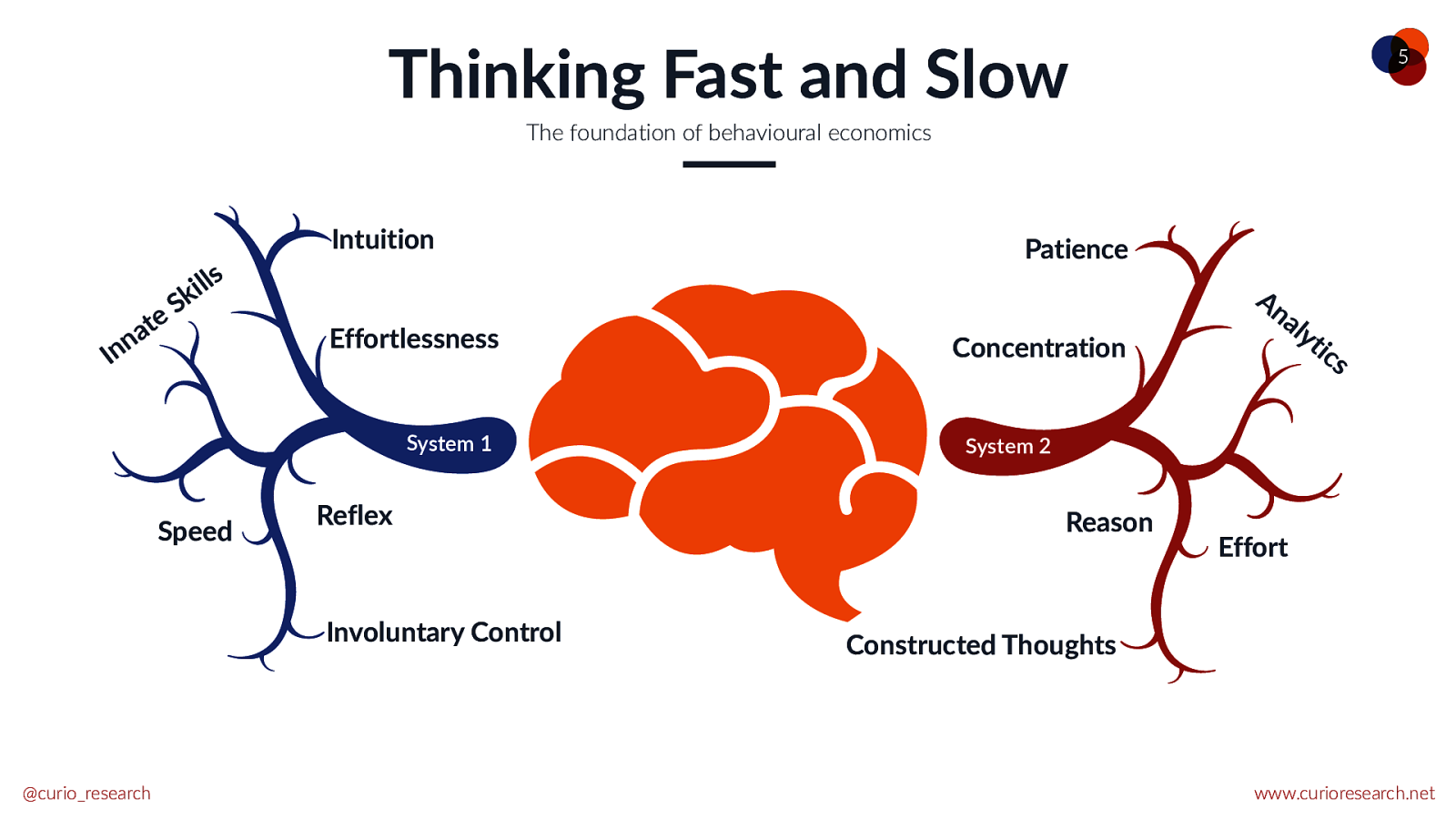
Thinking Fast and Slow 5 The foundation of behavioural economics Intuition s l l i k S e t na In Effortlessness System 1 Speed Reflex Involuntary Control @curio_research Patience Concentration An aly tic s System 2 Reason Effort Constructed Thoughts www.curioresearch.net
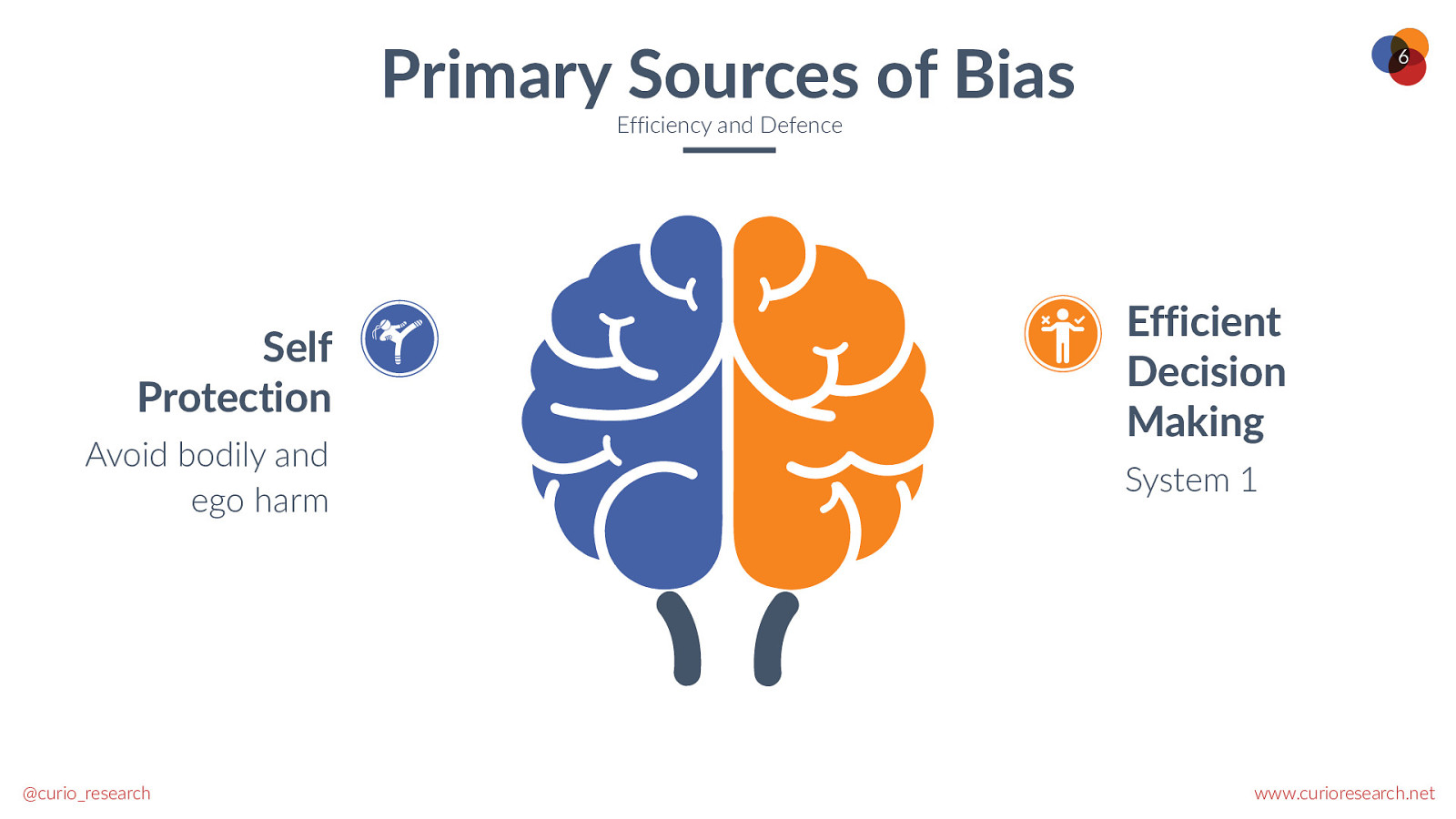
Primary Sources of Bias 6 Efficiency and Defence Self Protection Avoid bodily and ego harm @curio_research Efficient Decision Making System 1 www.curioresearch.net
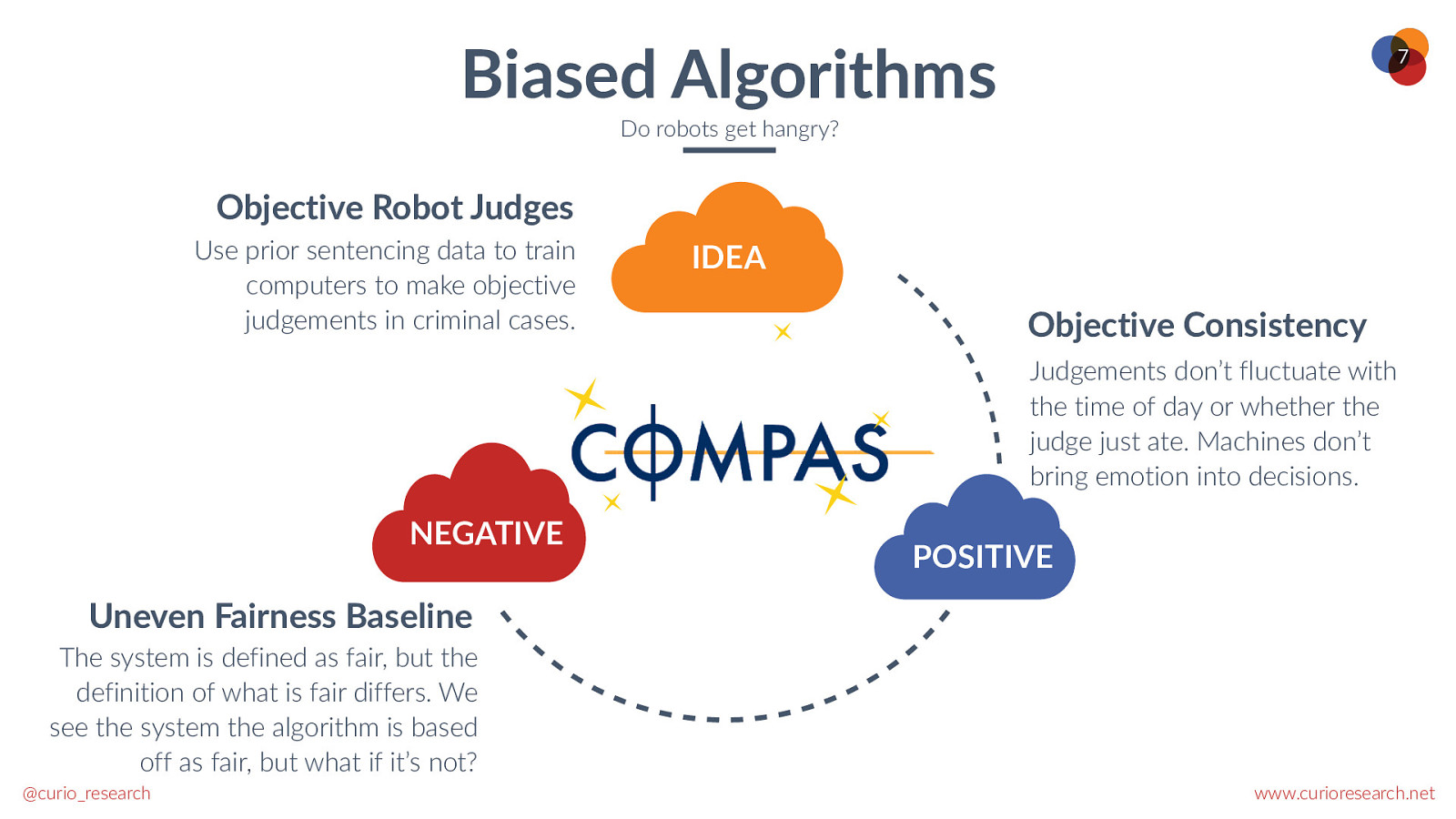
Biased Algorithms 7 Do robots get hangry? Objective Robot Judges Use prior sentencing data to train computers to make objective judgements in criminal cases. IDEA Objective Consistency Judgements don’t fluctuate with the time of day or whether the judge just ate. Machines don’t bring emotion into decisions. NEGATIVE POSITIVE Uneven Fairness Baseline The system