SCSI vs. ATA – More than an interface Dave Anderson, Jim Dykes, Erik Riedel Seagate Research April 2003
A presentation at 2nd Conference on File and Storage Technology (FAST) in April 2003 in San Francisco, CA, USA by erik riedel

SCSI vs. ATA – More than an interface Dave Anderson, Jim Dykes, Erik Riedel Seagate Research April 2003

Outline Marketplace • personal – desktop, low-end servers • enterprise – servers, workstations, arrays • consumer – appliances • mobile – laptops Mechanics & Electronics • choices, comparison Performance • the direct impact Reliability • factors Summary SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
Disc characteristics User-visible characteristics • Data rate ~ (2πr) x (density) x (rpm) • Capacity ~ (πr2) x (density) • Seek time ~ r Internal characteristics • Areal density – density • Platter size – r • Spindle speed – rpm SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
Areal density higher density, higher data rate Data rate ~ (2πr) x (density) x (rpm) Capacity ~ (πr2) x (density) Seek time ~ r higher density, higher capacity Areal density – density • how many bits you can squeeze in The bad news • requires more signal processing • tolerates less “noise” • harder to do track-following (servo) SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
Platter size larger platter, higher data rate Data rate ~ (2πr) x (density) x (rpm) Capacity ~ (πr2) x (density) larger platter, higher capacity Seek time ~ r Platter size – r • large, smaller, smallest bad news – larger platter, higher seek time More bad news • larger platter, more power SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology

Spindle speed faster platter, higher data rate Data rate ~ (2πr) x (density) x (rpm) Capacity ~ (πr2) x (density) Seek time ~ r Spindle speed – rpm • slow, fast, very fast The bad news • creates more “noise” • more (bad) vibration • more speed, more power SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
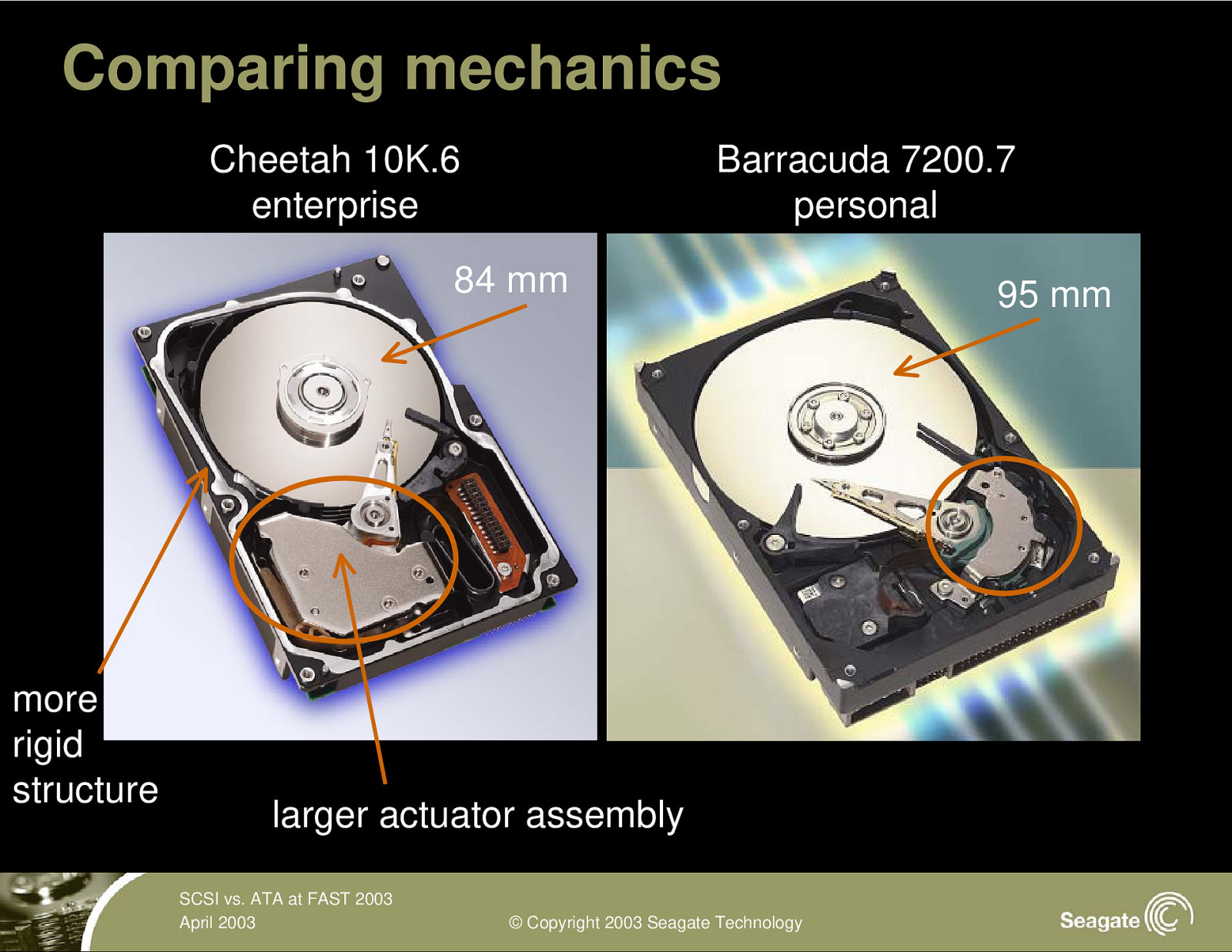
Comparing mechanics Cheetah 10K.6 enterprise Barracuda 7200.7 personal 84 mm more rigid structure larger actuator assembly SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology 95 mm
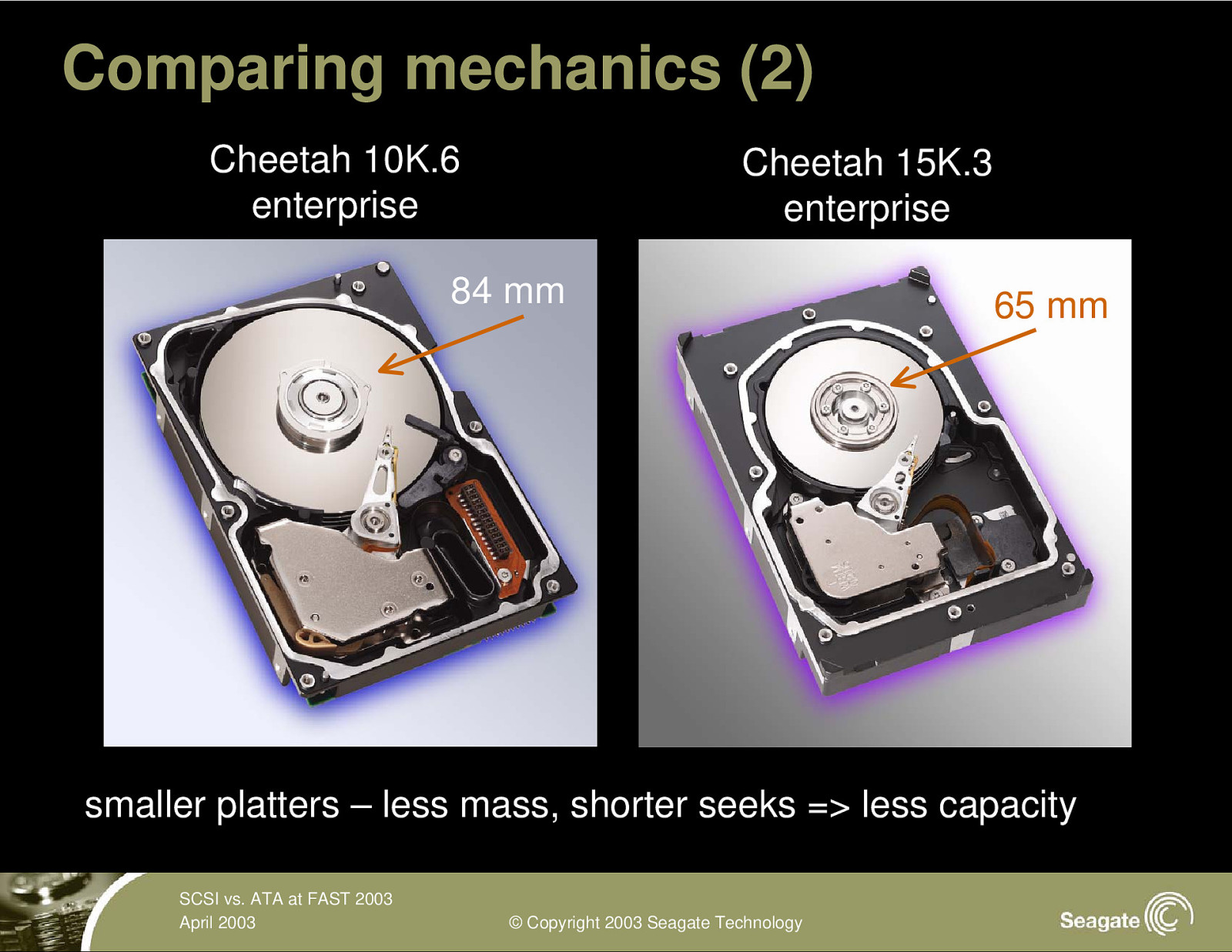
Comparing mechanics (2) Cheetah 10K.6 enterprise Cheetah 15K.3 enterprise 84 mm 65 mm smaller platters – less mass, shorter seeks => less capacity SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology

