Efficient & Convenient How To Build Big Storage As A Cloud Erik Riedel, PhD Technology & Architecture Cloud Infrastructure Group EMC © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 1
A presentation at MSST Conference in April 2012 in Pacific Grove, CA, USA by erik riedel

Efficient & Convenient How To Build Big Storage As A Cloud Erik Riedel, PhD Technology & Architecture Cloud Infrastructure Group EMC © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 1


from flickr/Blude, floppy disks for breakfast
from flickr/oskay, Raw materials
from flickr/jurvetson, SGI Detritus

• Load It Into A Rack from flickr/erinhillaw, Math/Physics Bike Rack and flickr/csavage31, Bike Racks

Conclusion • The “cloud” makes it more convenient to build a lot of applications more quickly – abstraction; consolidation; self-service • Applications that interact with a lot of data are a lot more interesting – analytics; big data; insights; collaboration • BUT many applications aren’t used very often, or not for very long – consolidation; virtualization; multi-tenancy • AND much (most?) stored data will never be accessed again
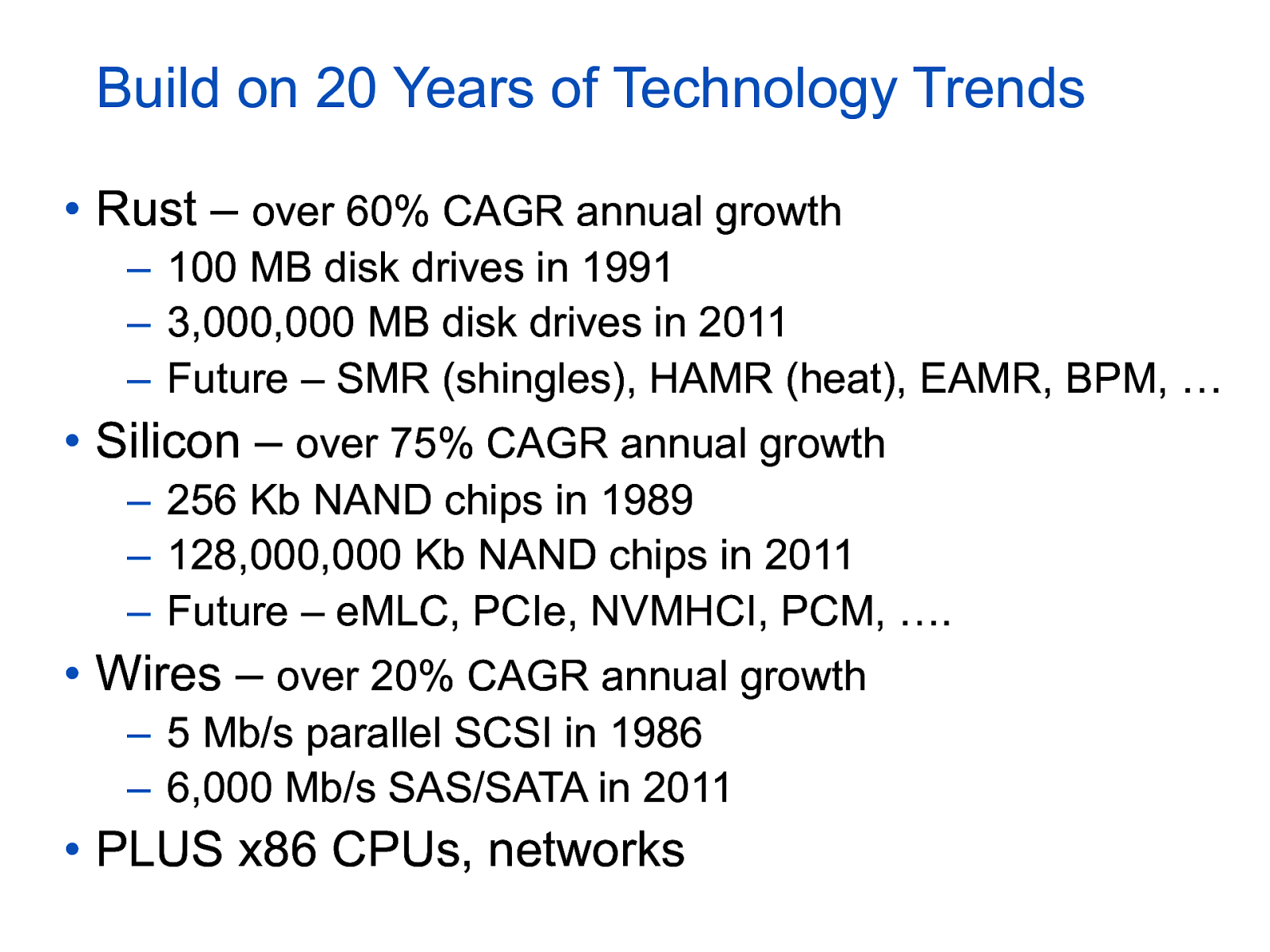
Build on 20 Years of Technology Trends • Rust – over 60% CAGR annual growth – 100 MB disk drives in 1991 – 3,000,000 MB disk drives in 2011 – Future – SMR (shingles), HAMR (heat), EAMR, BPM, … • Silicon – over 75% CAGR annual growth – 256 Kb NAND chips in 1989 – 128,000,000 Kb NAND chips in 2011 – Future – eMLC, PCIe, NVMHCI, PCM, …. • Wires – over 20% CAGR annual growth – 5 Mb/s parallel SCSI in 1986 – 6,000 Mb/s SAS/SATA in 2011 • PLUS x86 CPUs, networks

Build on 20 Years of Storage Research • APIs vs. mount points – “no slashes required” – blocks vs. files vs. objects vs. “APIs” • App-driven and policy-automated GUI – self-configuring, self-organizing, self-tuning, self-* • Built in data services – self-healing RAID • Unlimited namespace, dynamic – billions and billions of objects, large and small • Native multi-tenancy – security/auth, monitoring, resource isolation /

• The Cloud • Big Data • The Changes • Convenience – Easier • Efficiency – Bigger • Agility – Faster