is defined as fair, but the definition of what is fair differs. We see the system the algorithm is based off as fair, but what if it’s not? @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
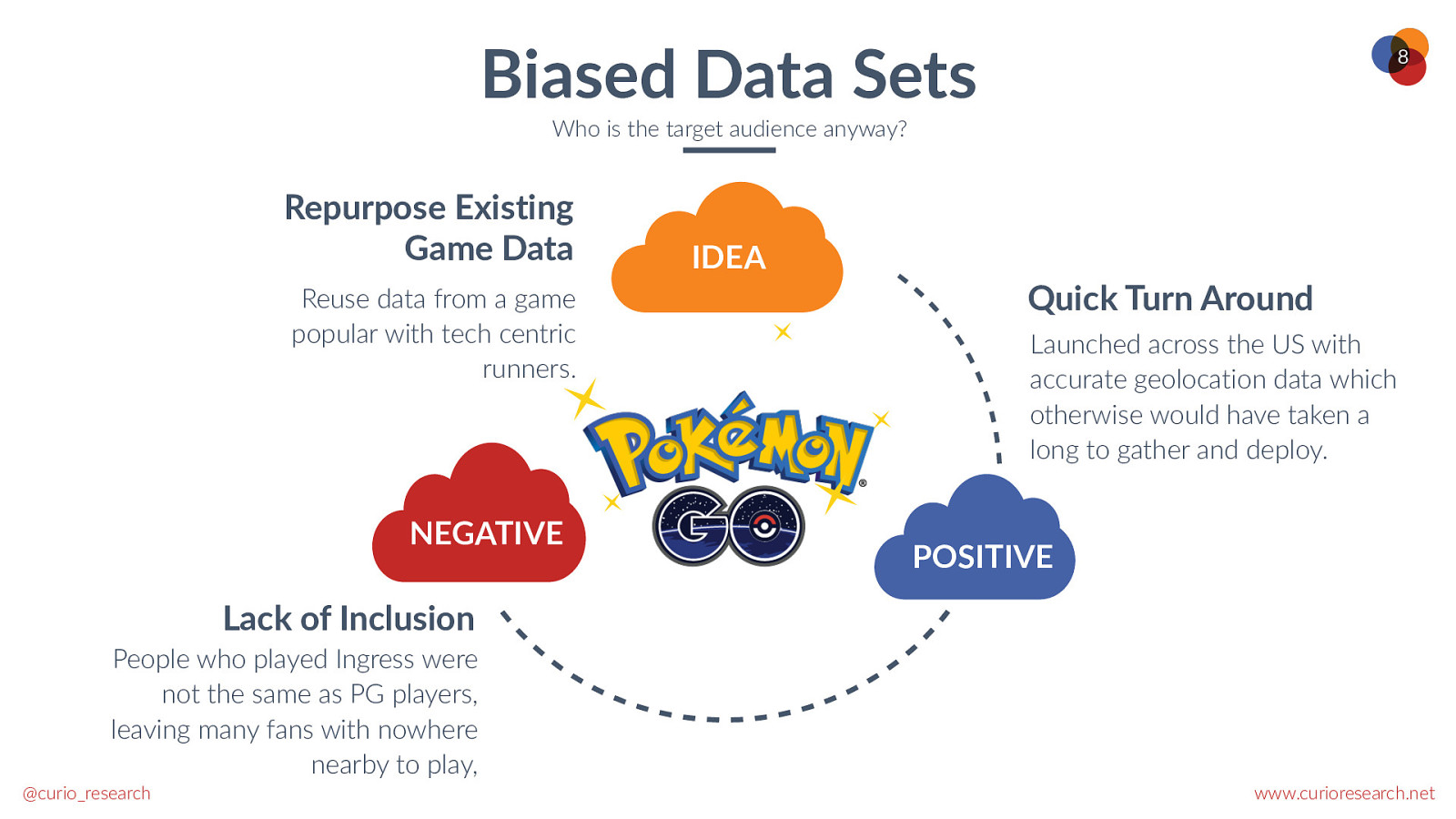
Biased Data Sets 8 Who is the target audience anyway? Repurpose Existing Game Data Reuse data from a game popular with tech centric runners. NEGATIVE IDEA Quick Turn Around Launched across the US with accurate geolocation data which otherwise would have taken a long to gather and deploy. POSITIVE Lack of Inclusion People who played Ingress were not the same as PG players, leaving many fans with nowhere nearby to play, @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
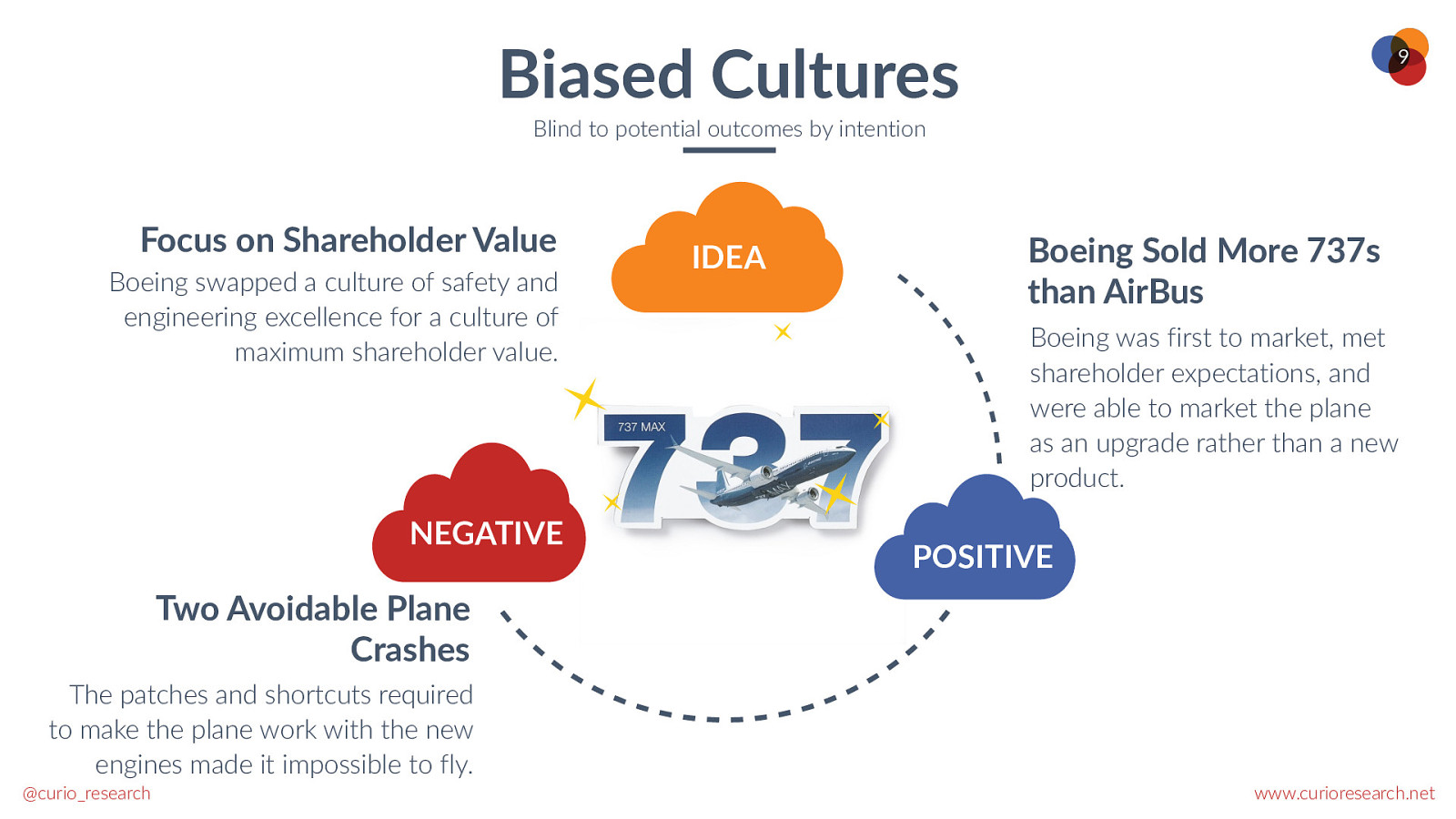
Biased Cultures 9 Blind to potential outcomes by intention Focus on Shareholder Value Boeing swapped a culture of safety and engineering excellence for a culture of