Mechanics summary Basic design choices • how high data rate • how much capacity • how small seek time Each one affects which parts you pull off the shelf • how you put them together depends on how they will be used • some decisions driven by the marketplace • some driven by cost SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology

Outline Marketplace • personal • enterprise Mechanics • choices – pick your parts • the choices made to date – comparison Electronics • comparison Performance • the direct impact Summary SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
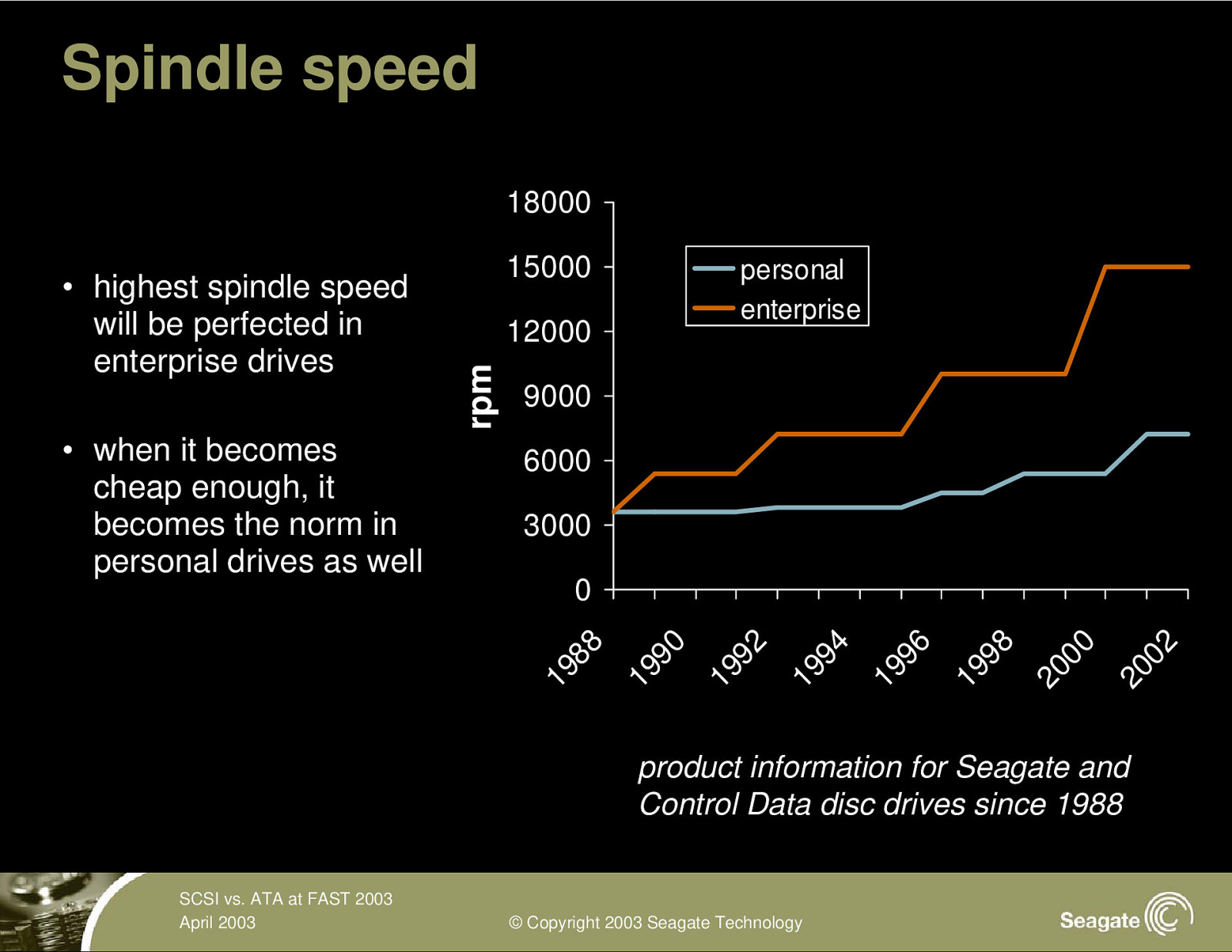
Spindle speed 18000 personal enterprise 12000 9000 6000 3000 20 02 20 00 19 98 19 96 19 94 19 92 19 90 0 19 88 • when it becomes cheap enough, it becomes the norm in personal drives as well 15000 rpm • highest spindle speed will be perfected in enterprise drives product information for Seagate and Control Data disc drives since 1988 SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
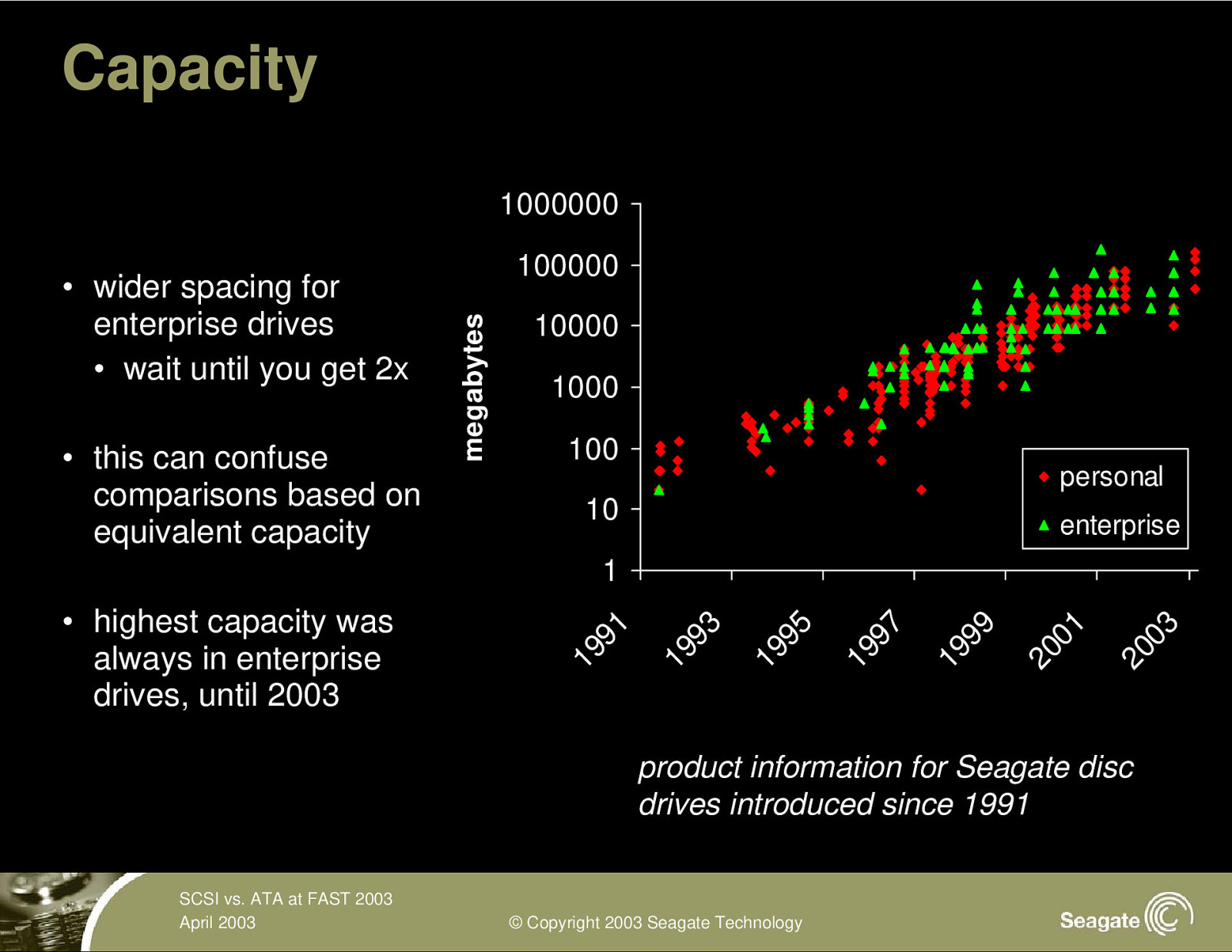