The Cloud © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 11

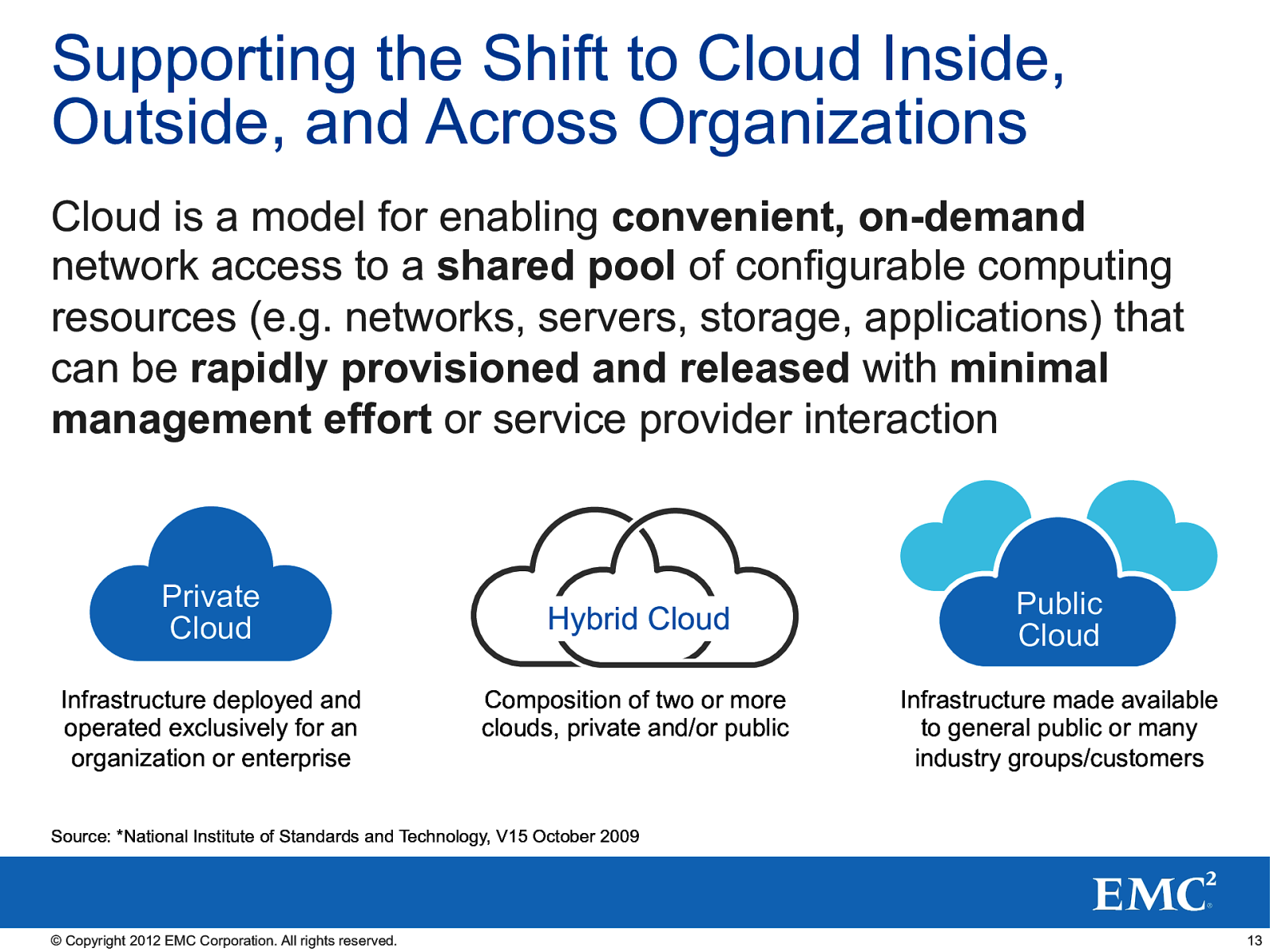
Supporting the Shift to Cloud Inside, Outside, and Across Organizations Cloud is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g. networks, servers, storage, applications) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction Private Cloud Infrastructure deployed and operated exclusively for an organization or enterprise Hybrid Cloud Composition of two or more clouds, private and/or public Public Cloud Infrastructure made available to general public or many industry groups/customers Source: *National Institute of Standards and Technology, V15 October 2009 © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 13
The Changes © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 14

Cloud is not about technology change, it’s about organizational change (not new to HPC users) © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 15
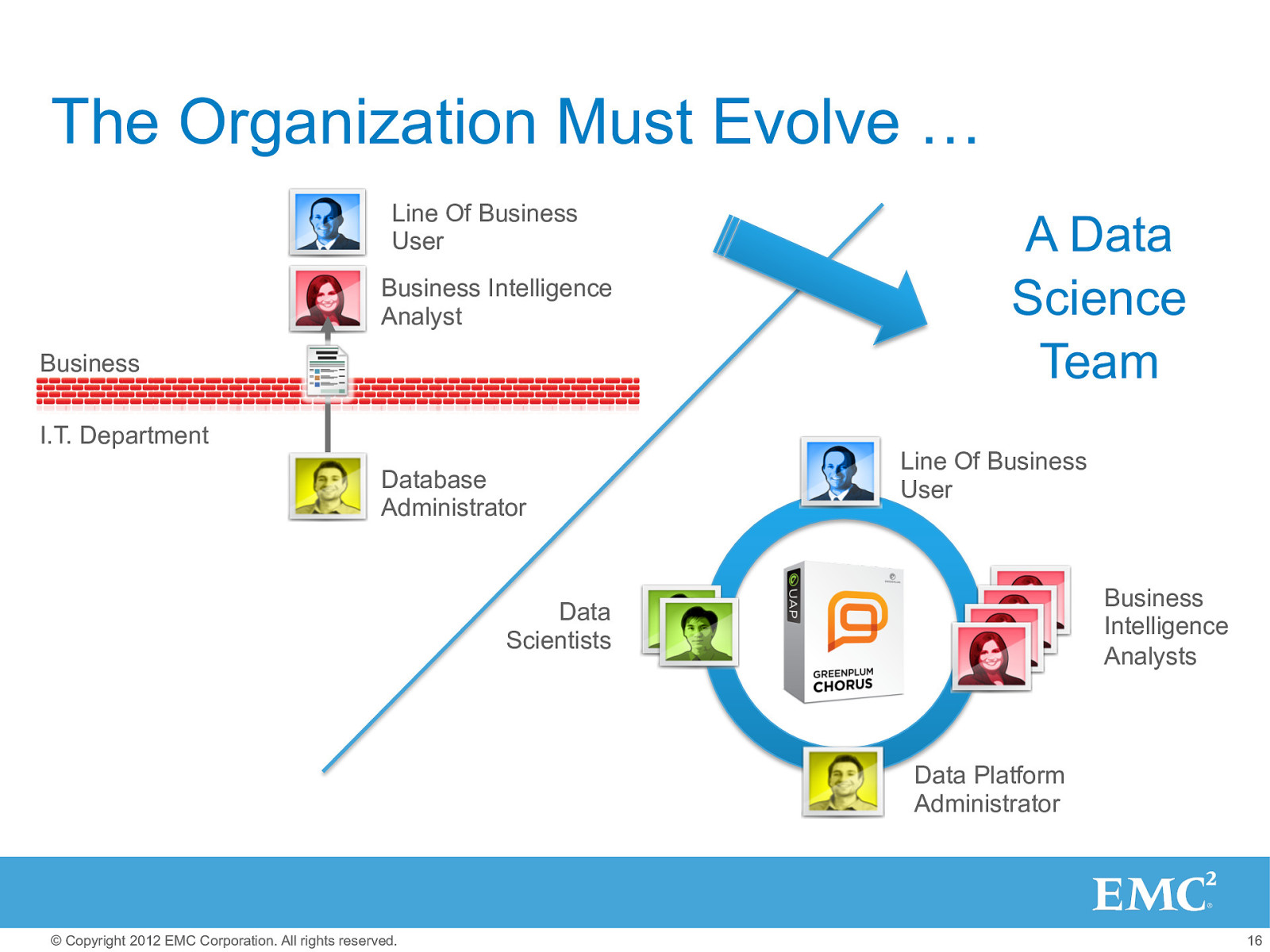
The Organization Must Evolve … Line Of Business User Business Intelligence Analyst Business I.T. Department Database Administrator A Data Science Team Line Of Business User Business Intelligence Analysts Data Scientists Data Platform Administrator © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 16

From September 2010, SNIA CloudBurst keynote by Geoffrey Moore

Why should employees accept a 50% reduction in their productivity when they come to the office on Monday morning? On the weekend, Google can answer any question I have, on Monday, I can’t get the answer to “who are my five biggest customers?” On the weekend, someone from my high school can find me and try to be my friend, on Monday, I can’t find my VP of Finance. Geoff Moore, Author, Crossing the Chasm SNIA CloudBurst, September 2010

Convenience Efficiency Agility © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 19