maximum shareholder value. NEGATIVE IDEA Boeing Sold More 737s than AirBus Boeing was first to market, met shareholder expectations, and were able to market the plane as an upgrade rather than a new product. POSITIVE Two Avoidable Plane Crashes The patches and shortcuts required to make the plane work with the new engines made it impossible to fly. @curio_research www.curioresearch.net

10 Bias is like polluted air • Impossible to avoid, but filterable. • Filtering requires identification of potential influencing biases. @curio_research www.curioresearch.net

11 Types of Bias Name Thy Enemies @curio_research www.curioresearch.net \

The World of Biases 12 Using bias to understand bias There are over 170 types of cognitive biases @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
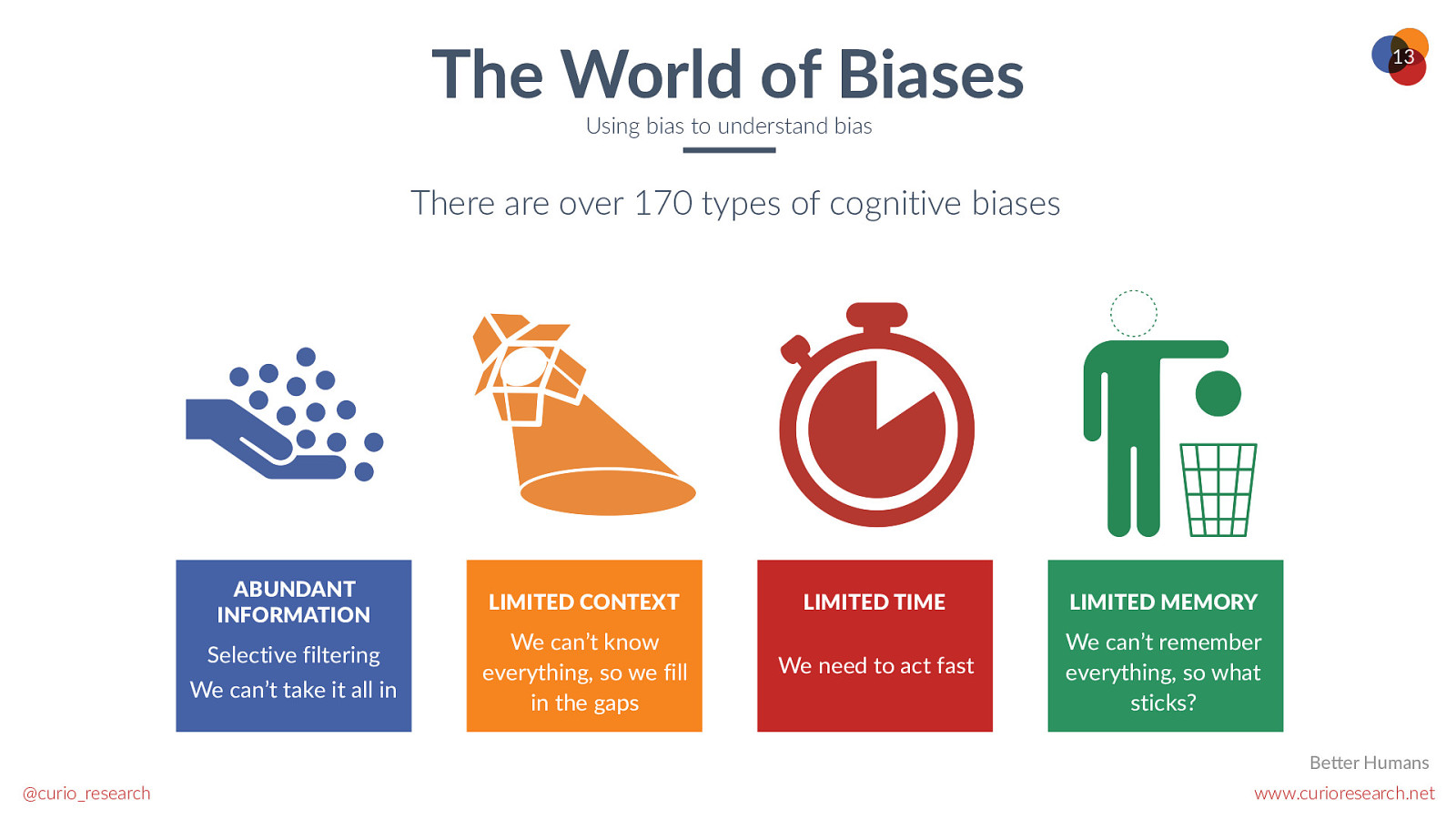