Capacity 1000000 • this can confuse comparisons based on equivalent capacity 100000 megabytes • wider spacing for enterprise drives • wait until you get 2x 10000 1000 100 personal 10 enterprise 20 03 20 01 19 99 19 97 19 95 19 93 • highest capacity was always in enterprise drives, until 2003 19 91 1 product information for Seagate disc drives introduced since 1991 SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
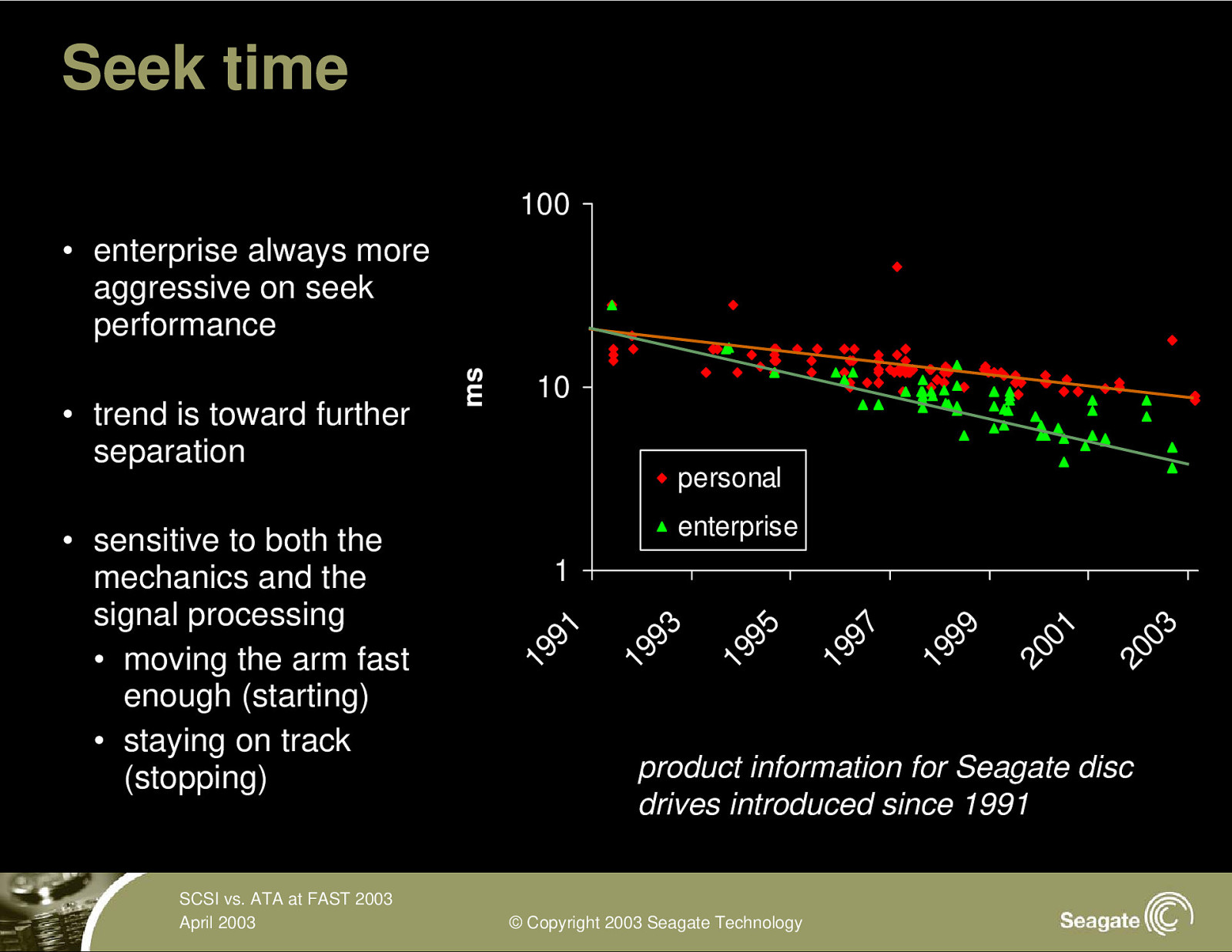
Seek time 100 SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 personal enterprise 20 03 20 01 19 99 19 97 19 95 1 19 93 • sensitive to both the mechanics and the signal processing • moving the arm fast enough (starting) • staying on track (stopping) 10 19 91 • trend is toward further separation ms • enterprise always more aggressive on seek performance product information for Seagate disc drives introduced since 1991 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
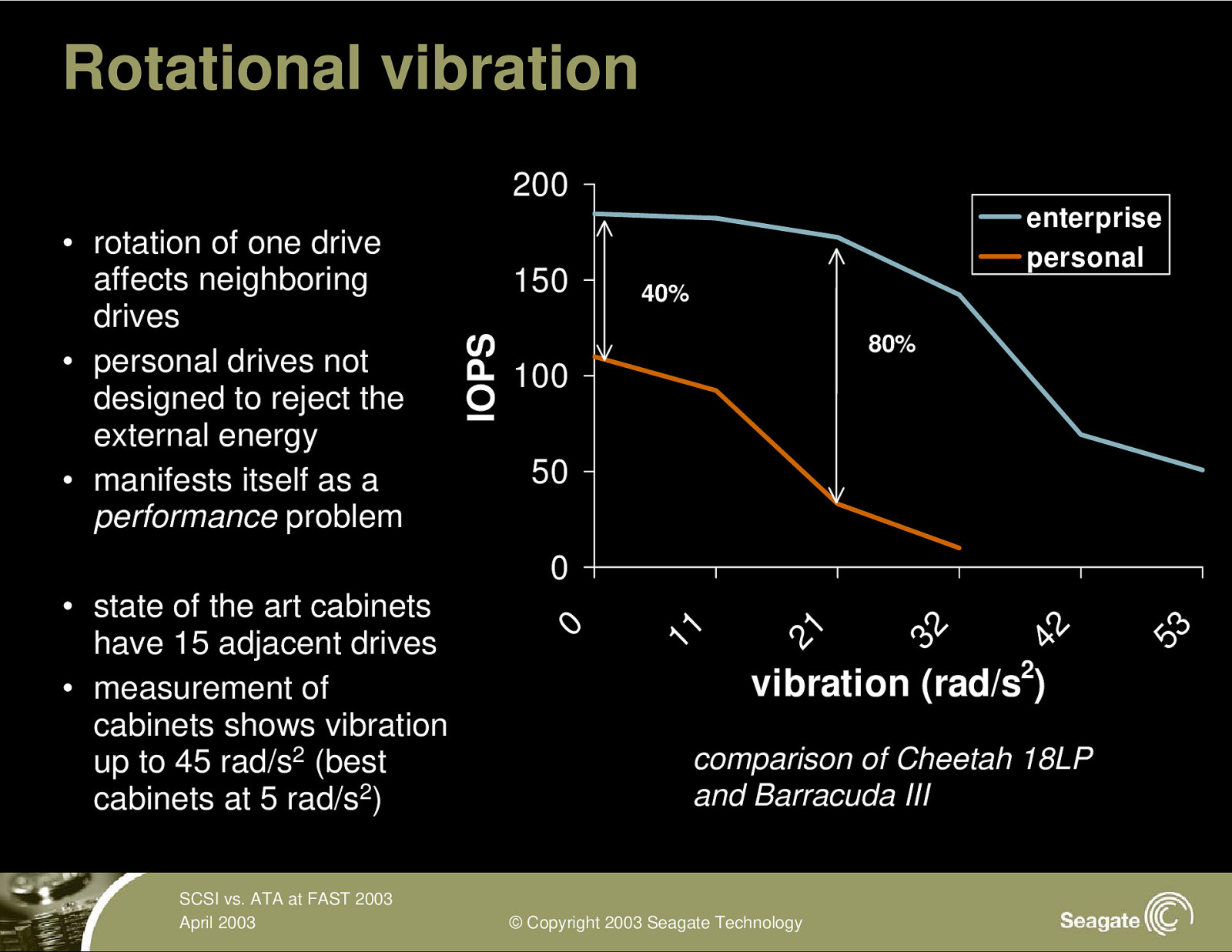
Rotational vibration 200 150 IOPS • rotation of one drive affects neighboring drives • personal drives not designed to reject the external energy • manifests itself as a performance problem enterprise personal 40% 80% 100 50 SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 vibration (rad/s2) comparison of Cheetah 18LP and Barracuda III © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology 53 42 32 21 11 • state of the art cabinets have 15 adjacent drives • measurement of cabinets shows vibration up to 45 rad/s2 (best cabinets at 5 rad/s2) 0 0

Outline Marketplace • personal • enterprise Mechanics • choices & comparison Electronics • this is the only place where interface matters directly Performance • the direct impact Summary SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
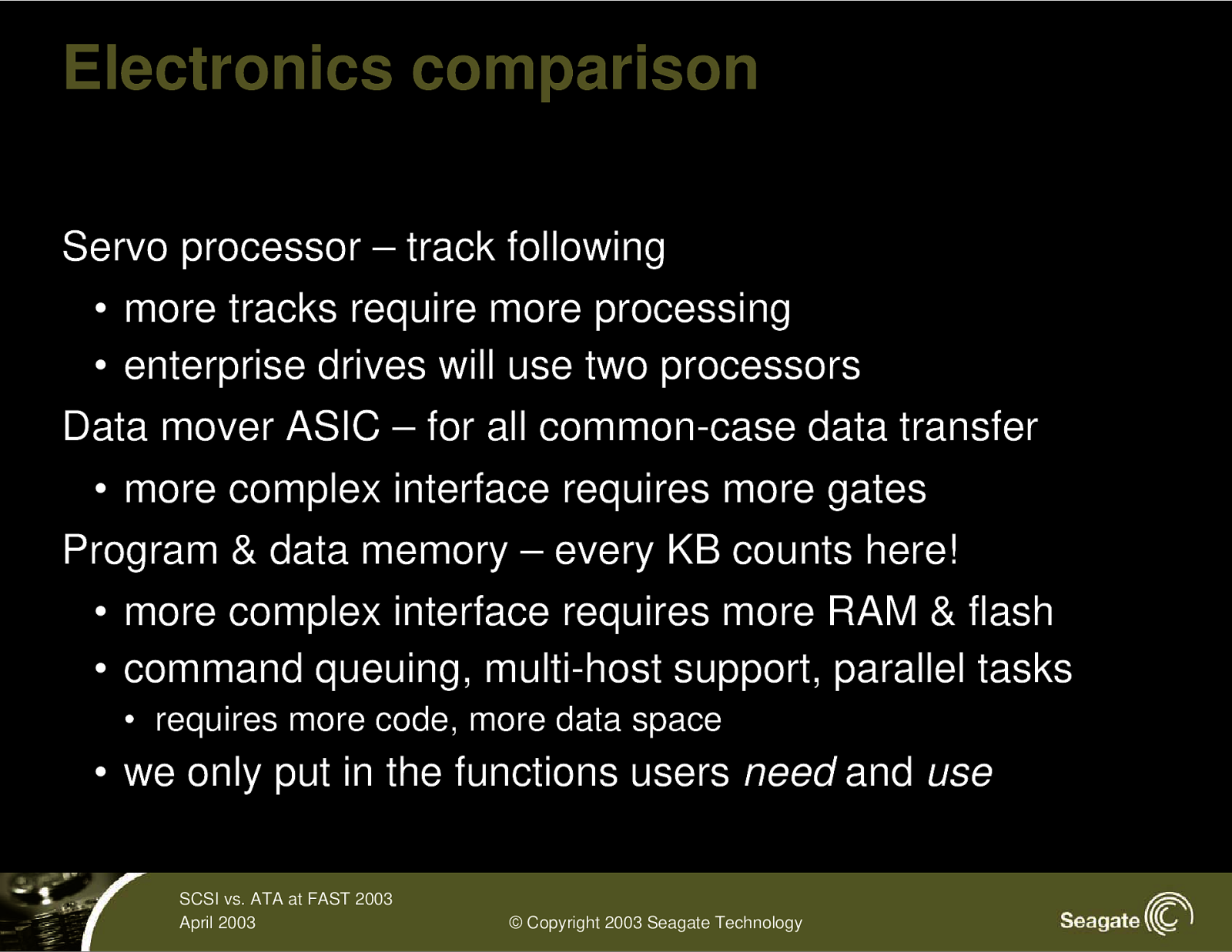
Electronics comparison Servo processor – track following • more tracks require more processing • enterprise drives will use two processors Data mover ASIC – for all common-case data transfer • more complex interface requires more gates Program & data memory – every KB counts here! • more complex interface requires more RAM & flash • command queuing, multi-host support, parallel tasks • requires more code, more data space • we only put in the functions users need and use SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
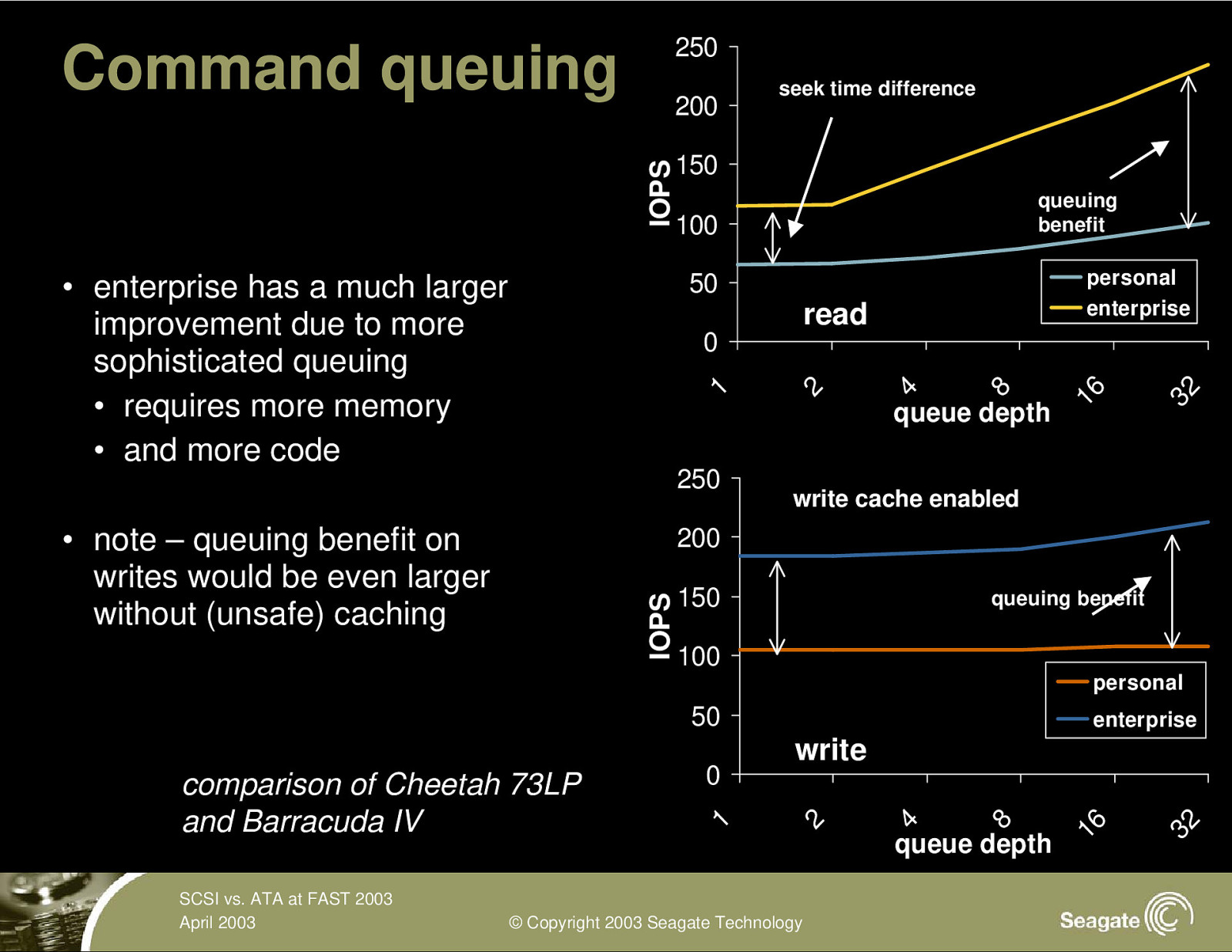