It’s not possible to “start over” and re-write all applications using scale-out design patterns in the first few months of a cloud deployment, but it is possible to adapt many legacy applications with the help of virtualization, so cloud infrastructure can support and enable both development models, including mixing the two.
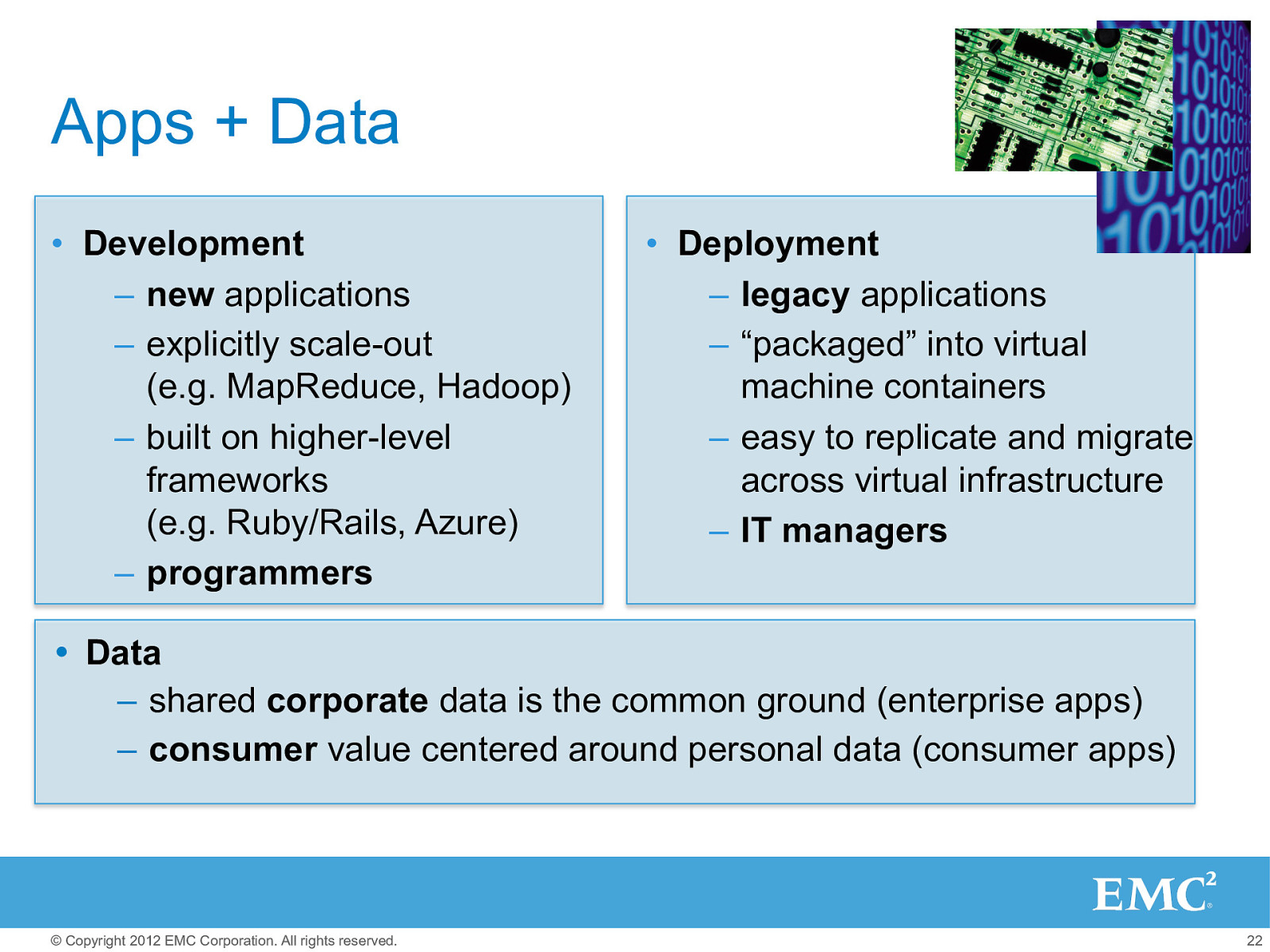
Apps + Data • Development – new applications – explicitly scale-out (e.g. MapReduce, Hadoop) – built on higher-level frameworks (e.g. Ruby/Rails, Azure) – programmers • Deployment – legacy applications – “packaged” into virtual machine containers – easy to replicate and migrate across virtual infrastructure – IT managers Data – shared corporate data is the common ground (enterprise apps) – consumer value centered around personal data (consumer apps) © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 22
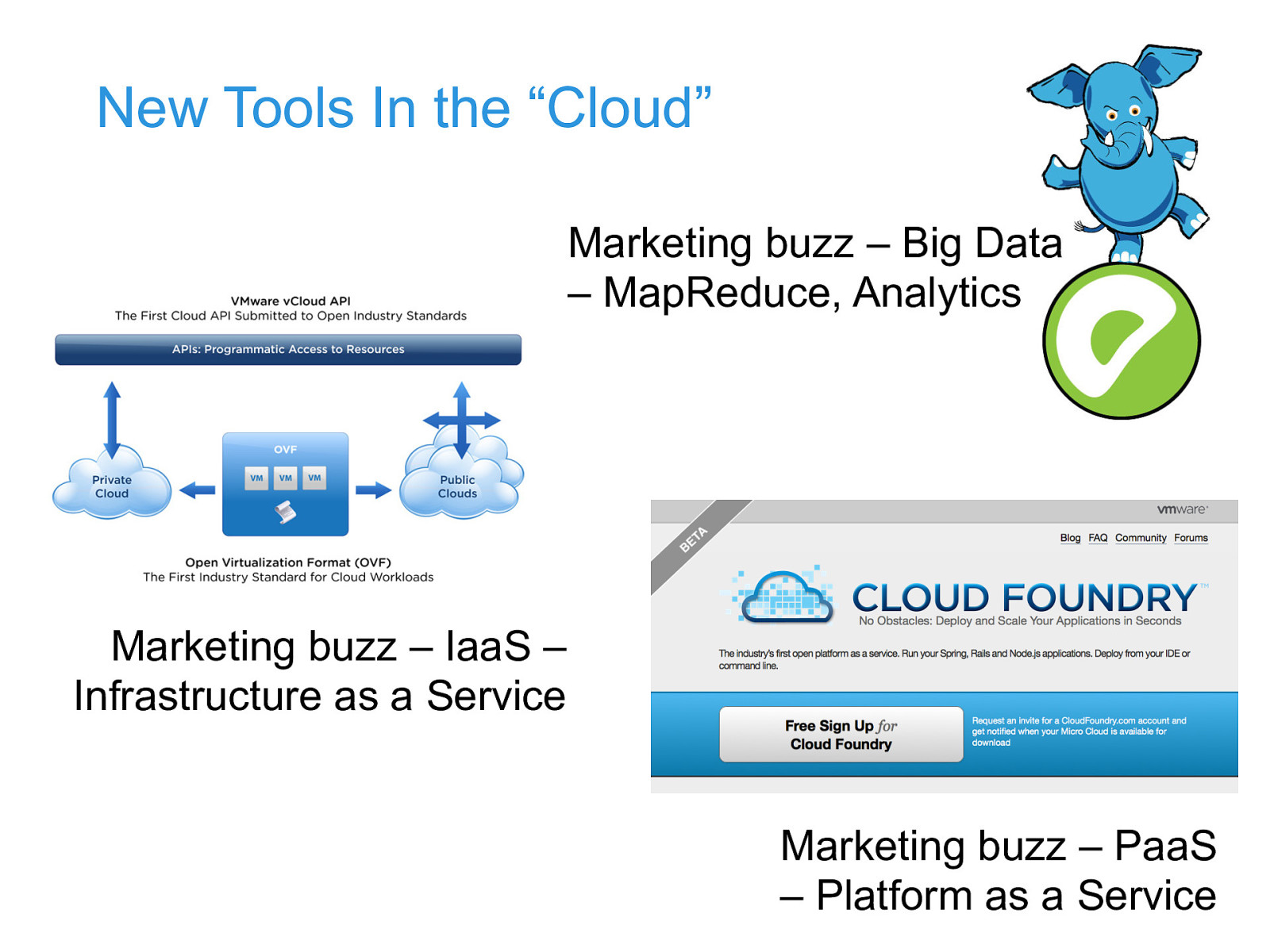
New Tools In the “Cloud” Marketing buzz – Big Data – MapReduce, Analytics Marketing buzz – IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service Marketing buzz – PaaS – Platform as a Service