The World of Biases 13 Using bias to understand bias There are over 170 types of cognitive biases ABUNDANT INFORMATION Selective filtering We can’t take it all in LIMITED CONTEXT We can’t know everything, so we fill in the gaps LIMITED TIME LIMITED MEMORY We need to act fast We can’t remember everything, so what sticks? Be@er Humans @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
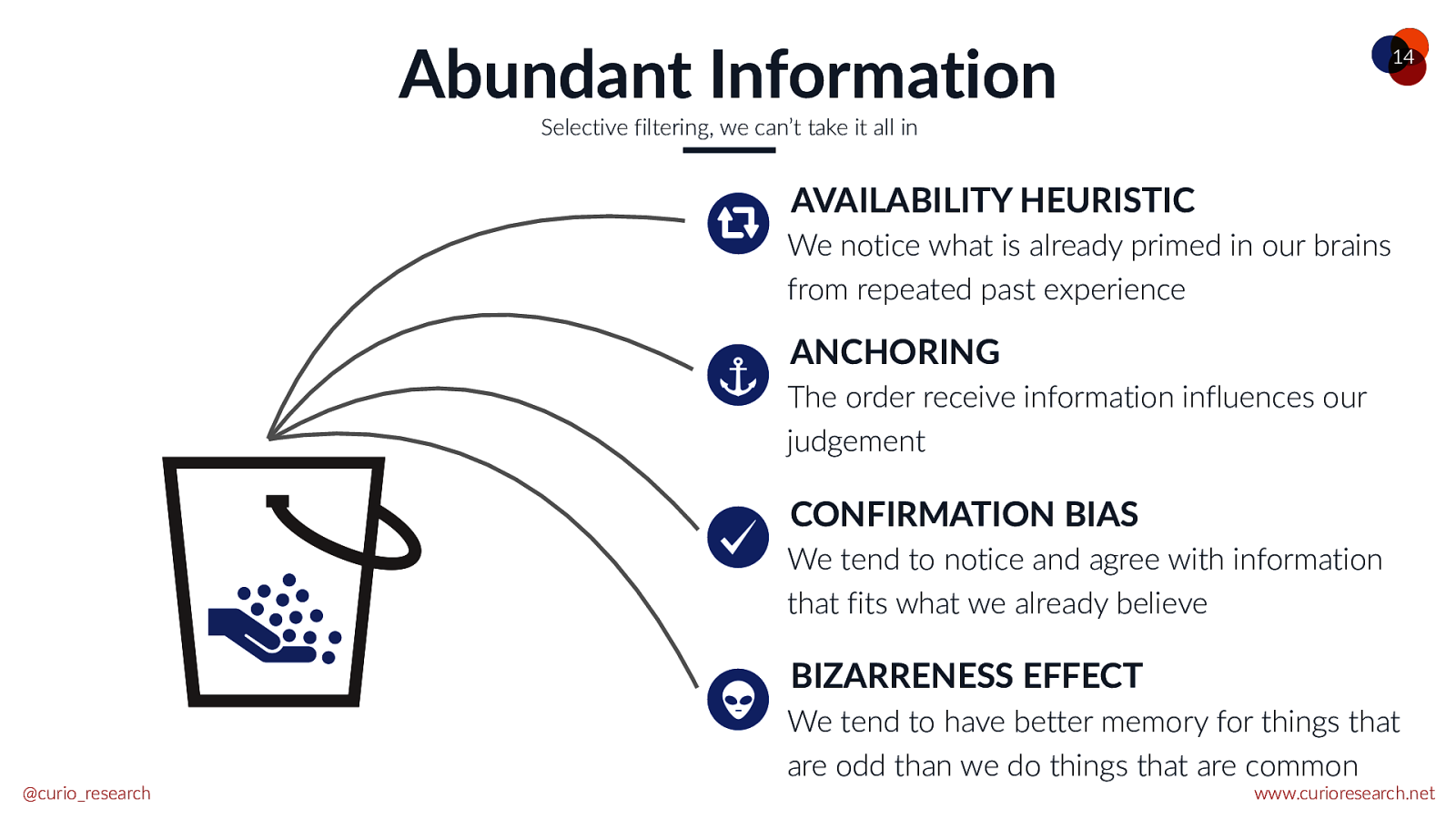
Abundant Information 14 Selective filtering, we can’t take it all in AVAILABILITY HEURISTIC We notice what is already primed in our brains from repeated past experience ANCHORING The order receive information influences our judgement CONFIRMATION BIAS We tend to notice and agree with information that fits what we already believe BIZARRENESS EFFECT @curio_research We tend to have better memory for things that are odd than we do things that are common www.curioresearch.net
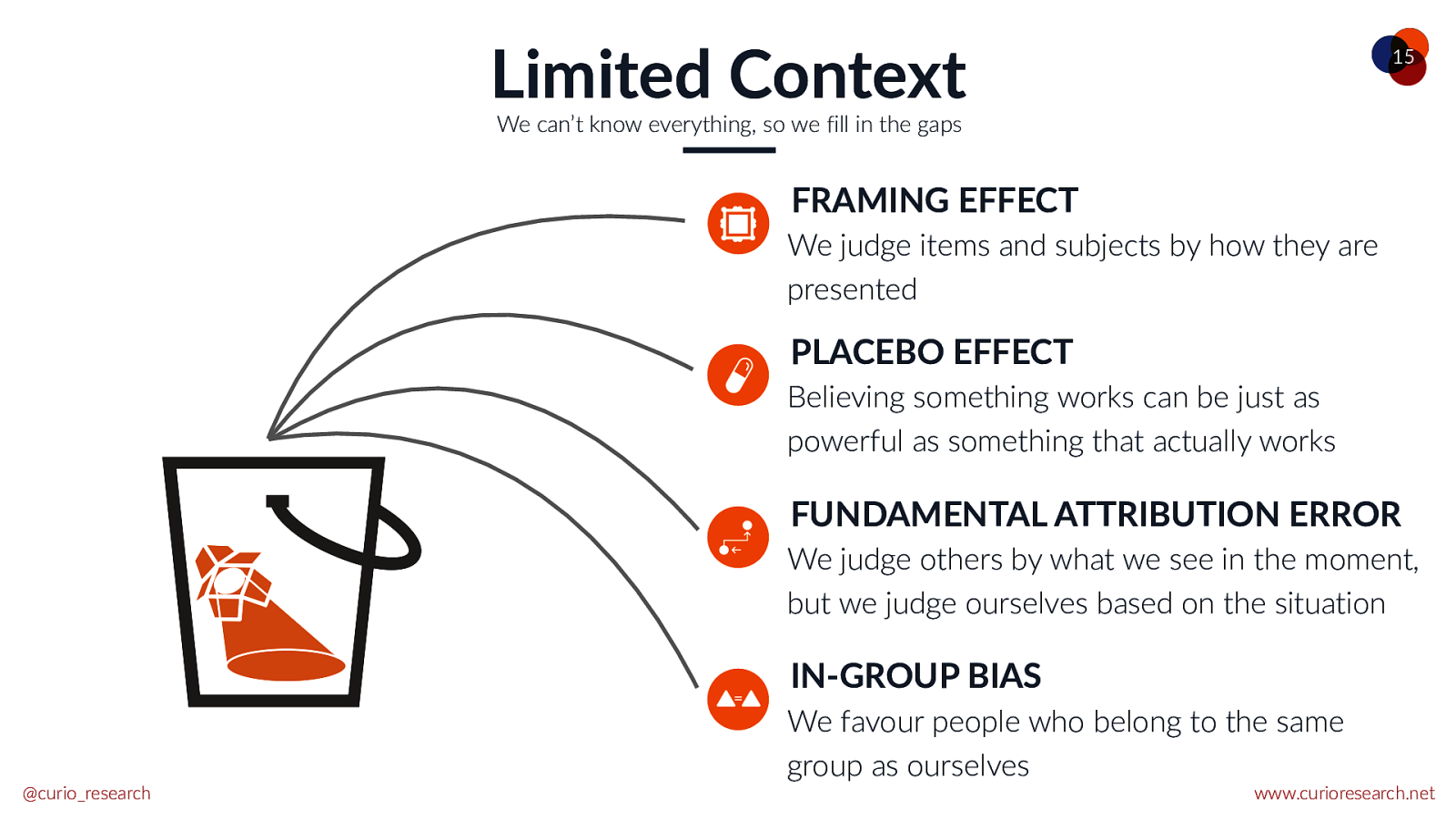