Command queuing 250 200 seek time difference IOPS 150 queuing benefit 100 personal enterprise 50 • enterprise has a much larger improvement due to more sophisticated queuing • requires more memory • and more code read 250 • note – queuing benefit on writes would be even larger without (unsafe) caching 32 queue depth 16 8 4 2 1 0 write cache enabled IOPS 200 150 queuing benefit 100 personal 50 SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology 32 queue depth 16 8 4 write 2 0 1 comparison of Cheetah 73LP and Barracuda IV enterprise

Outline Marketplace • personal • enterprise Mechanics • choices & comparison Electronics • this is the only place where interface matters directly Performance • the direct impact Summary SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
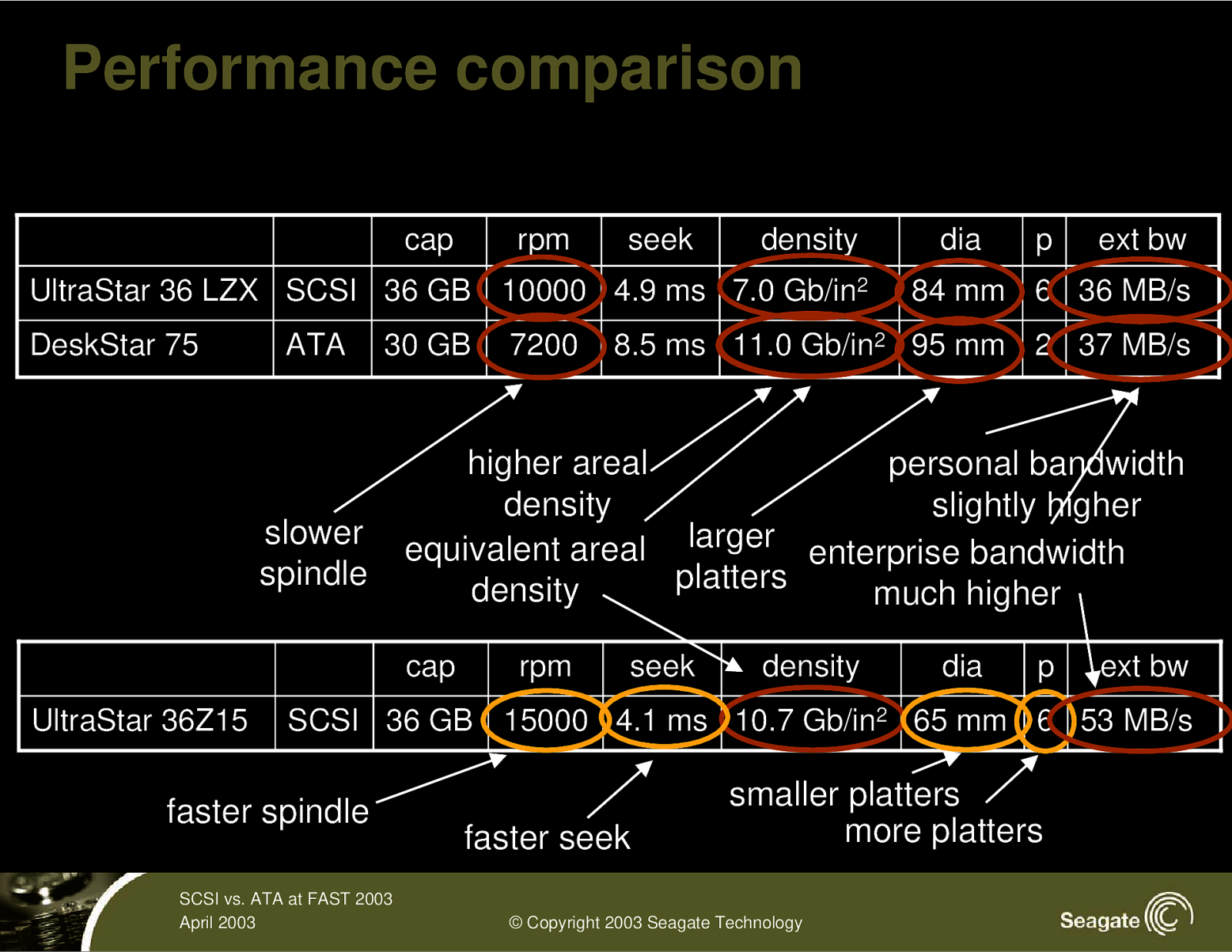
Performance comparison cap rpm seek density UltraStar 36 LZX SCSI 36 GB 10000 4.9 ms 7.0 Gb/in2 DeskStar 75 ATA 30 GB slower spindle p ext bw 84 mm 6 36 MB/s 8.5 ms 11.0 Gb/in2 95 mm 2 37 MB/s higher areal personal bandwidth density slightly higher equivalent areal larger enterprise bandwidth platters density much higher cap UltraStar 36Z15 7200 dia rpm seek density dia p ext