New Tools in the “Cloud” (2) • Key takeaways – IaaS and PaaS and MapReduce are “closed loop” infrastructures – allows cross-layer optimization – apps cannot be deployed except at the “direction” of the system – allows end-to-end optimization – configuration, scheduling, – logging and monitoring are constant • needed to get high utilization rates ($$) • needed to send out bills ($$) • need high rates of “multi-tenancy” to be efficient ($$) – this leads to a significant level of “predictability”

Convenience Efficiency Agility © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 25

Most Data Is Idle • About 80% of stored data will never be accessed again • Disk drives have long been designed around this key fact of the digital world • Amortize a relatively small amount of expensive read/write electronics and fancy material science over a large and cheap magnetic media
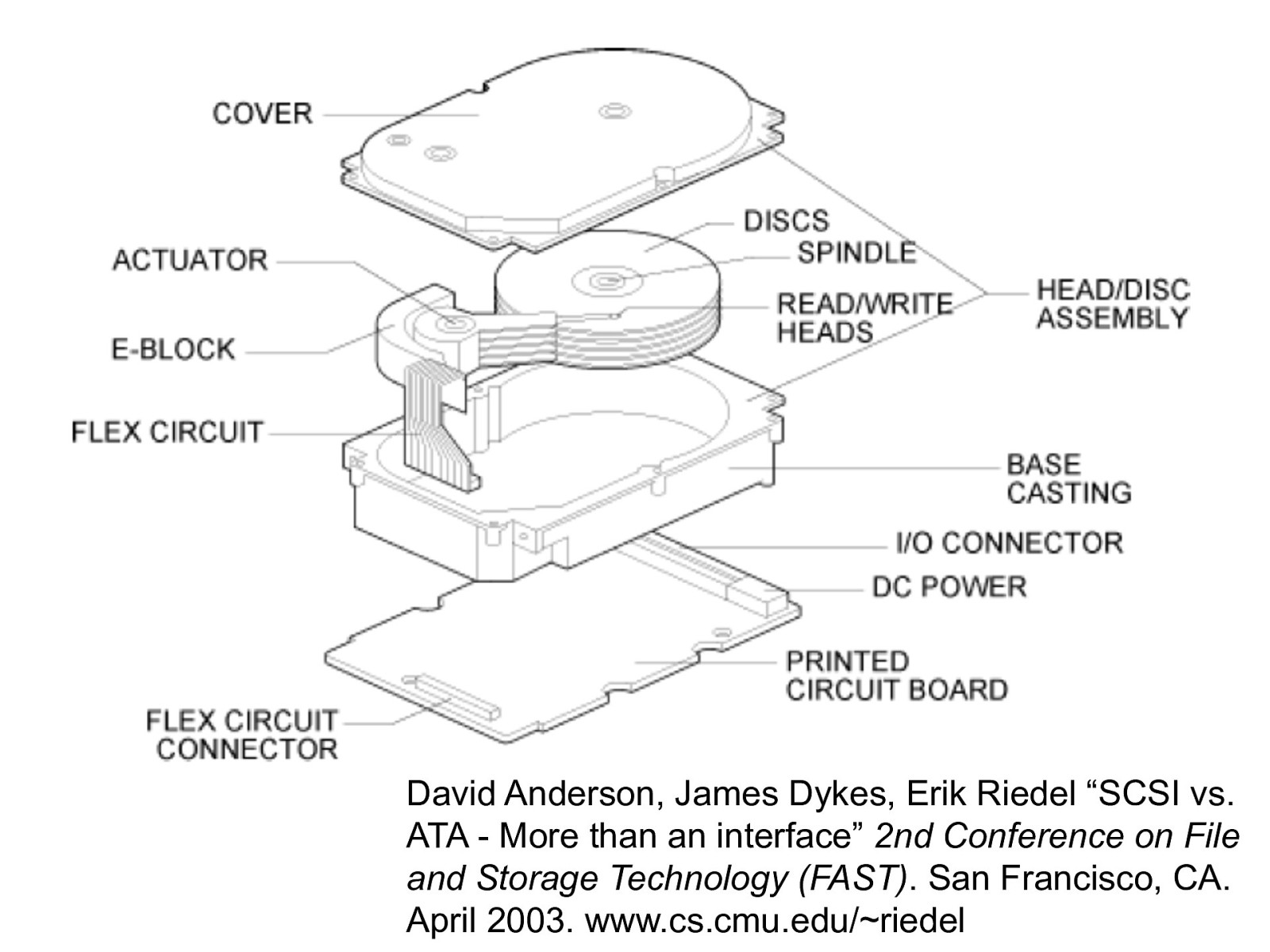
David Anderson, James Dykes, Erik Riedel “SCSI vs. ATA - More than an interface” 2nd Conference on File and Storage Technology (FAST). San Francisco, CA. April 2003. www.cs.cmu.edu/~riedel