Limited Context 15 We can’t know everything, so we fill in the gaps FRAMING EFFECT We judge items and subjects by how they are presented PLACEBO EFFECT Believing something works can be just as powerful as something that actually works FUNDAMENTAL ATTRIBUTION ERROR We judge others by what we see in the moment, but we judge ourselves based on the situation IN-GROUP BIAS @curio_research We favour people who belong to the same group as ourselves www.curioresearch.net
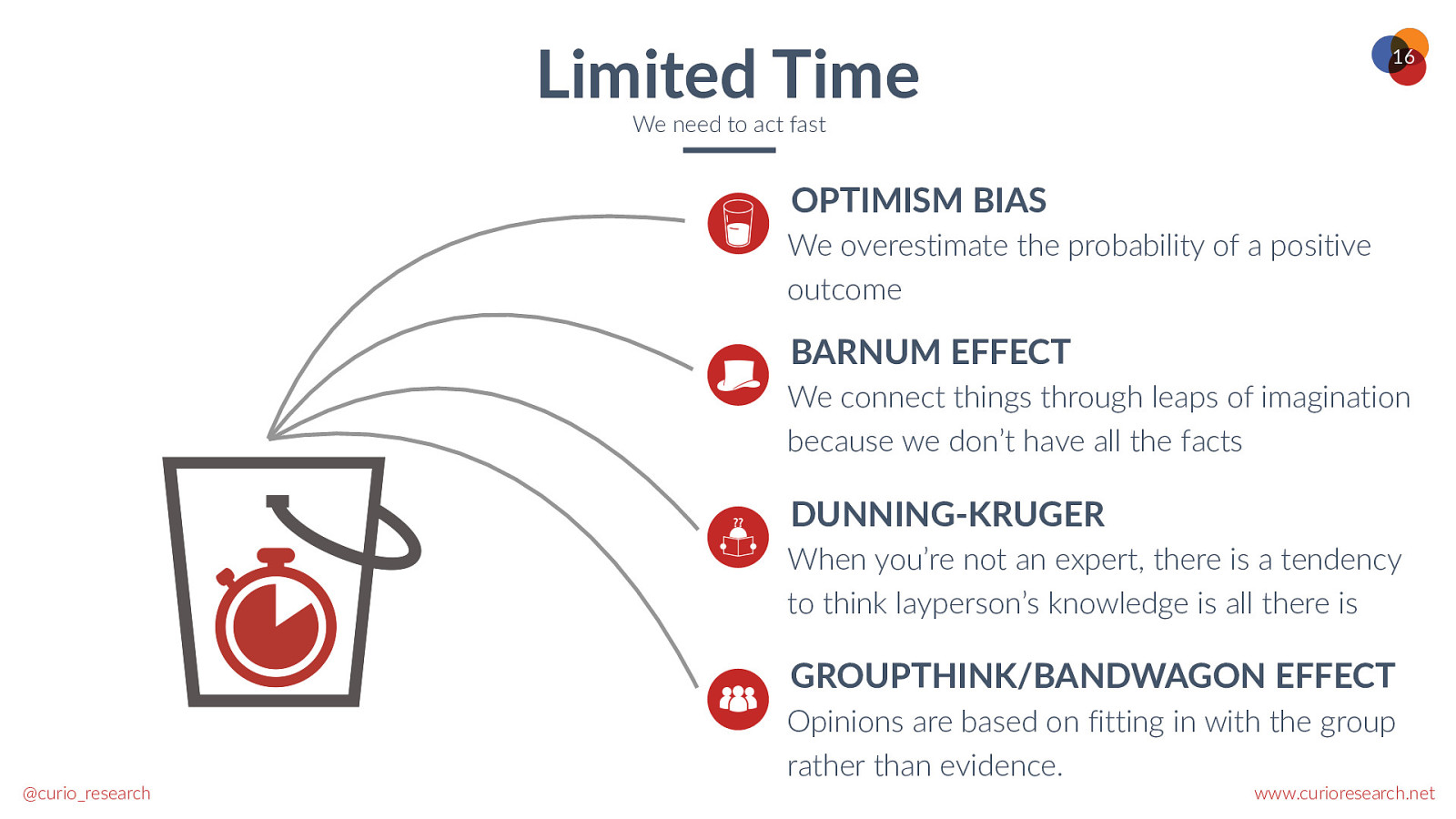
Limited Time 16 We need to act fast OPTIMISM BIAS We overestimate the probability of a positive outcome BARNUM EFFECT We connect things through leaps of imagination because we don’t have all the facts DUNNING-KRUGER When you’re not an expert, there is a tendency to think layperson’s knowledge is all there is GROUPTHINK/BANDWAGON EFFECT @curio_research Opinions are based on fitting in with the group rather than evidence. www.curioresearch.net
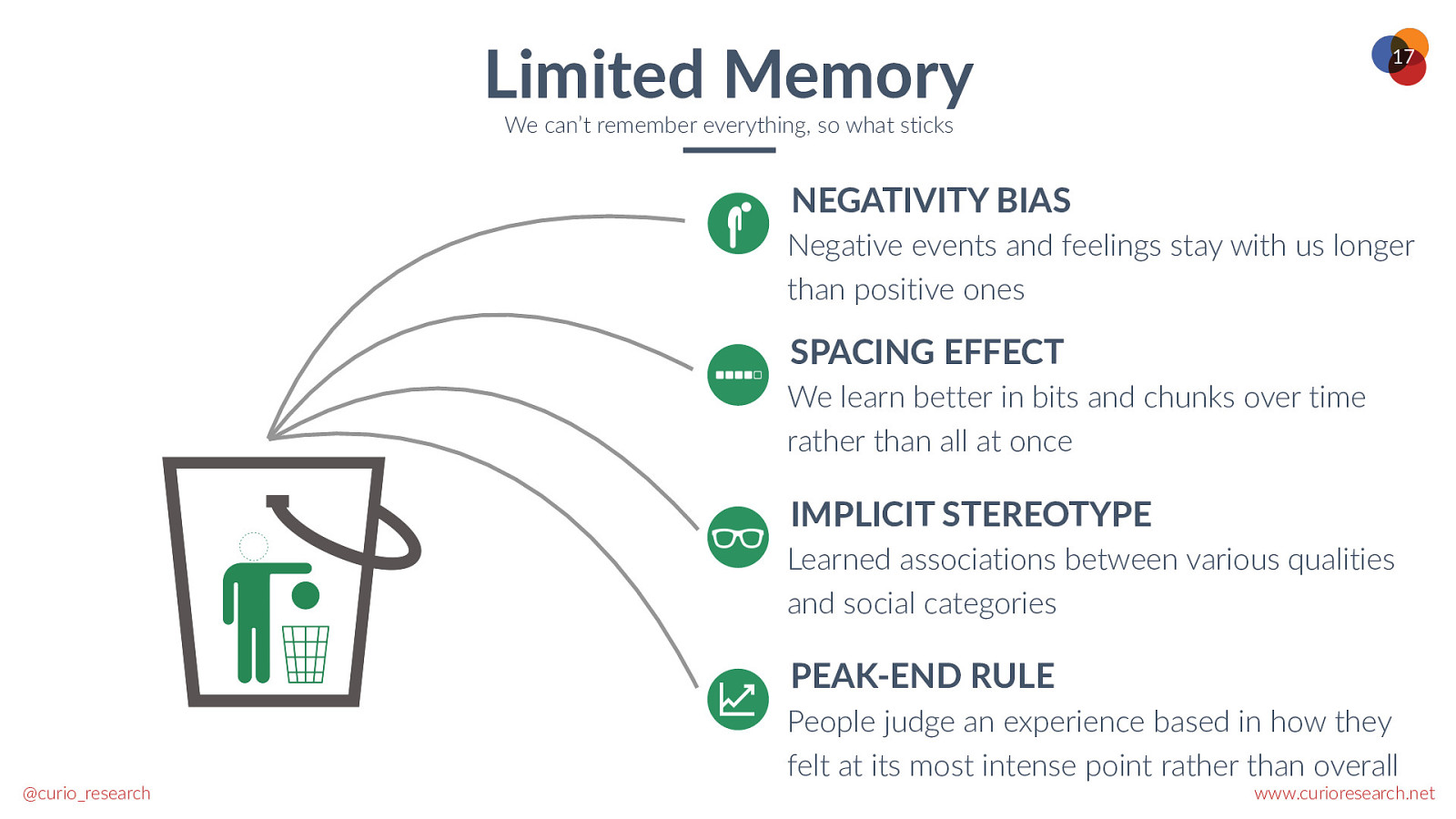