bw SCSI 36 GB 15000 4.1 ms 10.7 Gb/in2 65 mm 6 53 MB/s faster spindle SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 faster seek smaller platters more platters © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
Summary and conclusions Drives are designed from the ground up to meet a specific set of usage characteristics • more sophisticated than just $ / GB If you want to understand the state-of-the-art • make sure you look at enterprise drives • and make sure you are comparing apples to apples There is room for a wider variety of models • tell us what points are worthwhile SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology

More Details? Just ask. dave.b.anderson@seagate.com james.e.dykes@seagate.com erik.riedel@seagate.com SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology

Detail Slides SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
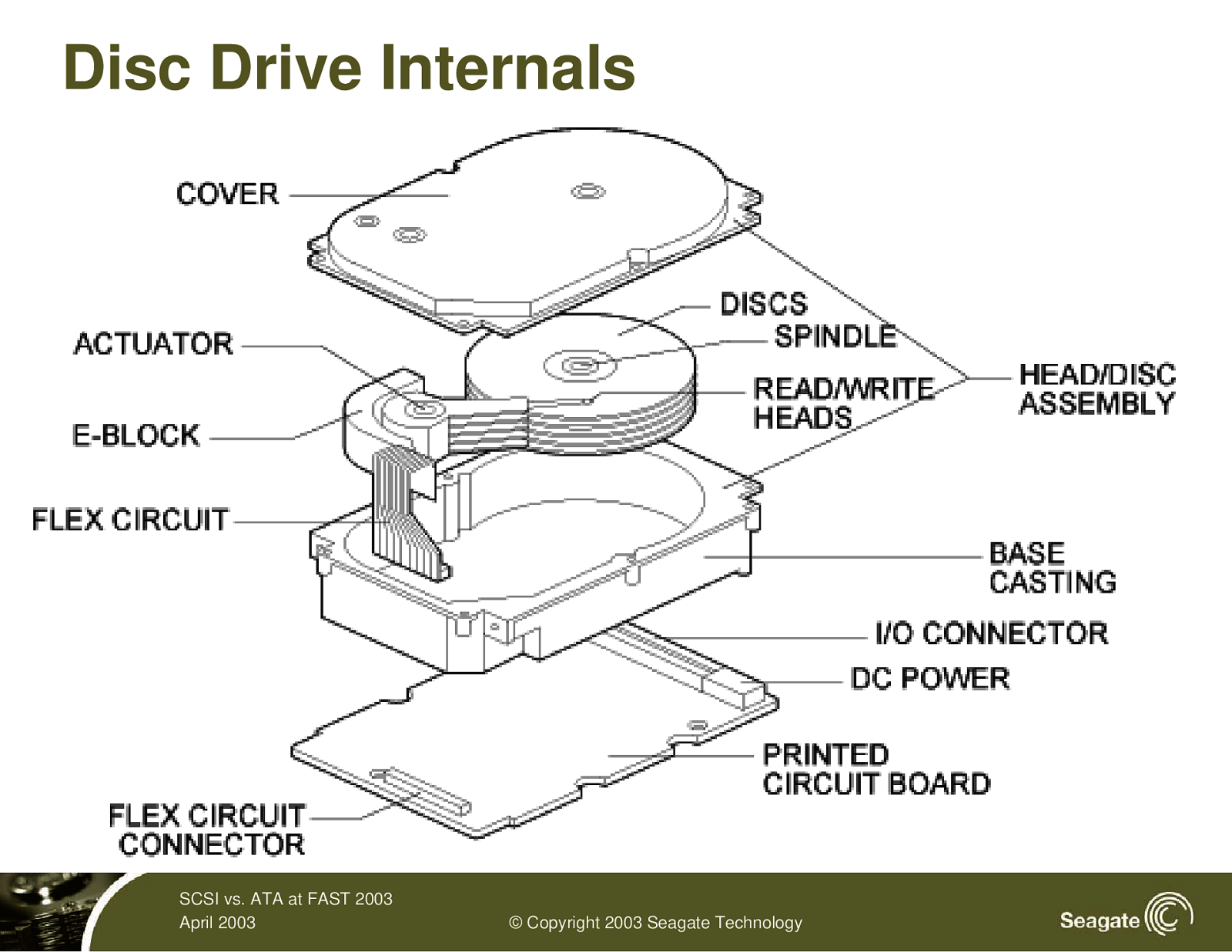
Disc Drive Internals SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
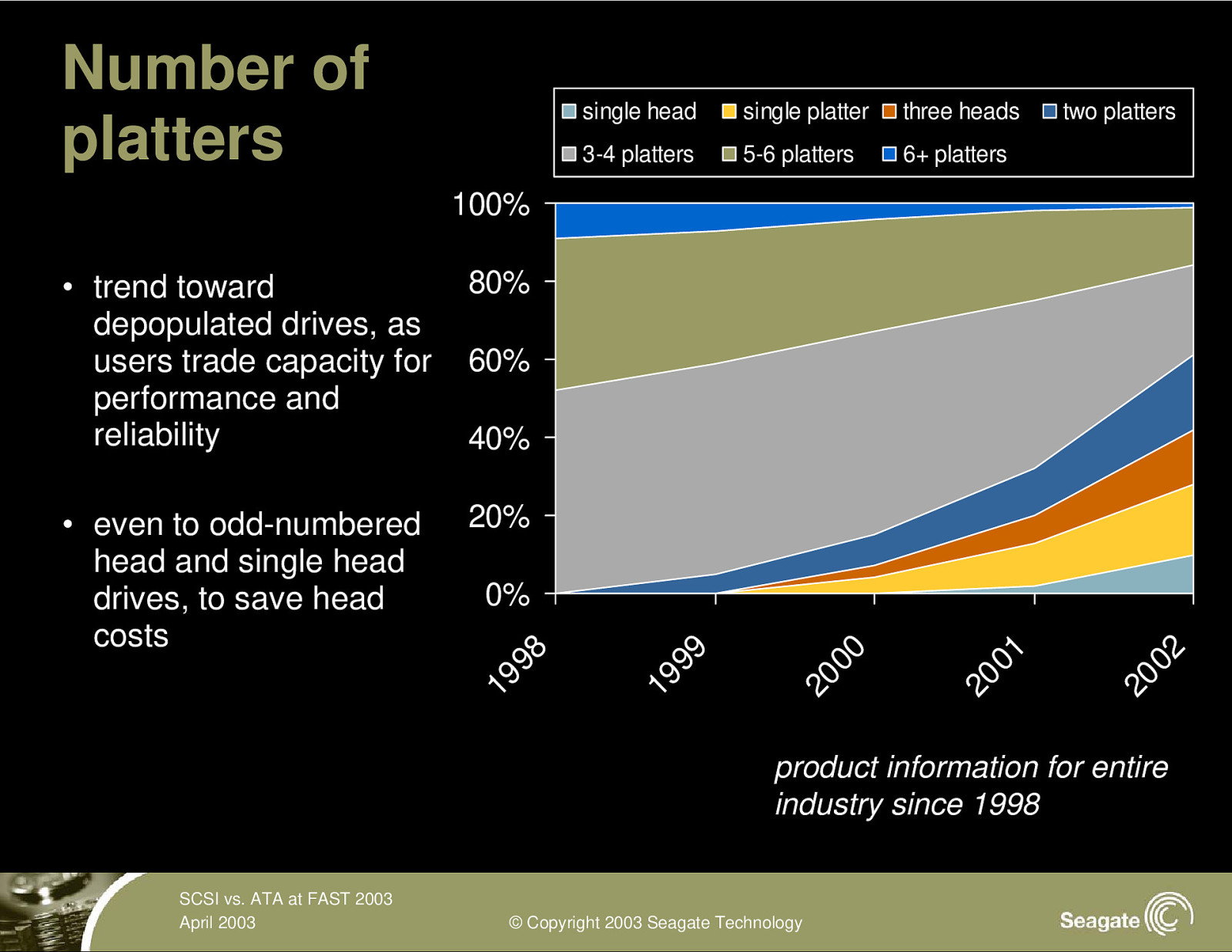