Consumer Example (At My House) Sid The Science Kid Super Why! Meet the Press Dinosaur Train Nova Steelers Games Baby Einstein
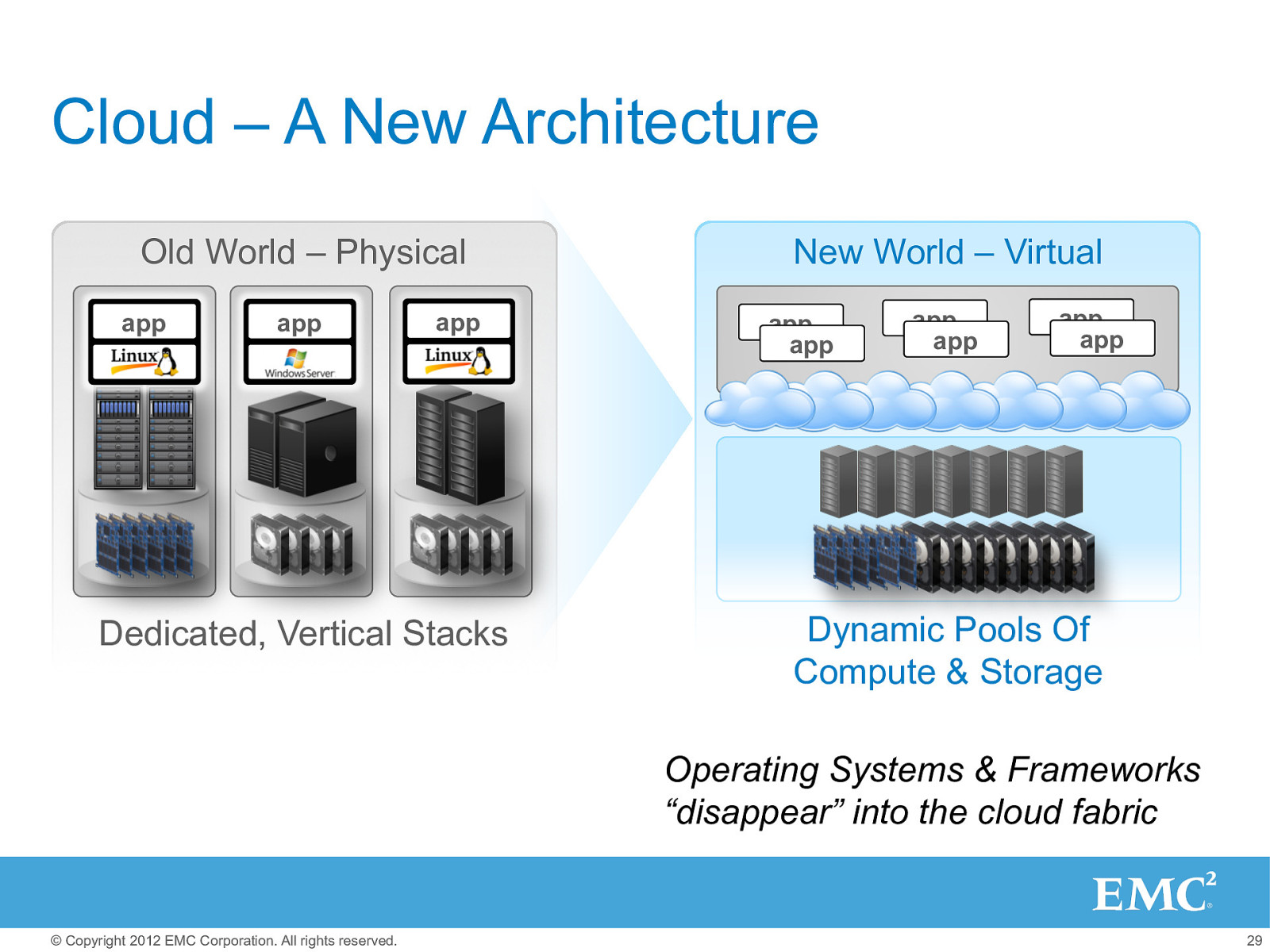
Cloud – A New Architecture Old World – Physical app app app Dedicated, Vertical Stacks New World – Virtual app app app app app app Dynamic Pools Of Compute & Storage Operating Systems & Frameworks “disappear” into the cloud fabric © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 29
• high capacity drives (as many as possible) • x86 servers/controllers (as few as possible) • SAS backplanes/cables (not too many, not too few) Promo Code 1 Front (tray pulled out) © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 30
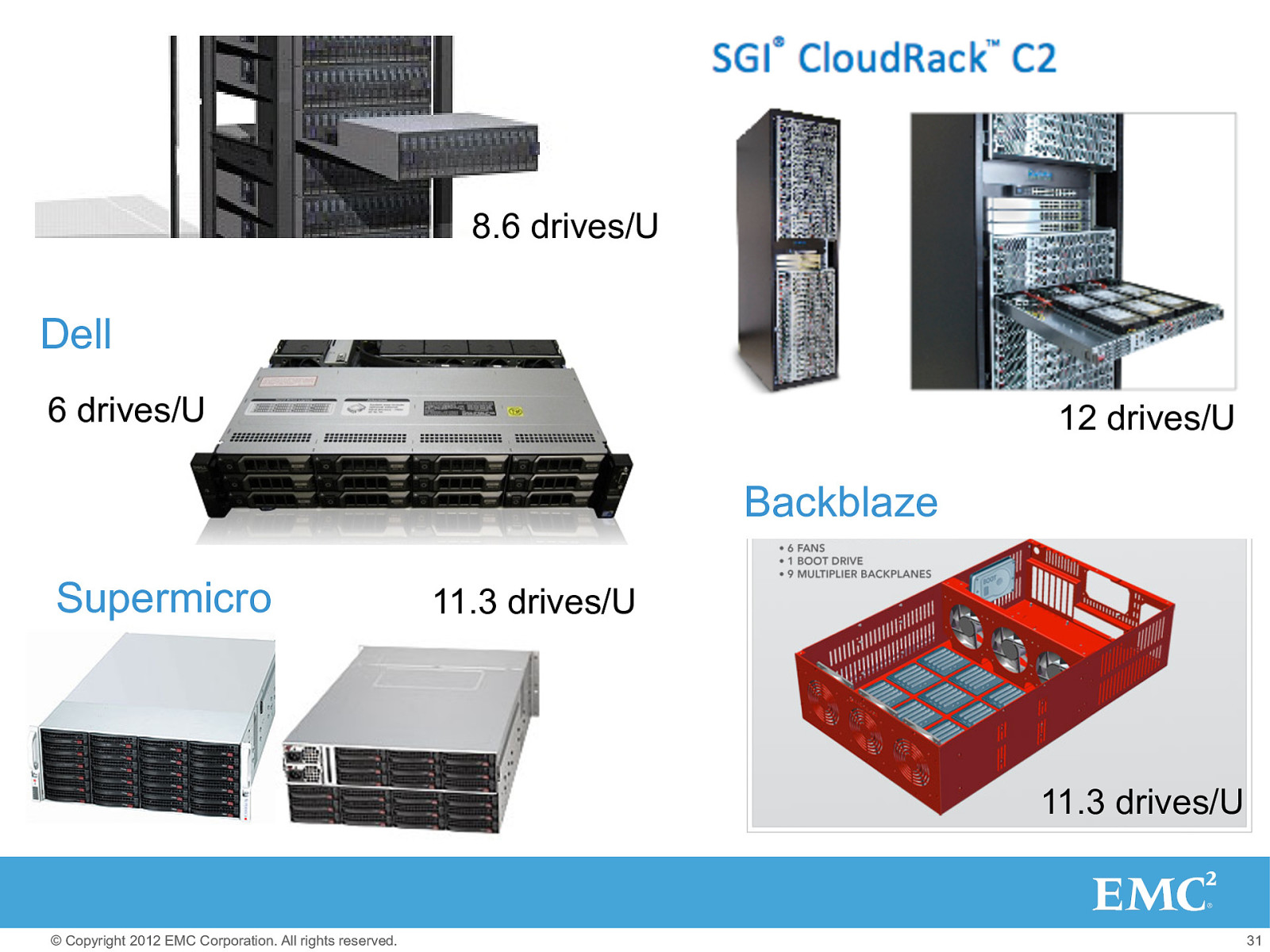
8.6 drives/U Dell 6 drives/U 12 drives/U Promo Code 1 Front (tray pulled out) Supermicro Backblaze 11.3 drives/U 11.3 drives/U © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 31
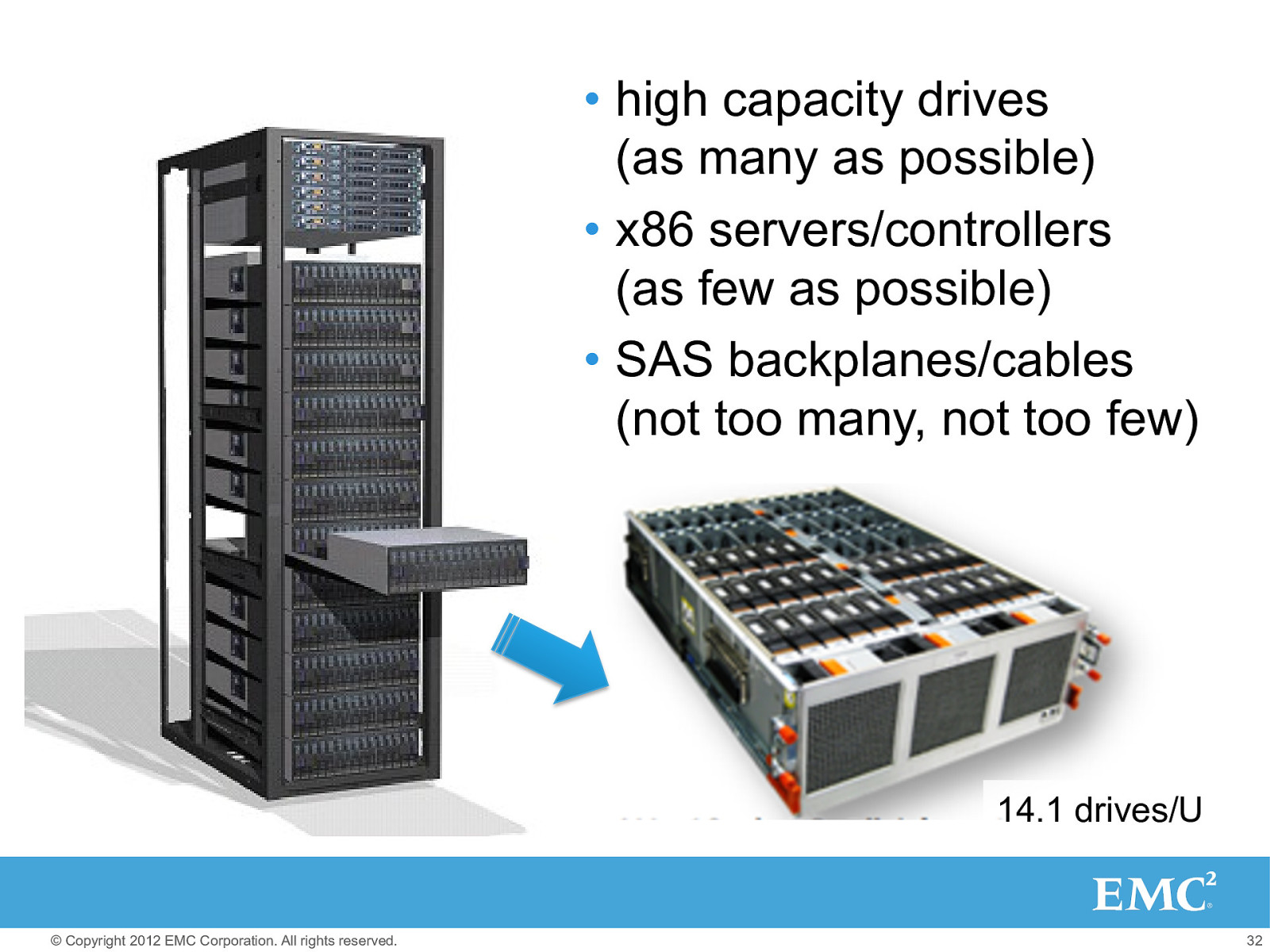
• high capacity drives (as many as possible) • x86 servers/controllers (as few as possible) • SAS backplanes/cables (not too many, not too few) 14.1 drives/U Promo Code 1 Front (tray pulled out) © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 32