Limited Memory 17 We can’t remember everything, so what sticks NEGATIVITY BIAS Negative events and feelings stay with us longer than positive ones SPACING EFFECT We learn better in bits and chunks over time rather than all at once IMPLICIT STEREOTYPE Learned associations between various qualities and social categories PEAK-END RULE @curio_research People judge an experience based in how they felt at its most intense point rather than overall www.curioresearch.net

18 Let’s Explore Biases with Cards! This will probably be fun. Maybe. No promises. www.curioresearch.net Photo by Jen Theodore on Unsplash

19 Avoiding Biased Decisions Move at a steady pace and make good choices @curio_research www.curioresearch.net

20 REMEMBER Bias is unavoidable, but it is manageable @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
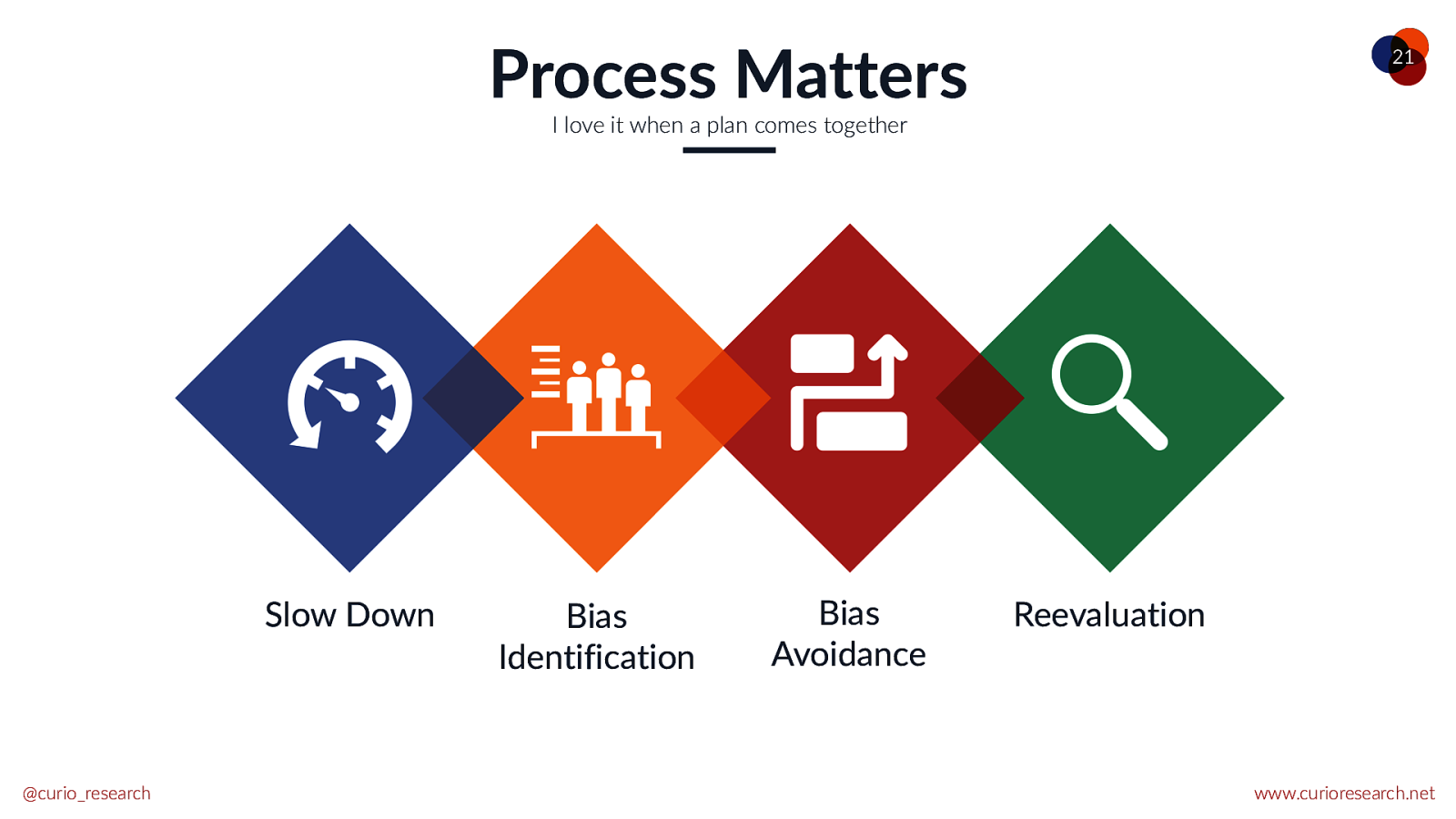