Number of platters single head single platter three heads 3-4 platters 5-6 platters 6+ platters two platters 100% • trend toward depopulated drives, as users trade capacity for performance and reliability 80% • even to odd-numbered head and single head drives, to save head costs 20% 60% 40% 20 02 20 01 20 00 19 99 19 98 0% product information for entire industry since 1998 SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
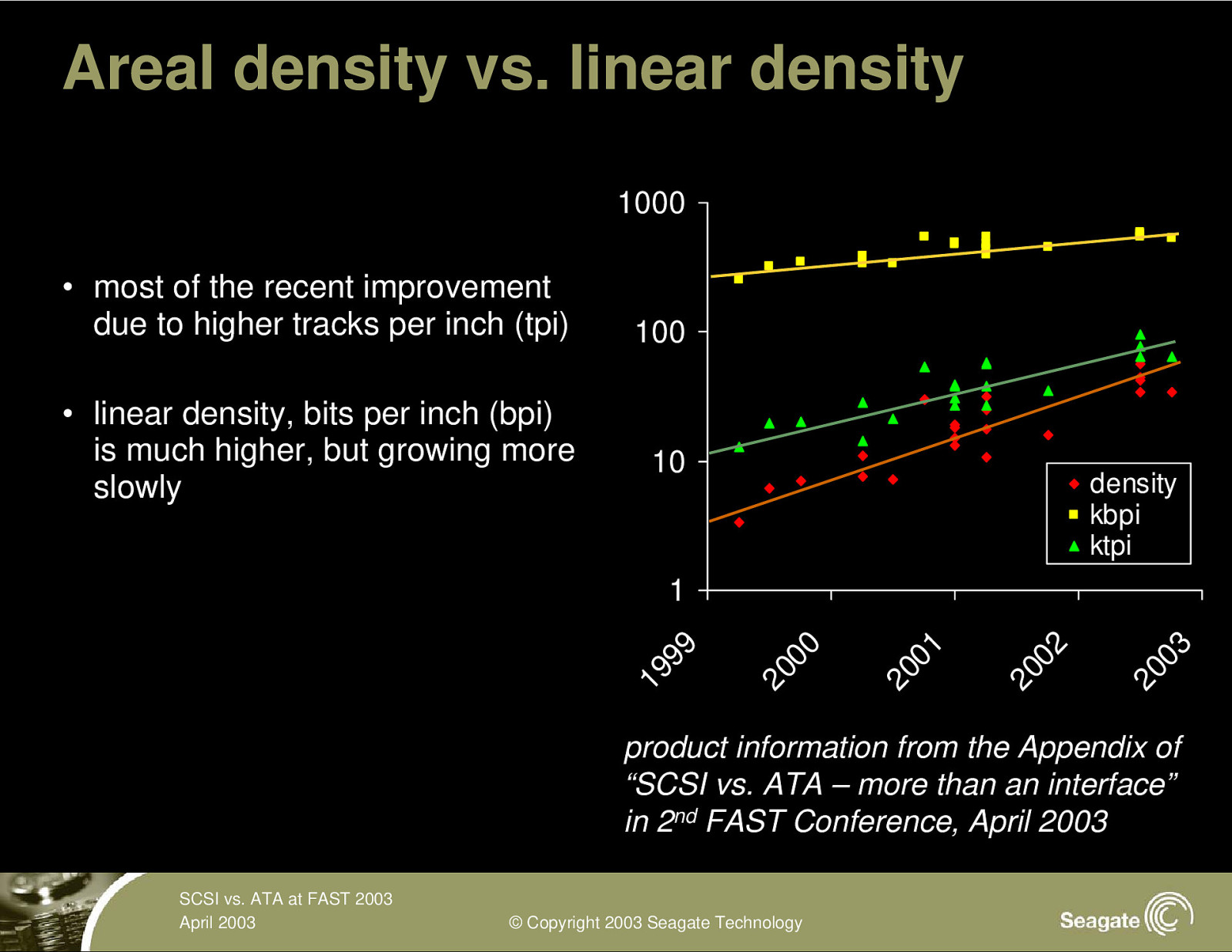
Areal density vs. linear density 1000 • most of the recent improvement due to higher tracks per inch (tpi) • linear density, bits per inch (bpi) is much higher, but growing more slowly 100 10 density kbpi ktpi 20 03 20 02 20 01 20 00 19 99 1 product information from the Appendix of “SCSI vs. ATA – more than an interface” in 2nd FAST Conference, April 2003 SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology
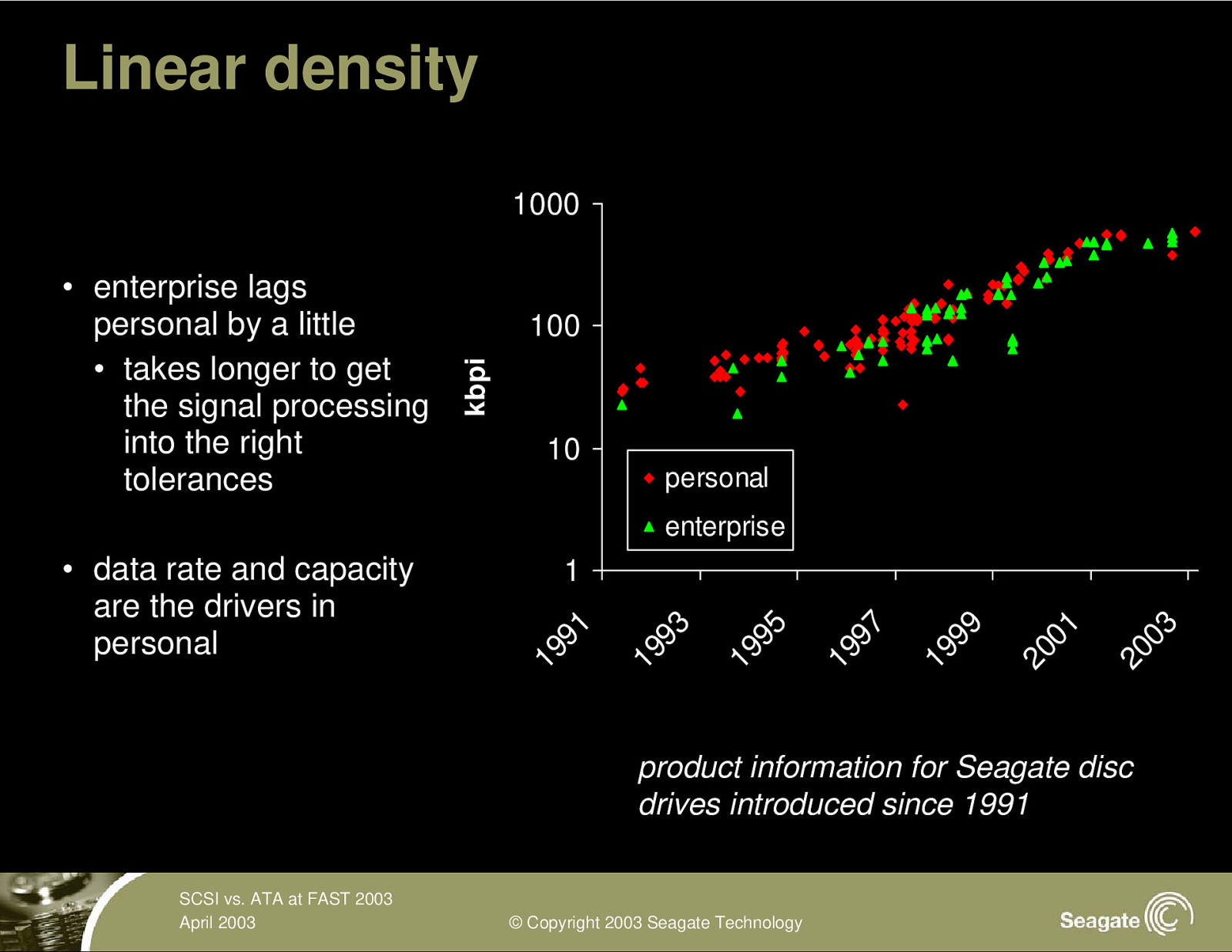
Linear density 1000 100 kbpi • enterprise lags personal by a little • takes longer to get the signal processing into the right tolerances 10 personal enterprise 20 03 20 01 19 99 19 97 19 95 19 93 1 19 91 • data rate and capacity are the drivers in personal product information for Seagate disc drives introduced since 1991 SCSI vs. ATA at FAST 2003 April 2003 © Copyright 2003 Seagate Technology