Convenience Efficiency Agility © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 33

Most Data Access Is Predictable • Caching • Prefetching • Tiering • Staging • Hierarchical Storage Mgmt • all these tools have been known for years • just need to open our toolbox, sharpen some of them to apply to today’s infrastructure/apps

Get Predictability Into Storage • Key challenge is how to translate what “the system” knows about apps and behaviors and “SLAs” into guidance for our system-level tools (caching, prefetching, tiering, etc.) • Secondary challenge is avoiding “surprises” – where performance or availability or durability don’t meet the SLAs (“quality of service”) • Good news is that the new infrastructures have some powerful new ways to help us

One Example New Tool – Stunning picture from flickr/Yohei Yamashita, stun gun • “The amount of time the virtual machine is stunned is dependent on the amount of memory to be written to disk for such an operation, and the speed and responsiveness of the datastore’s backing storage.” – VMware KnowledgeBase http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do? language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1013163
What About Flash? © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 37

What About Flash? • About 80% of stored data will never be accessed again • About 80% of the rest will be accessed predictably • That leaves (maybe) 4% of stored data that potentially requires “quick” random access • => Buy as much flash as you can afford, use disks for the rest
What About Flash – How Much? • 1.2 million PB estimated total data in 2010 • 25% unique => leaves 300,000 PB • 80% idle => leaves 60,000 PB • 80% predictable => leaves 12,000 PB • at $1/GB for flash, that requires $12b • is that affordable? • (note – the world bought ~$40b of HDD in 2010) www.zdnet.com/blog/service-oriented/size-of-the-data-universe-12-zettabytes-and-growing-fast/4750 www.computerworld.com/s/article/9180943/NAND_flash_memory_pricing_to_plummet_to_1_per_GB recently – “the price of flash has not been dropping as fast as the suppliers predicted”, August 2011

A Few Words About Software © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 40
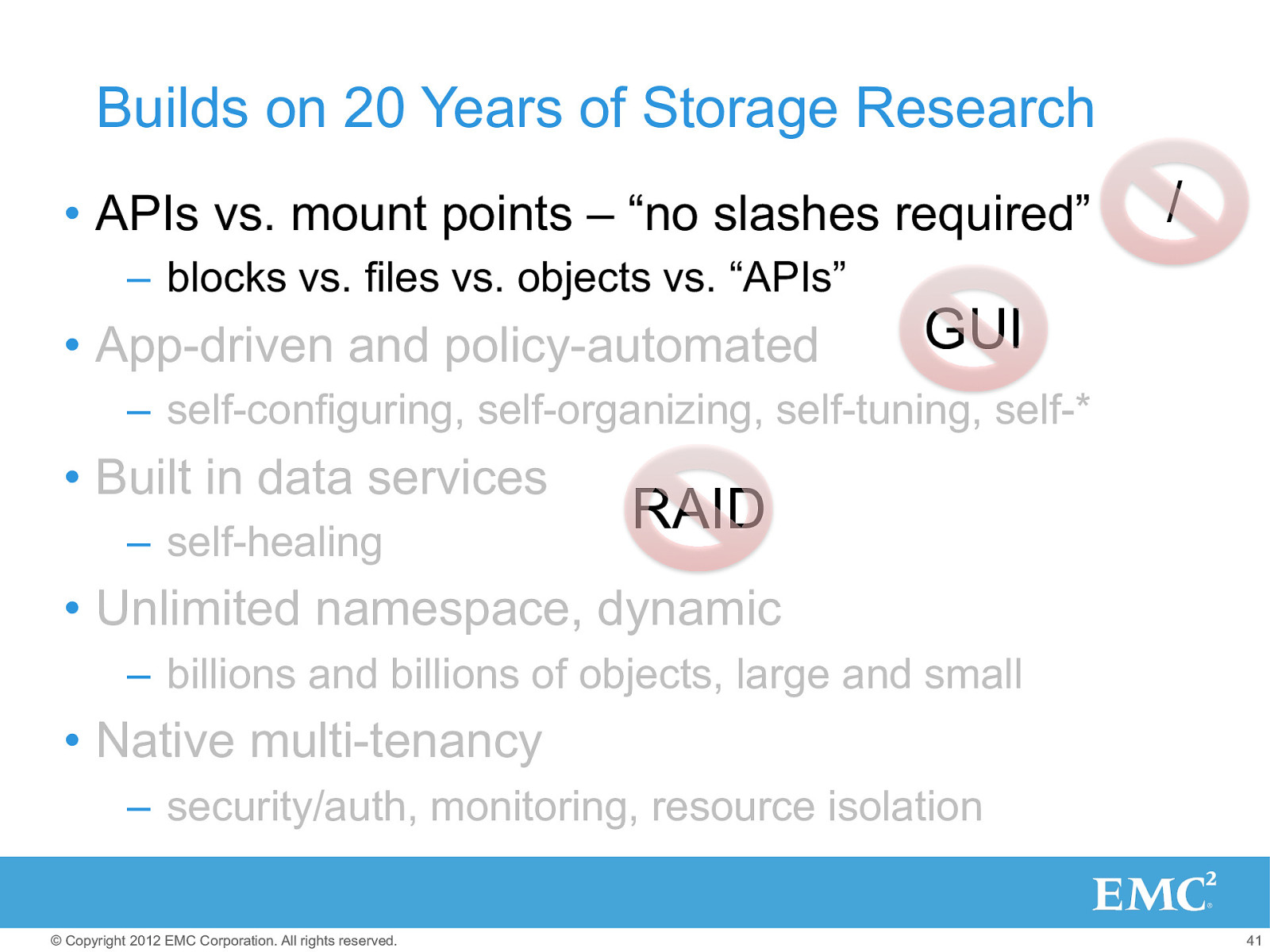
Builds on 20 Years of Storage Research • APIs vs. mount points – “no slashes required” – blocks vs. files vs. objects vs. “APIs” • App-driven and policy-automated / GUI – self-configuring, self-organizing, self-tuning, self-* • Built in data services – self-healing RAID • Unlimited namespace, dynamic – billions and billions of objects, large and small • Native multi-tenancy – security/auth, monitoring, resource isolation © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 41