Process Matters 21 I love it when a plan comes together Slow Down @curio_research Bias Identification Bias Avoidance Reevaluation www.curioresearch.net

22 B i a s e s A r e Av o i d e d o n P u r p o s e , Not By Accident @curio_research www.curioresearch.net

Take Good Notes 23 It works for Comey, it will work for you Write it down or it never happened Get agreement on goals What is the understanding of risk? Revisit after the decision is in action @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
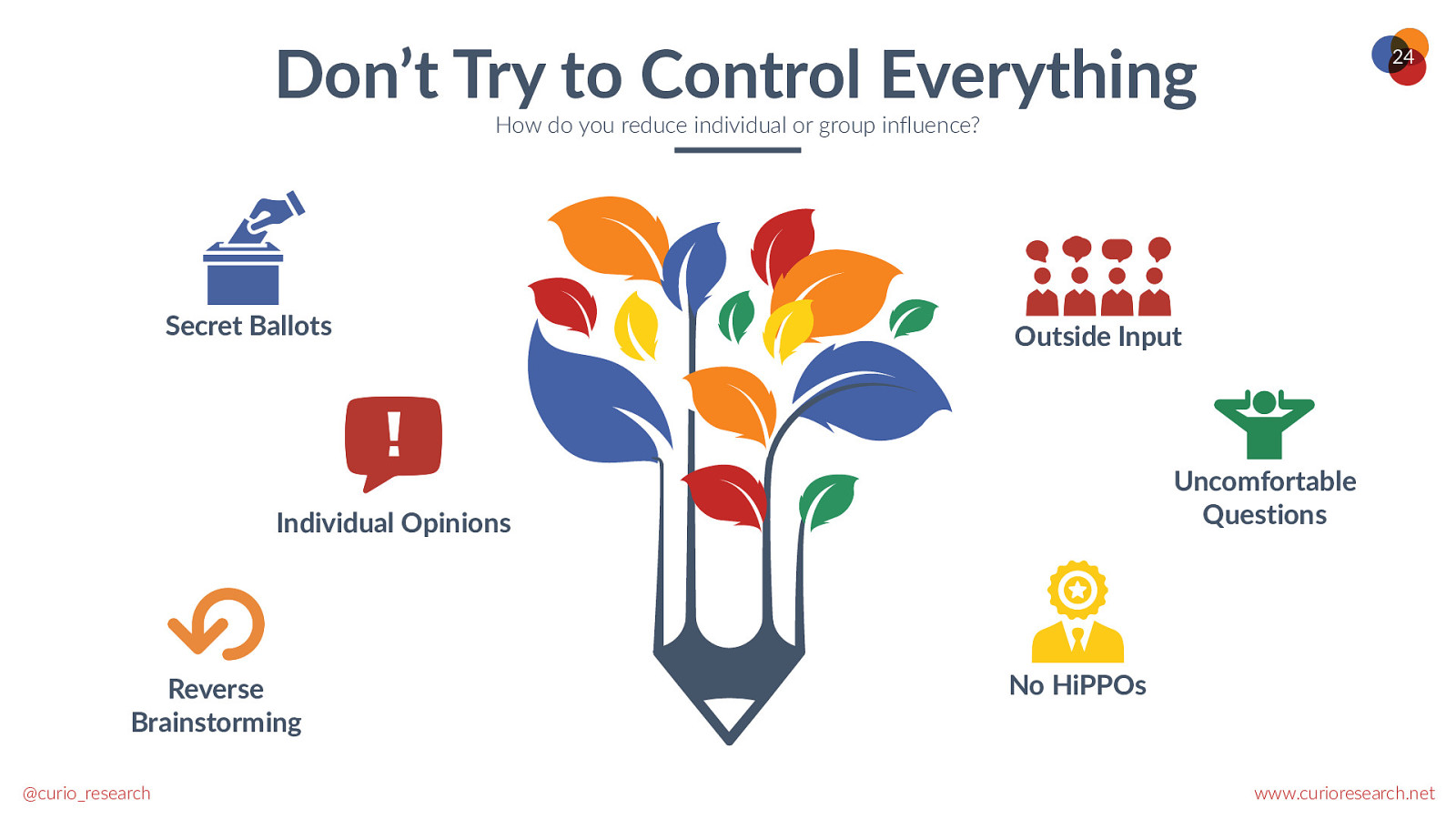
Don’t Try to Control Everything 24 How do you reduce individual or group influence? Secret Ballots Outside Input Uncomfortable Questions Individual Opinions Reverse Brainstorming @curio_research No HiPPOs www.curioresearch.net

25 If we are all in agreement on the decision - then I propose we postpone further discussion of this matter until our next meeting to give ourselves time to develop disagreement and perhaps gain some understanding of what the decision is all about. A L F R E D P. S LOA N CEO of GM @curio_research www.curioresearch.net

26 Hypotheses were made to be disproved •Researchers don’t try to prove their theories. They try to disprove them. •If an idea can withstand counter evidence, it’s probably a good idea. @curio_research www.curioresearch.net
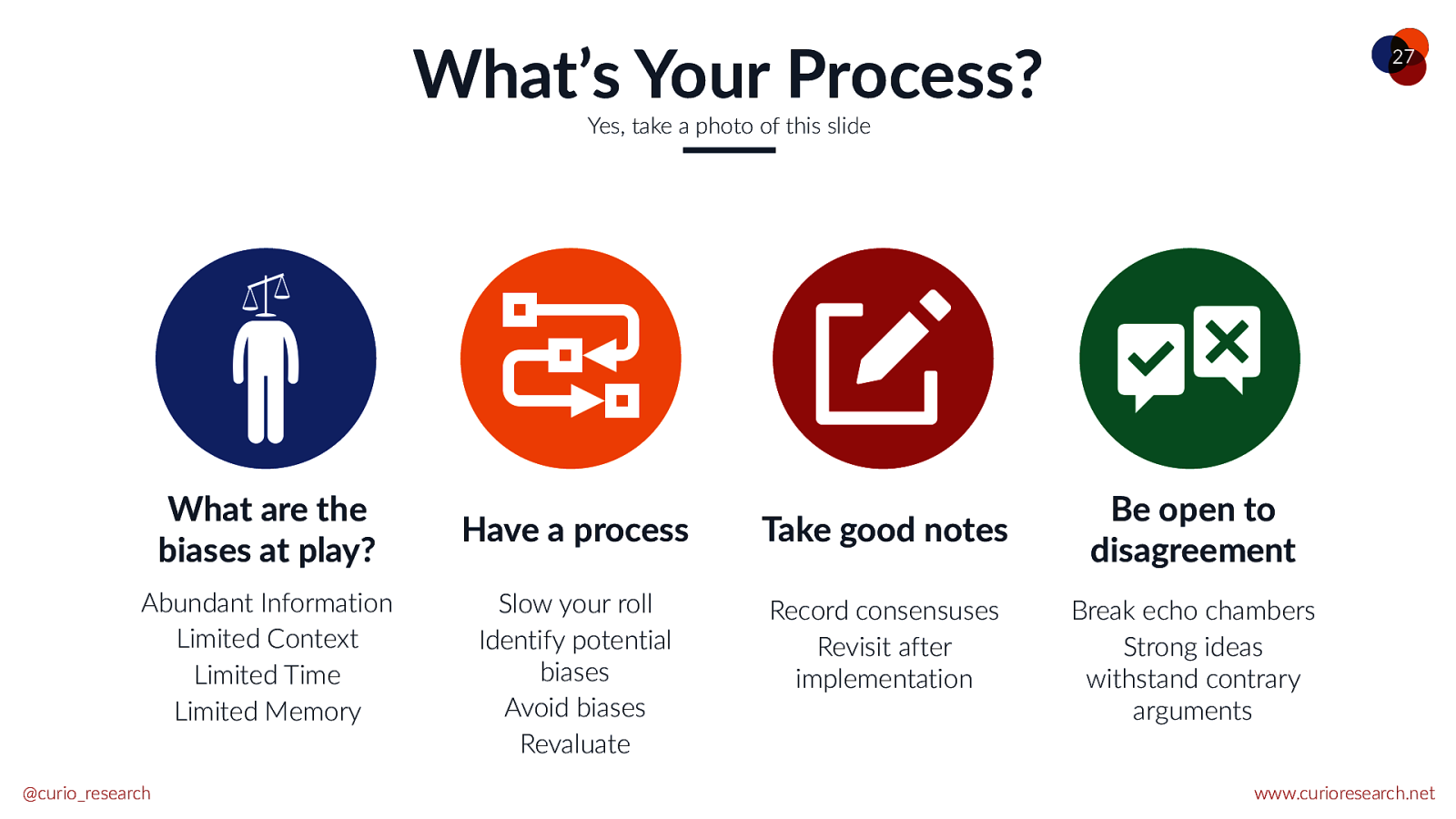
What’s Your Process? 27 Yes, take a photo of this slide What are the biases at play? Abundant Information Limited Context Limited Time Limited Memory @curio_research Have a process Take good notes Slow your roll Identify potential biases Avoid biases Revaluate Record consensuses Revisit after implementation Be open to disagreement Break echo chambers Strong ideas withstand contrary arguments www.curioresearch.net

28 THANK YOU LAUREN ISAACSON @CURIO_RESEARCH WWW.CURIORESEARCH.NET @curio_research www.curioresearch.net