Summary What Changes © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 42

Conclusion • The “cloud” makes it more convenient to build a lot of applications more quickly – abstraction; consolidation; self-service • Applications that interact with a lot of data are a lot more interesting – analytics; big data; insights; collaboration • BUT many applications aren’t used very often, or not for very long – consolidation; virtualization; multi-tenancy • AND much (most?) stored data will never be accessed again

Call To Action • Standards for interop in clouds (CDMI) and long-term data preservation (LTR) – www.snia.org/forums/csi – www.snia.org/sites/default/files/LTRcloud.pdf • Analytics and Big Data Committee (ABDC) – www.snia.org/forums/abdc • Green storage (GSI) and Power Efficiency Measurement (Emerald) – www.snia.org/forums/green sniaemerald.com/ • ENERGY STAR for Data Center Storage (EPA) – www.energystar.gov/index.cfm?c=new_specs.enterprise_storage • Open Compute Project – opencompute.org/

© Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 45

Questions? © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 46


References • Geoff Moore “Partly Cloudy: Business and Innovation in the Internet Era” September 2010 – www.snia.org/cloud/Cloudburst/Moore_SNIA_Keynote.pdf • Peter Mell & Tim Grance “The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing” October 2009 – csrc.nist.gov/groups/SNS/cloud-computing/cloud-def-v15.doc • EMC Atmos – BIG. SMART. ELASTIC. – www.emc.com/atmos – www.youtube.com/watch?v=LANlUxC1yQY © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 48

Big Data © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 49

IN 2010 THE DIGITAL UNIVERSE WAS 1.2 ZETTABYTES 1,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 Source: 2010 IDC Digital Universe Study © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved.

Data Sources Are Expanding INFORMATION IN THE ENTERPRISE WILL GROW 50X IN THE NEXT 10 YEARS Source: 2011 IDC Digital Universe Study © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 51
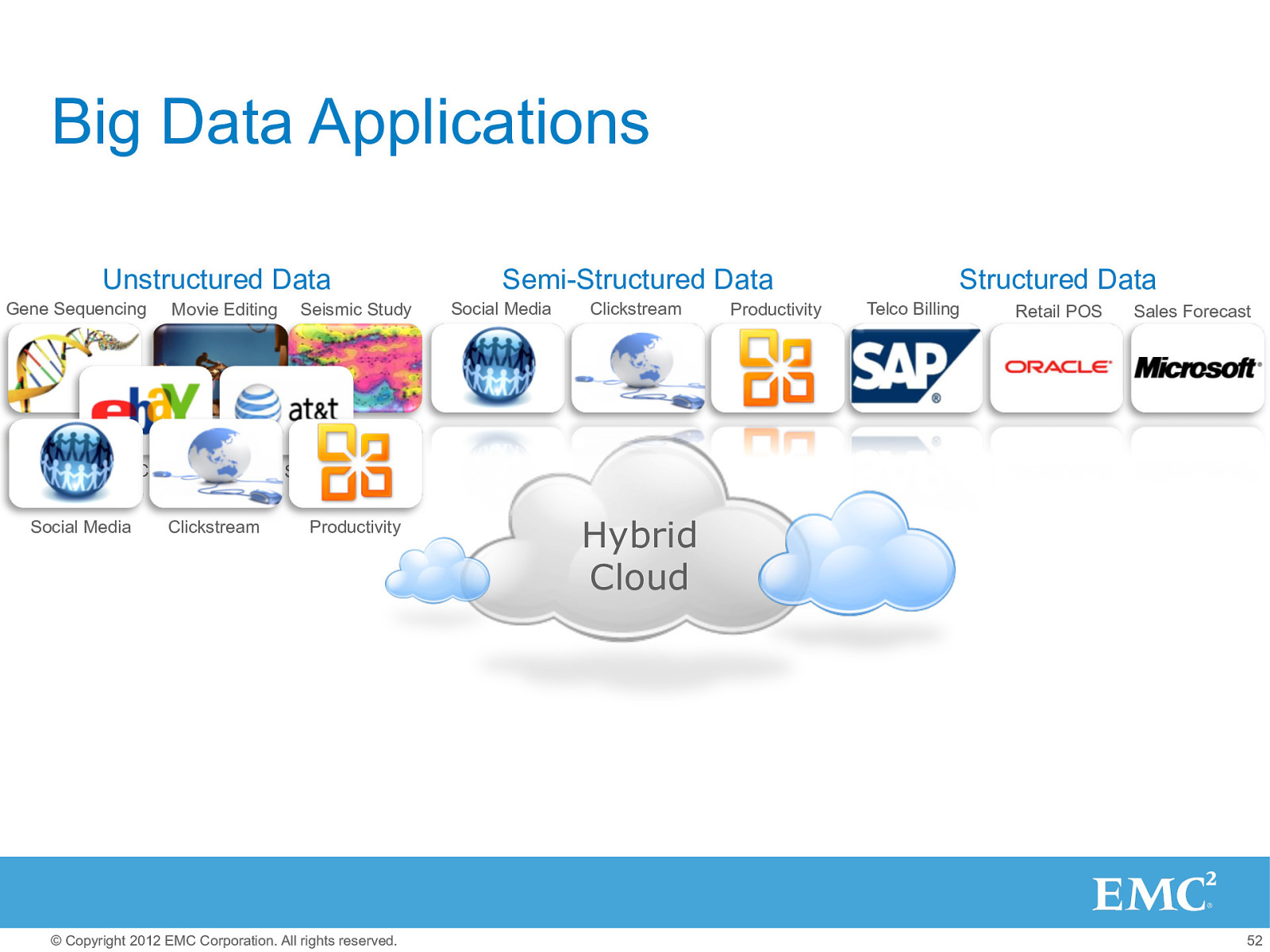
Big Data Applications Unstructured Data Gene Sequencing Movie Editing Web Content Social Media Seismic Study Semi-Structured Data Social Media Clickstream Productivity Structured Data Telco Billing Retail POS Sales Forecast Storage Services Clickstream Productivity © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. Hybrid Cloud 52
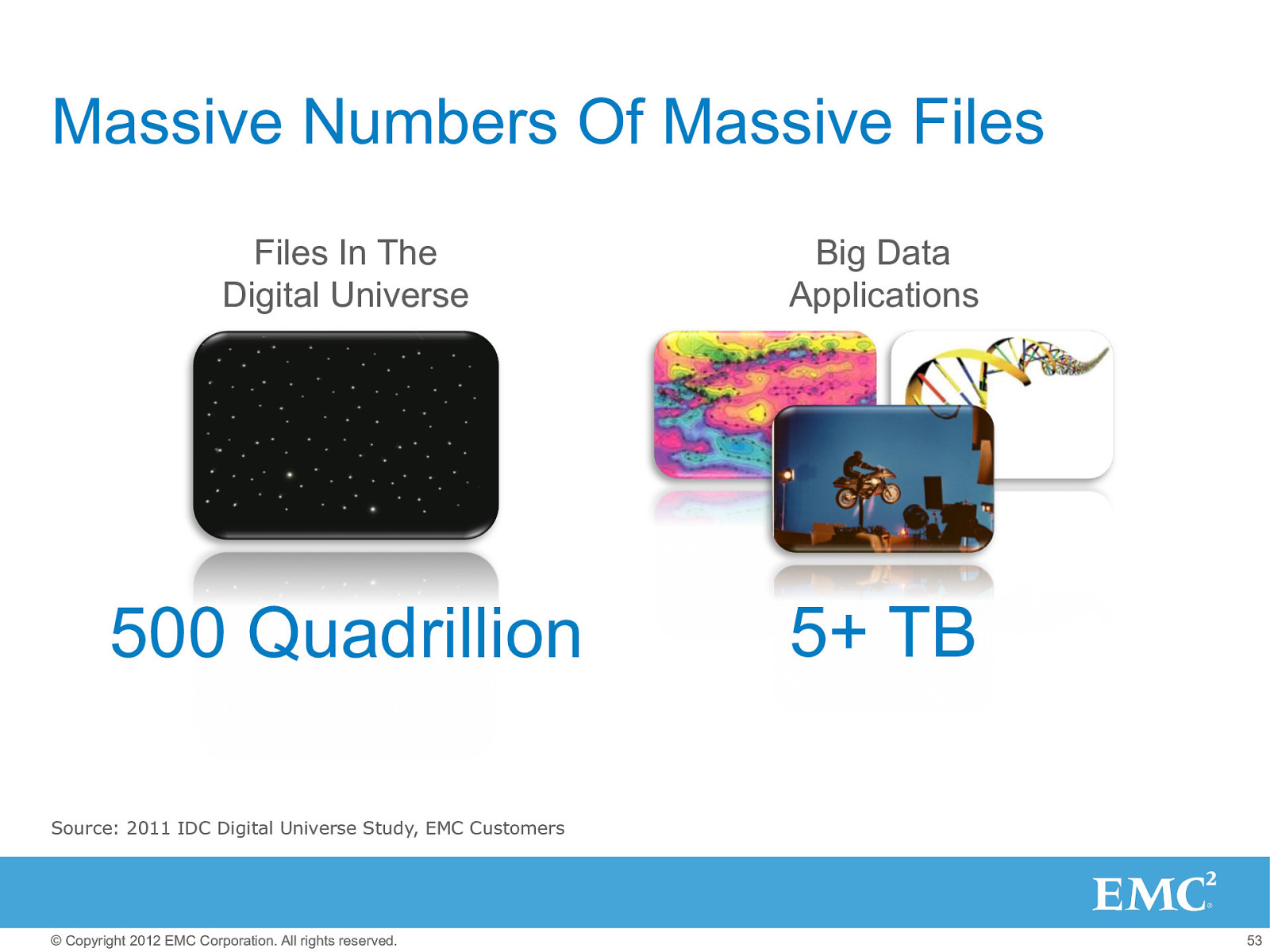
Massive Numbers Of Massive Files Files In The Digital Universe Big Data Applications 500 Quadrillion 5+ TB Source: 2011 IDC Digital Universe Study, EMC Customers © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 53
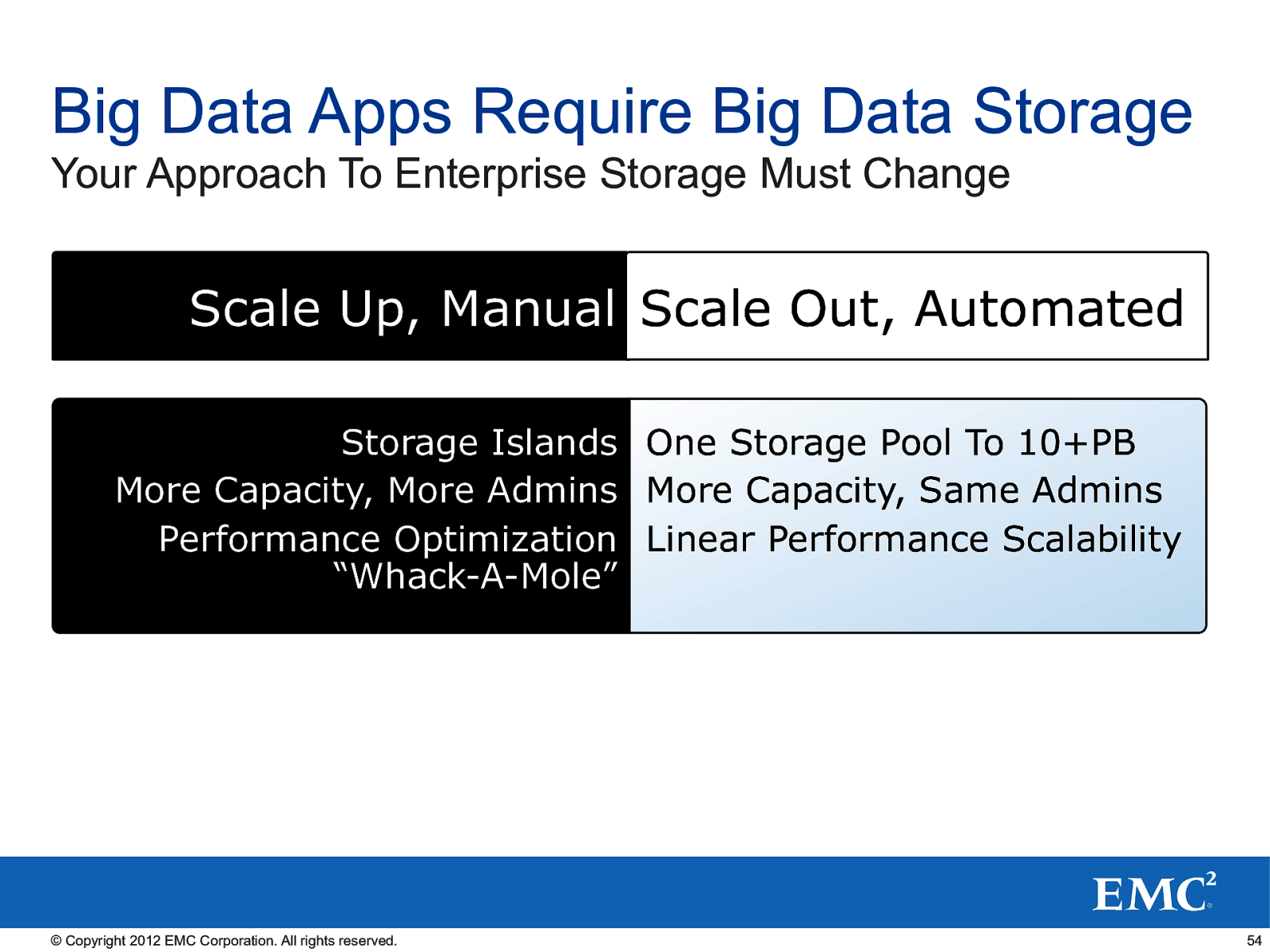
Big Data Apps Require Big Data Storage Your Approach To Enterprise Storage Must Change Scale Up, Manual Scale Out, Automated Storage Islands One Storage Pool To 10+PB More Capacity, More Admins More Capacity, Same Admins Performance Optimization Linear Performance Scalability “Whack-A-Mole” © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 54

EMC Atmos BIG. SMART. ELASTIC. www.emc.com/atmos www.youtube.com/watch?v=LANlUxC1yQY © Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved. 55